NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Fink HA, Hemmy LS, Linskens EJ, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Clinical Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia: A Systematic Review [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Apr. (Comparative Effectiveness Review, No. 223.)

Diagnosis and Treatment of Clinical Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia: A Systematic Review [Internet].
Show detailsAppendix Table C.1QUADAS-2 Risk of bias assessment for studies of classification accuracy of brief cognitive tests
| Study | Risk of Bias: Patient Selection (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Risk of Bias: Index Test (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Risk of Bias: Reference Standard (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Risk of Bias: Flow and Timing (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Applicability Concerns: Patient Selection (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Applicability Concerns: Index Test (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Applicability Concerns: Reference Standard (0=low, 1=high or unclear) | Total Score | ROB Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashendorf 20081 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Bondi 19932 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Brodaty 19975 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Brown 20096 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Buschke 19997 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Cahn 19978 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Cahn 19959 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Cahn 199610 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Canning 200411 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Cerhan 200212 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Chandler 200513 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Chapman 201014 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Clark 201015 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Clark 201416 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Coen 199617 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Connor 200518 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| De Jager 200319 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Elamin 201620 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Esteban-Santillas 199821 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Ewers 201222 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Galasko 199023 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Gavett 200924 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Gomez 200625 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Grober 200826 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Grober 200827 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Hackett 201828 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | High |
| Hollocks 201829 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Johnson 200330 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
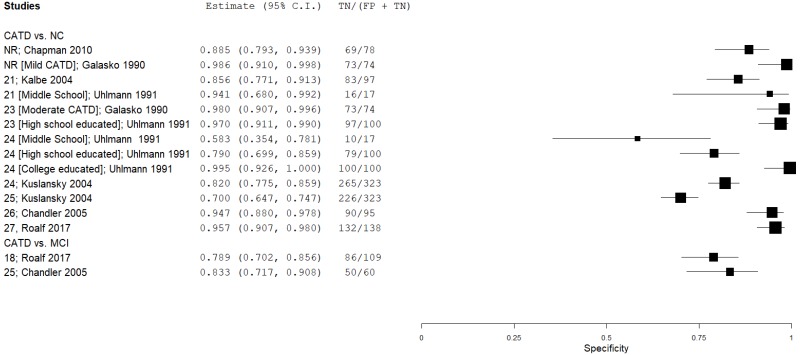
| Kalbe 200431 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Knopman 198932 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Kuslansky 200233 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Kuslansky 200434 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Lange 200635 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Lee 199636 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Logsdon 198937 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Loewenstein 200138 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Mahoney 200539 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Maruff 201340 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Mathuranath 200041 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Mendez 199242 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Mendiondo 200343) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Millar 201744 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Monsch 199245 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Monsch 199546 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Montgomery 201747 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Morgan 201048 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Parsey 201149 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Low |
| Petersen 199450 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Quarmley 201751 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Roalf 201352 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High |
| Roalf 201753 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Salmon 200254 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | Medium |
| Solomon 199855 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Springate 201456 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Storandt 198957 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Sunderaraman 201558 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
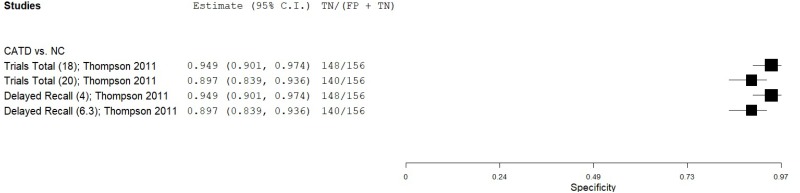
| Thompson 201159 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Tremont 201160 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Troster 19961 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Trzepacz 201562 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Tuokko 199263 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Uhlmann 199164 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | Medium |
| Welsh 199165 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Welsh 199266 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
| Wolf-Klein 198967 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | Medium |
| Zainal 201668 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Medium |
Appendix Table C.2Classification accuracy results for brief cognitive tests designed as individual stand-alone tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Test/Test Type | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brief Alzheimer Screen (BAS) | Mendiondo 200343 | 171 | NC | 203 | Weighted sum score | 22 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.46 |
| BAS | Mendiondo 200343 | 171 | NC | 203 | Weighted sum score | 23 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.46 |
| BAS | Mendiondo 200343 | 503 | NC | 657 | Weighted sum score | 26 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.43 |
| Brief Memory and Executive Test (BMET) | Hollocks 201729 | 51 | NC | 51 | Total score | 13 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.50 |
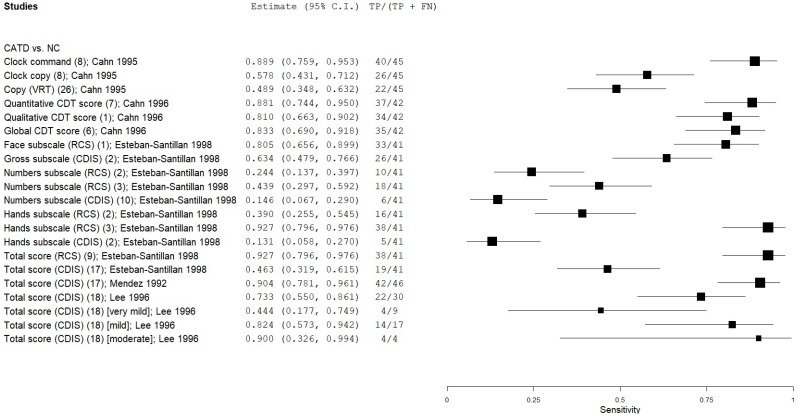
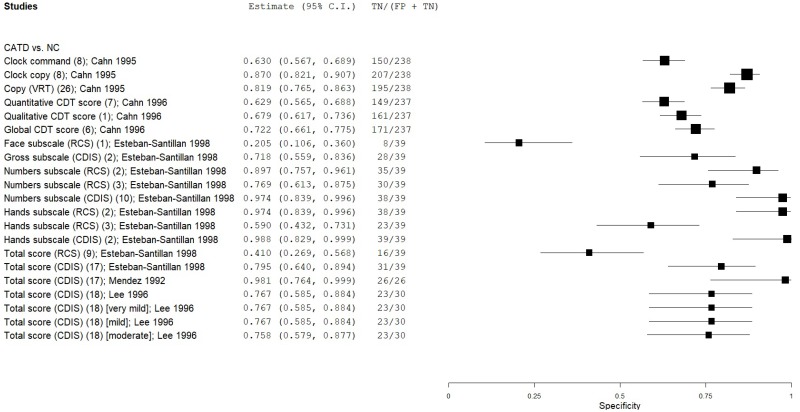
| Clock Drawing | Cahn 199610 | 42 | NC | 237 | Qualitative CDT score | 1* | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.95 | 0.15 |
| Clock Drawing | Cahn 199610 | 42 | NC | 237 | Global CDT score | 6 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.34 | 0.96 | 0.15 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Mendez CDIS gross | 2 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Mendez CDIS numbers | 10 | 0.15 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Mendez CDIS hands | 2 | 0.12 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Mendez CDIS total | 17 | 0.46 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 30 | NC | 30 | Mendez CDIS total | 18 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Mendez 199242 | 46 | NC | 26 | Mendez CDIS total | 19* | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.64 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 9 | NC | 30 | Mendez CDIS total (very mild CATD) | 18 | 0.44 | 0.77 | 0.36 | 0.82 | 0.23 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 17 | NC | 30 | Mendez CDIS total (mild CATD) | 18 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.36 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 4 | NC | 30 | Mendez CDIS total (moderate CATD) | 18 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.12 |
| Clock Drawing | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Rouleau copy | 7 | 0.57 | 0.87 | 0.45 | 0.91 | 0.16 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Rouleau face | 1 | 0.81 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Rouleau numbers | 3 | 0.44 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Rouleau hands | 3 | 0.93 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 0.89 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Rouleau total | 7 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 0.97 | 0.16 |
| Clock Drawing | Cahn 199610 | 42 | NC | 237 | Rouleau total | 7 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 0.30 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
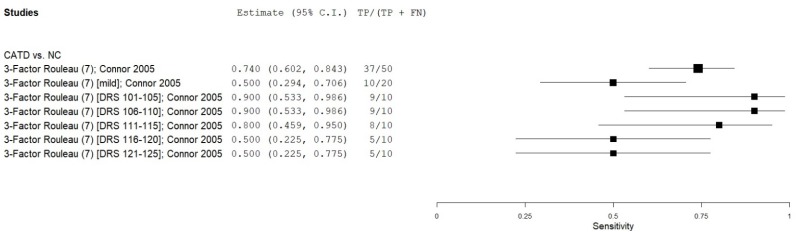
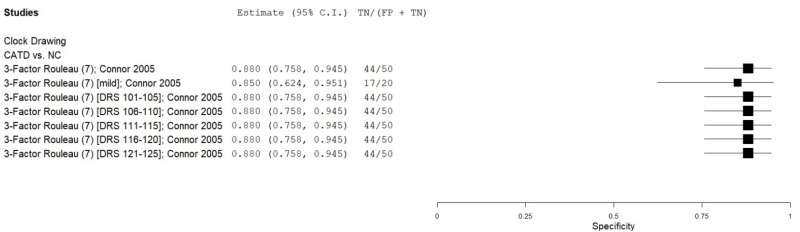
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 50 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total | 7 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Esteban-Santillan 199821 | 41 | NC | 39 | Rouleau total | 9 | 0.93 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.51 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 20 | NC | 20 | Rouleau total (mild CATD) | 7 | 0.5 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total (DRS 101-105) | 7 | 0.9 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 0.98 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total (DRS 106-110) | 7 | 0.9 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 0.98 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total (DRS 111-115) | 7 | 0.8 | 0.88 | 0.57 | 0.96 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total (DRS 116-120) | 7 | 0.5 | 0.88 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Rouleau total (DRS 121-125) | 7 | 0.5 | 0.88 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | Shulman scale | 3* | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 8 | NC | 28 | Shulman scale (MMSE 24+) | 3* | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.22 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 20 | NC | 28 | Shulman scale (MMSE <24) | 3* | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.42 |
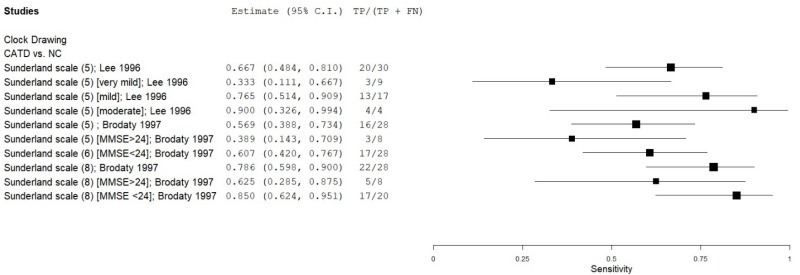
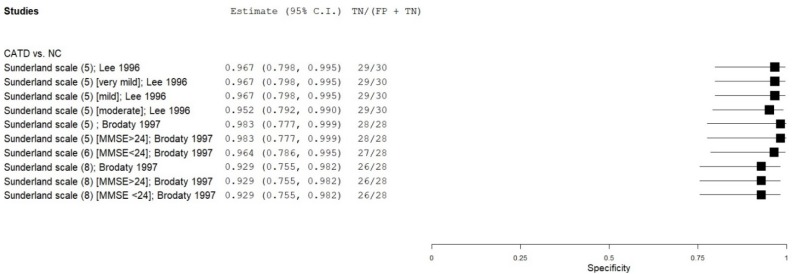
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 30 | NC | 30 | Sunderland scale | 5 | 0.67 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.75 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | Sunderland scale | 5 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | Sunderland scale | 8 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 8 | NC | 28 | Sunderland scale (MMSE 24+) | 5 | 0.38 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.22 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 8 | NC | 28 | Sunderland scale (MMSE 24+) | 8 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.90 | 0.22 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 20 | NC | 28 | Sunderland scale (MMSE <24) | 8 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.42 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 9 | NC | 30 | Sunderland scale (very mild CATD) | 5 | 0.33 | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.23 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 17 | NC | 30 | Sunderland scale (mild CATD) | 5 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.36 |
| Clock Drawing | Lee 199636 | 4 | NC | 30 | Sunderland scale (moderate CATD) | 5 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.12 |
| Clock Drawing | Tuokko 199263 | 58 | NC | 62 | Tuokko drawing | 3* | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.48 |
| Clock Drawing | Tuokko 199263 | 58 | NC | 62 | Tuokko setting | 13 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.97 | 0.48 |
| Clock Drawing | Tuokko 199263 | 58 | NC | 62 | Tuokko reading | 13 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.48 |
| Clock Drawing | Tuokko 199263 | 58 | NC | 62 | Tuokko combined score | 2* | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.48 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 50 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated | 5* | 0.52 | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 20 | NC | 20 | Watson abbreviated (mild CATD) | 5* | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated (DRS 101-105) | 5* | 0.60 | 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated (DRS 106-110) | 5* | 0.60 | 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated (DRS 111-115) | 5* | 0.60 | 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated (DRS 116-120) | 5* | 0.60 | 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Watson abbreviated (DRS 121-125) | 5* | 0.20 | 0.84 | 0.20 | 0.84 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Wolf-Klein 198967 | 105 | NC | 109 | Wolf-Klein abbreviated | 5 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.49 |
| Clock Drawing | Wolf-Klein 198967 | 121 | NC | 130 | Wolf-Klein scale | 5 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.48 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | Wolf-Klein scale | 6 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | Wolf-Klein scale | 8 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 50 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale | 8 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 8 | NC | 28 | Wolf-Klein scale (MMSE 24+) | 6 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.22 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 8 | NC | 28 | Wolf-Klein scale (MMSE 24+) | 8 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 0.96 | 0.22 |
| Clock Drawing | Brodaty 19975 | 20 | NC | 28 | Wolf-Klein scale (MMSE <24) | 8 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.42 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 20 | NC | 20 | Wolf-Klein scale (mild CATD) | 8 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale (DRS 101-105) | 8 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale (DRS 106-110) | 8 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale (DRS 111-115) | 8 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.42 | 0.95 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale (DRS 116-120) | 8 | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.35 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Wolf-Klein scale (DRS 121-125) | 8 | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.35 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| Clock Drawing | Parsey 201149 | 33 | MCI | 33 | CLOX 1 modified Rouleau | 11 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.50 |
| Clock Drawing | De Jager 200319 | 55 | MCI | 29 | CLOX 1 total | 11 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.61 | 0.65 |
| Clock Drawing | De Jager 200319 | 55 | MCI | 29 | CLOX 2 copy | 13 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.50 | 0.65 |
| Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE) | Chapman 201014 | 55 | NC | 78 | Total score | NR | 0.56 | 0.88 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.41 |
| MMSE | Kalbe 200431 | 88 | NC | 97 | Total score | 21 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.48 |
| MMSE | Kuslansky 200434 | 57 | NC | 323 | Total score | 24 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.42 | 0.95 | 0.15 |
| MMSE | Kuslansky 200434 | 57 | NC | 323 | Total score | 25 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 0.97 | 0.15 |
| MMSE | Chandler 200513 | 95 | NC | 95 | Total score | 26 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.50 |
| MMSE | Roalf 201753 | 340 | NC | 138 | Total score | 27 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.71 |
| MMSE | Galasko 199023 | 24 | NC | 74 | Total score (Mild CATD) | NR | 0.79 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.24 |
| MMSE | Galasko 199023 | 50 | NC | 74 | Total score (Moderate CATD) | 23 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.40 |
| MMSE | Uhlmann 199164 | 23 | NC | 17 | Total score (Middle School) | 21 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.79 | 0.58 |
| MMSE | Uhlmann 199164 | 23 | NC | 17 | Total score (Middle School) | 24 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 1.00 | 0.58 |
| MMSE | Uhlmann 199164 | 33 | NC | 30 | Total score (High school) | 23 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.81 | 0.52 |
| MMSE | Uhlmann 199164 | 33 | NC | 30 | Total score (High school) | 24 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.52 |
| MMSE | Uhlmann 199164 | 53 | NC | 54 | Total score (College+) | 24 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.50 |
| MMSE | Chandler 200513 | 95 | MCI | 60 | Total score | 25 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.61 |
| MMSE | Roalf 201753 | 340 | MCI | 109 | Total score | 18 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.55 | 0.76 |
| Memory Impairment Screen (MIS) | Buschke 19997 | 39 | NC | 433 | Total score | 4 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.66 | 0.99 | 0.08 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 28 | NC | 212 | Total score | 4 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.12 |
| MIS | Buschke 19997 | NC | 433 | Total score (Mild CATD) | 4 | 0.79 | 0.96 | NA | NA | NA | |
| MIS | Buschke 19997 | NC | 433 | Total score (Moderate CATD) | 4 | 0.95 | 0.96 | NA | NA | NA | |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 4 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 0.5) | 4 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 0.02 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 4 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 0.5) | 5 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.02 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 16 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 1.0) | 4 | 0.81 | 0.97 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 0.07 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 6 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 2.0) | 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.03 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 6 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 2.0) | 4 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.03 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 2 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 3.0) | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.01 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 2 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 3.0) | 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.01 |
| MIS | Kuslansky 200233 | 2 | NC | 212 | Total score (CDR 3.0) | 3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.01 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) | Quarmley 2017*51 | 231 | NC | 155 | Total score | 23 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.60 |
| MoCA | Roalf 201753 | 340 | NC | 138 | Total score | 22 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.71 |
| MoCA | Roalf 201753 | 340 | NC | 138 | Total score – modified short version | 10 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.71 |
| MoCA | Roalf 201753 | 340 | MCI | 109 | Total score | 24 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.76 |
| MoCA | Roalf 201753 | 340 | MCI | 109 | Total score – modified short version | 6 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.91 | 0.43 | 0.76 |
| MoCA | Trzepacz 201562 | 100 | MCI | 299 | Total score | 19 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.25 |
| MoCA | Quarmley 2017*51 | 231 | MCI | 110 | Total score | 19 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.68 |
| 7 Minute Screen (7MS) | Solomon 199855 | 60 | NC | 60 | Total score | 0.3, 0.7 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| 7MS | Solomon 199855 | 60 | NC | 60 | Total score | 0.1, 0.9 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.50 |
| 7MS | Solomon 199855 | 30 | NC | 30 | Total score (confirmation sample) | 0.1, 0.9 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.50 |
| 7MS | Solomon 199855 | 35 | NC | 60 | Total score (MMSE 21+) | 0.1, 0.9 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.37 |
| 7MS | Solomon 199855 | NC | Total score (MMSE 24+) | 0.1, 0.9 | 0.98 | 1.00 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Minnesota Cognitive Acuity Screen (MCAS) | Tremont 201160 | 50 | aMCI | 100 | Total score | 42.5 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.33 |
| Test Your Memory (TYM) | Brown 20096 | 94 | NC | 282 | Total score | 42 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.25 |
Abbreviations: aMCI=amnestic mild cognitive impairment; BAS=Brief Alzheimer Screen; BMET=Brief Memory and Executive Test; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; CDIS=clock drawing interpretation scale; CDT=clock drawing test; Comp=comparator; MCAS=Minnesota Cognitive Acuity Screen; MCI=Mild Cognitive Impairment; MIS=Memory Impairment Screen; MMSE=Mini-Mental State Exam; MoCA; Montreal Cognitive Assessment; NC=normal control; NR=not reported; NPV=negative predictive value; PPV=positive predictive value; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; TYM=Test Your Memory; 7MS=7 Minute Screen
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cut point are associated with worse cognition
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.3Classification accuracy results for brief cognitive batteries in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Cognitive Battery | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut Point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
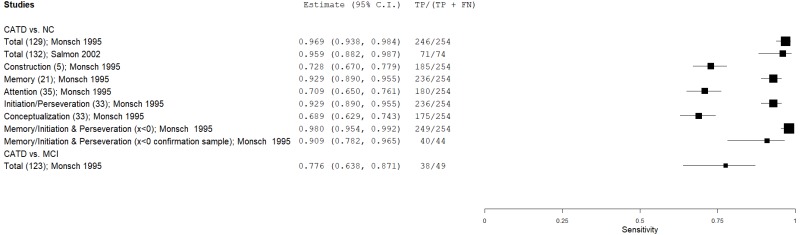
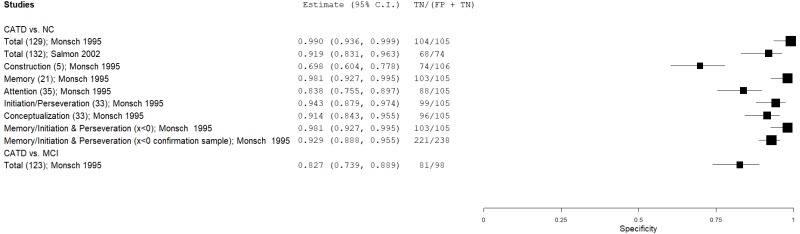
| Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) | Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Total score | 129 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.71 |
| Salmon 200254 | 74 | NC | 74 | Total score | 132 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Construction score | 5 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Memory score | 21 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Attention score | 35 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Initiation & Preservation score | 33 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Conceptualization score | 33 | 0.69 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 254 | NC | 105 | Memory/Initiation & Preservation | x<0 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.71 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 44 | NC | 238 | Memory/Initiation & Preservation | x<0 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.71 | 0.98 | 0.16 | |
| Monsch 199546 | 76 | NC | 105 | Memory/Initiation & Preservation (mild CATD) | x<0 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.42 | |
| Springate 201456 | 49 | MCI | 98 | Total score | 123 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.70 | 0.88 | 0.33 | |
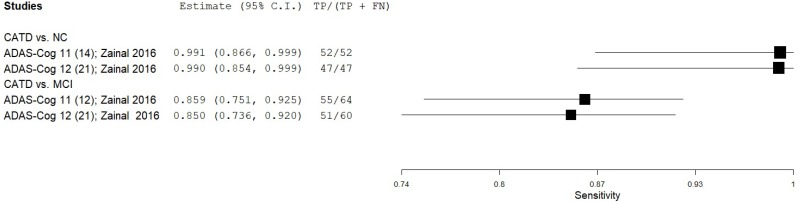
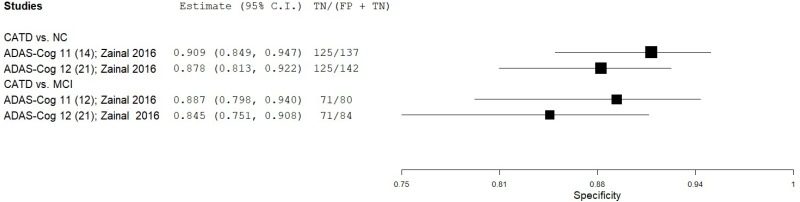
| Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment ScaleCognitive (ADAS-Cog) | Zainal 201668 | 64 | NC | 125 | Total Score (ADAS-Cog 11) | 14* | 0.81 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.34 |
| Zainal 201668 | 64 | NC | 125 | Total Score (ADAS-Cog 12) | 21* | 0.73 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.34 | |
| Zainal 201668 | 64 | MCI | 80 | Total Score (ADAS-Cog 11) | 12* | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.44 | |
| Zainal 201668 | 64 | MCI | 80 | Total Score (ADAS-Cog 12) | 21* | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.44 | |
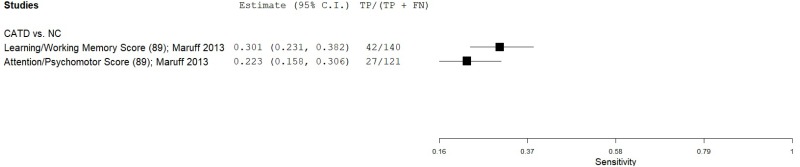
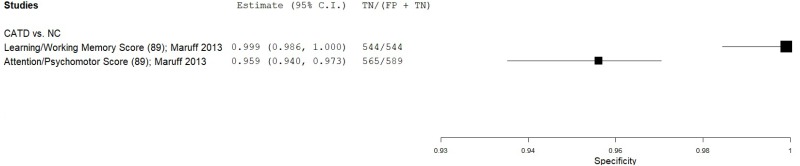
| Cogstate Brief Battery (CBB) | Maruff 201340 | 42 | NC | 642 | Learning/Working Memory | 89 | 1.00 | 0.847 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.06 |
| Maruff 201340 | 51 | NC | 659 | Attention/Psychomotor | 89 | 0.53 | 0.857 | 0.22 | 0.96 | 0.07 | |
| Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD) Neuropsychological Battery | Chandler 200513 | 95 | NC | 95 | CERAD Total Score | 77 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.50 |
| Chandler 200513 | 95 | MCI | 60 | CERAD Total Score | 68 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.61 | |
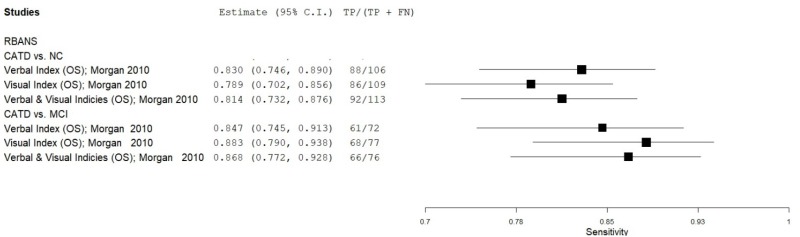
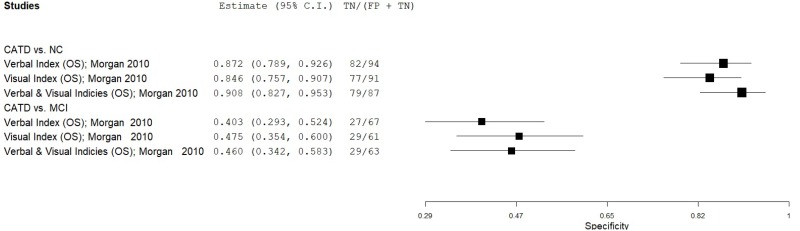
| Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) | Morgan 201048 | 100 | NC | 100 | Verbal Index | NR | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.50 |
| Morgan 201048 | 100 | NC | 100 | Visual Index | NR | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.50 | |
| Morgan 201048 | 100 | NC | 100 | Verbal & Visual Indices | NR | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.50 | |
| Morgan 201048 | 100 | MCI | 38 | Verbal Index | NR | 0.61 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 0.72 | |
| Morgan 201048 | 100 | MCI | 38 | Visual Index | NR | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.48 | 0.72 | |
| Morgan 201048 | 100 | MCI | 38 | Verbal & Visual Indices | NR | 0.66 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.45 | 0.72 | |
| Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Version Three (ACE-III) | Elamin 201620 | 31 | NC | 28 | Total score | 88 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.53 |
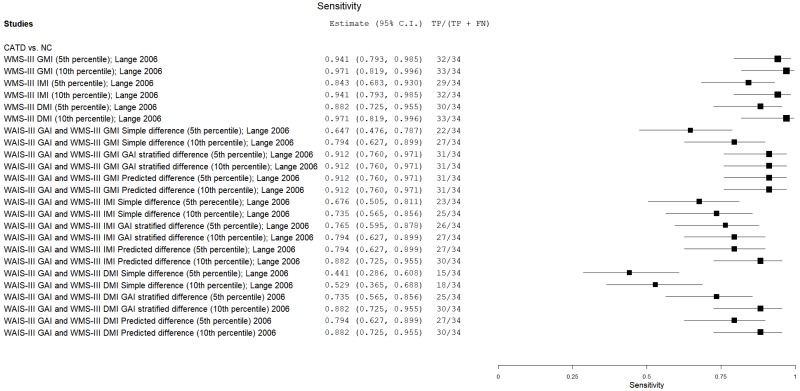
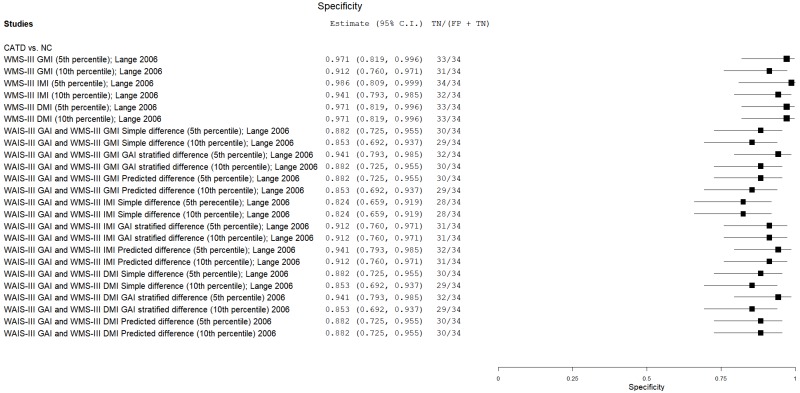
| Wechsler Memory Scales (WMS) | Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III General Memory Index | 5th percentile | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.50 |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III General Memory Index | 10th percentile | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III Immediate Memory Index | 5th percentile | 0.85 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III Immediate Memory Index | 10th percentile | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III Delayed Memory Index | 5th percentile | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WMS-III Delayed Memory Index | 10th percentile | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: simple difference | 5th percentile | 0.68 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: simple difference | 10th percentile | 0.74 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: GAI stratified difference | 5th percentile | 0.76 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: GAI stratified difference | 10th percentile | 0.79 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: predicted difference | 5th percentile | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III IMI: predicted difference | 10th percentile | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: simple difference | 5th percentile | 0.65 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: simple difference | 10th percentile | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: GAI stratified difference | 5th percentile | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: GAI stratified difference | 10th percentile | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: predicted difference | 5th percentile | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III GMI: predicted difference | 10th percentile | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: simple difference | 5th percentile | 0.44 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: simple difference | 10th percentile | 0.53 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: GAI stratified difference | 5th percentile | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.78 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: GAI stratified difference | 10th percentile | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: predicted difference | 5th percentile | 0.79 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.50 | |
| Lange 200635 | 34 | NC | 34 | WAIS-III GAI, WMS-III DMI: predicted difference | 10th percentile | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) | Logsdon 198937 | 44 | NC | 54 | WAIS-R Fuld Profile69 | Fuld criteria (Y/N) | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.45 |
Abbreviations: ACE=Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination; ADAS-Cog=Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; CBB=Cogstate Brief Battery; CERAD=Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease; Comp=comparator; DMI=delayed memory index; DRS=Dementia Rating ability index; GMI=General Memory Index; IMI=immediate memory index; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; NC=normal control; NR=not reported; Scale; GAI=general NPV=negative predictive value; PPV=positive predictive value; RBANS= Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; WAIS=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cut point indicate CATD
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.4Classification accuracy results for memory tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Memory Test | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut Point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List Learning Tests – Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive (ADAS-Cog) | Zainal 201668 | 64 | NC | 125 | All Recall Trials & Recognition | 14* | 0.77 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.34 |
| Zainal 201668 | 64 | MCI | 80 | All Recall Trials & Recognition | 14* | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.35 | 0.44 | |
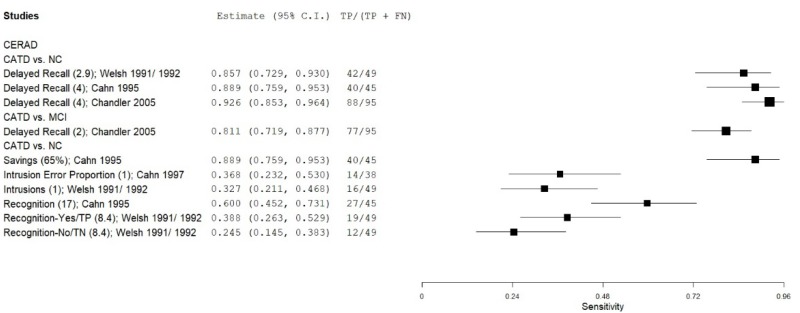
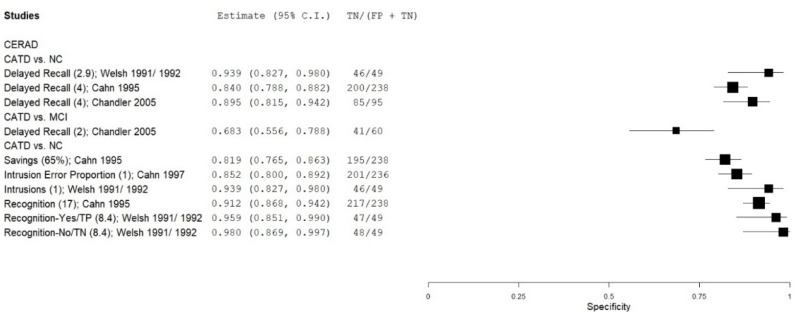
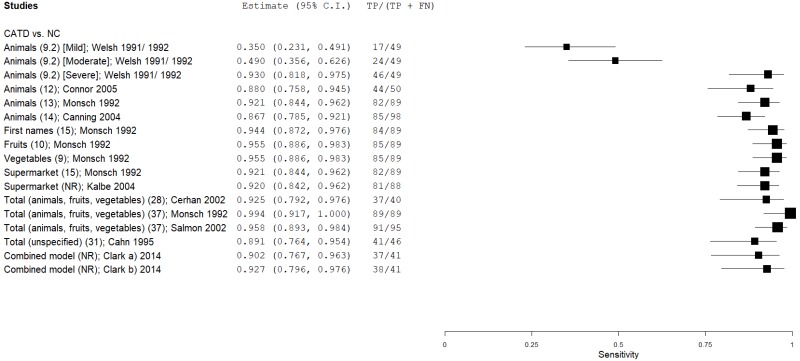
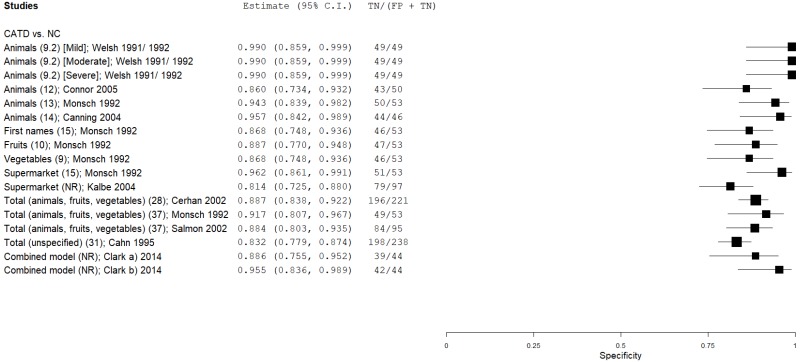
| List Learning Tests – Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD) | Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Delayed Recall & Recognition | NR | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.50 |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 1 (Mild CATD) | 2 | 0.41 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.62 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 1 (Moderate CATD) | 2 | 0.67 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.74 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 1 (Severe CATD) | 2 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 2 (Mild CATD) | 4 | 0.49 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 2 (Moderate CATD) | 4 | 0.74 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.78 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 2 (Severe CATD) | 4 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 3 (Mild CATD) | 5 | 0.41 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.62 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 3 (Moderate CATD) | 5 | 0.59 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.71 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | List Trial 3 (Severe CATD) | 5 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.50 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Delayed Recall | 4 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.51 | 0.97 | 0.16 | |
| Chandler 200513 | 95 | NC | 95 | Delayed Recall | 4 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Delayed Recall (Mild CATD) | 3 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Delayed Recall (Moderate CATD) | 3 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Delayed Recall (Severe CATD) | 3 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Savings, Retention | 65% | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 0.97 | 0.16 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Savings, Retention (Mild CATD) | 47% | 0.62 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.72 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Savings, Retention (Moderate CATD) | 47% | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Savings, Retention (Severe CATD) | 47% | 0.82 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 0.50 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Recognition | 17 | 0.60 | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.92 | 0.16 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition Yes (Mild CATD) | 9 | 0.39 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition Yes (Moderate CATD) | 9 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition Yes (Severe CATD) | 9 | 0.73 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition No (Mild CATD) | 7 | 0.25 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition No (Moderate CATD) | 7 | 0.32 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.59 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Recognition No (Severe CATD) | 7 | 0.48 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.65 | 0.50 | |
| Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Intrusion proportion | 0 | 0.37 | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.89 | 0.14 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | % Intrusions (Mild CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.58 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | % Intrusions (Moderate CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.33 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.58 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | % Intrusions (Severe CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.62 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.71 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 1 (Mild CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.14 | 0.96 | 0.78 | 0.53 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 1 (Moderate CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.16 | 0.96 | 0.80 | 0.53 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 1 (Severe CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.14 | 0.96 | 0.78 | 0.53 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 2 (Mild CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.33 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 2 (Moderate CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.27 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 2 (Severe CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.33 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 3 (Mild CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.20 | 0.94 | 0.77 | 0.54 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 3 (Moderate CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.35 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.59 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Trial 3 (Severe CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.39 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.61 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Delayed Recall (Mild CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.27 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 0.55 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Delayed Recall (Moderate CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.26 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.55 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Intrusions Delayed Recall (Severe CATD) | 2 SDs** | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.50 | |
| Chandler 200513 | 95 | MCI | 60 | Delayed Recall | 2 | 0.81 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.61 | |
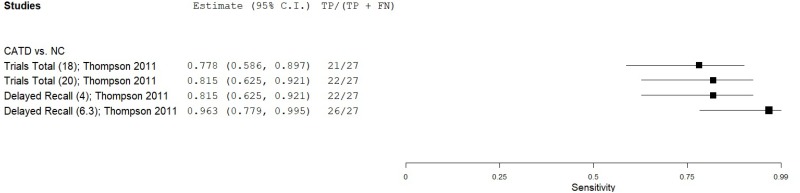
| List Learning Tests - Cogstate International Shopping List Test (ISLT) | Thompson 201159 | 27 | NC | 156 | Trials Total (at 95% specificity) | 18 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.96 | 0.15 |
| Thompson 201159 | 27 | NC | 156 | Trials Total (at 90% specificity) | 20 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.59 | 0.97 | 0.15 | |
| List Learning Tests - Delayed Word Recall (DWR) | Knopman 198932 | 28 | NC | 55 | Delayed Recall | 2 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.34 |
| List Learning Tests – DemTect | Kalbe 200431 | 88 | NC | 97 | Delayed Recall | NR | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.48 |
| List Learning Tests – Hopkins Verbal Learning Test (HVLT) | Kuslansky 200434 | 57 | NC | 323 | Trials Total | 14 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.39 | 0.98 | 0.15 |
| De Jager 200319 | 55 | MCI | 29 | Trials Total | 15 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.65 | |
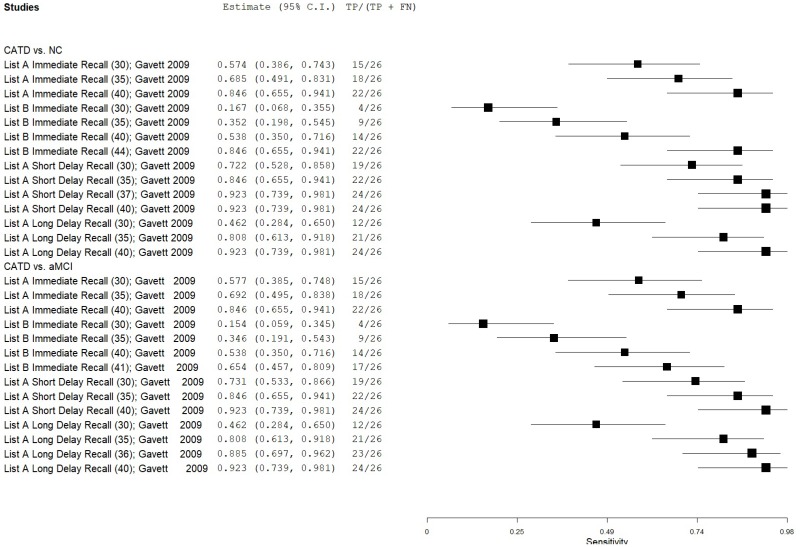
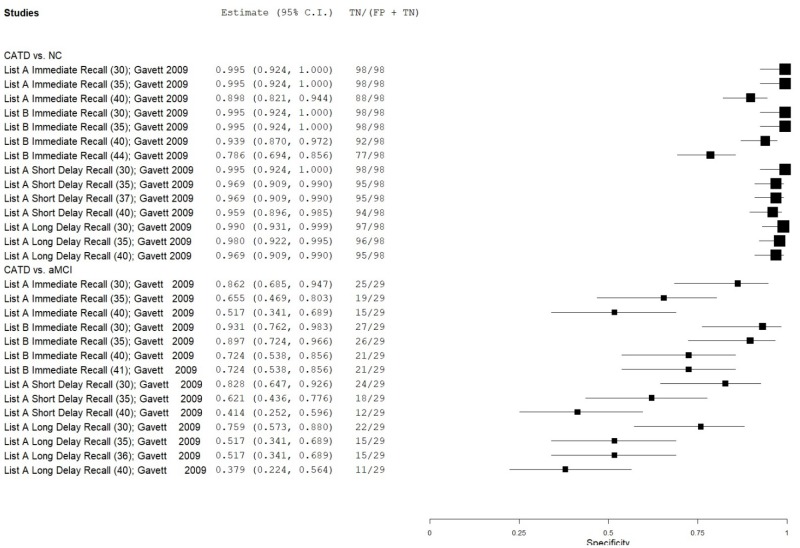
| List Learning Tests – Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) | Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Immediate Recall | 35 | 0.69 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.21 |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Immediate Recall | 40 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.69 | 0.96 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List B Immediate Recall | 35 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List B Immediate Recall | 44 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.52 | 0.95 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Short Delay Recall | 35 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Short Delay Recall | 37 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Long Delay Recall | 35 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | NC | 98 | List A Long Delay Recall | 40 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 0.21 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Immediate Recall | 30 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Immediate Recall | 35 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List B Immediate Recall | 35 | 0.35 | 0.90 | 0.76 | 0.61 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List B Immediate Recall | 41 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Short Delay Recall | 30 | 0.73 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Short Delay Recall | 35 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.82 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Long Delay Recall | 35 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.47 | |
| Gavett 200924 | 26 | aMCI | 29 | List A Long Delay Recall | 36 | 0.89 | 0.52 | 0.62 | 0.84 | 0.47 | |
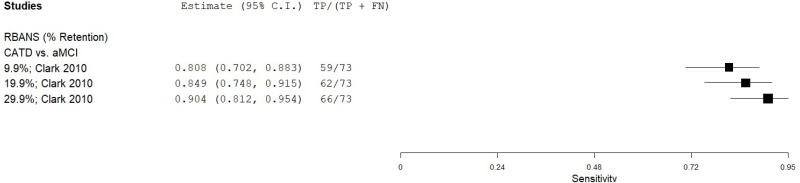
| List Learning Tests - Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) | Clark 201015 | 73 | aMCI | 44 | Savings, Retention | 29.9% | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.62 |
| List Learning Tests – Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test (FCSRT) | Grober 200826 | 35 | NC | 283 | Free Recall | 24 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.30 | 0.97 | 0.11 |
| Millar 201744 | 64 | NC | 519 | Free Recall | NR | 0.91 | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0.99 | 0.11 | |
| Grober 200826 | 35 | NC | 283 | Total Recall | 44 | 0.71 | 0.94 | 0.59 | 0.96 | 0.11 | |
| Prose Recall – Wechsler Memory Scales (WMS) Logical Memory (LM) | Johnson 200330 | 31 | NC | 47 | Veridical Reproduction | NR | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.89 | 0.40 |
| Johnson 200330 | 98 | NC | 82 | Veridical Reproduction (very mild CATD) | NR | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.54 | |
| Johnson 200330 | 31 | NC | 47 | Veridical & Gist Recall | NR | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.40 | |
| Johnson 200330 | 31 | NC | 47 | Distortion of Text | NR | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.40 | |
| Johnson 200330 | 98 | NC | 82 | Distortion of Text (very mild CATD) | NR | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.54 | |
| Salmon 200254 | 27 | NC | 27 | Delayed Recall | 9 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.50 | |
| Millar 201744 | 64 | NC | 519 | Delayed Recall | NR | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.34 | 0.96 | 0.11 | |
| Prose Recall – Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) | Clark 201015 | 73 | aMCI | 44 | Savings, Retention | 59.9% | 0.85 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.62 |
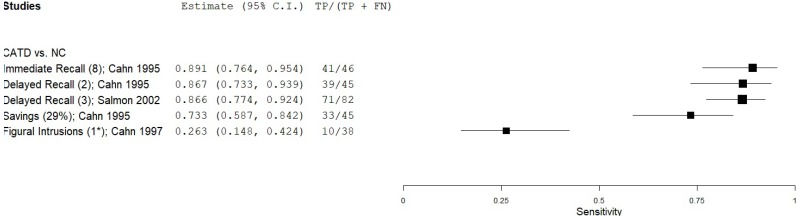
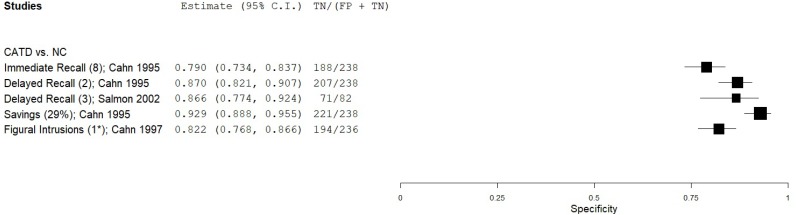
| Figure Recall - Wechsler Memory Scales (WMS) Visual Reproduction (VR) | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Immediate Recall | 8 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.16 |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Delayed Recall | 2 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 0.97 | 0.16 | |
| Salmon 200254 | 82 | NC | 82 | Delayed Recall | 3 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.50 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Savings, Retention | 29% | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.95 | 0.16 | |
| Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Figural Intrusions | 1* | 0.27 | 0.82 | 0.19 | 0.87 | 0.14 | |
| Other Memory Tests – The Placing Test | De Jager 200319 | 40 | MCI | 28 | Total | 10 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.59 |
| De Jager 200319 | 39 | MCI | 28 | Objects | 6 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.58 | |
| De Jager 200319 | 39 | MCI | 28 | Faces | 5 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.58 | |
| Other Memory Tests - Wechsler Memory Scales (WMS) Logical Memory (LM) + Visual Reproduction (VR) | Troster 199361 | 58 | NC | 69 | Savings, Retention | NR | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 0.46 |
| Other Memory Tests - Fuld Object Memory Evaluation (FOME) | Loewenstein 200138 | 268 | NC | 144 | Trials Total (age 59-68) | 19 | 0.93 | 1.00 | NA | NA | 0.65 |
| Loewenstein 200138 | 268 | NC | 144 | Trials Total (age 69-78) | 17 | 0.94 | 1.00 | NA | NA | 0.65 | |
| Loewenstein 200138 | 268 | NC | 144 | Trials Total (age 69-78) | 18 | 0.94 | 1.00 | NA | NA | 0.65 | |
| Loewenstein 200138 | 268 | NC | 144 | Trials Total (age 79-90) | 18 | 0.95 | 0.94 | NA | NA | 0.65 | |
| Other Memory Tests – Process Dissociation Procedure | Millar 201744 | 64 | NC | 519 | Recollection Estimate | NR | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.11 |
Abbreviations: ADAS-Cog=Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale; aMCI=amnestic mild cognitive impairment; CERAD=Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; CogState ISLT= Cogstate International Shopping List Test; Comp=comparator; DRS=dementia rating scale; DWR=Delayed Word Recall; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; FOME=Fuld Object Memory Evaluation; HVLT= Hopkins Verbal Learning Test; LM=logical memory; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; NAB=Neuropsychological Assessment Battery; NC=normal control; NR=not reported; NPV=negative predictive value; PPV=positive predictive value; RBANS= Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; SD=standard deviation; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale; VR=visual reproduction
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cutpoint indicate CATD
- **
indicates 2 standard deviations below the control mean
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.5Classification accuracy results for executive tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Executive Test | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
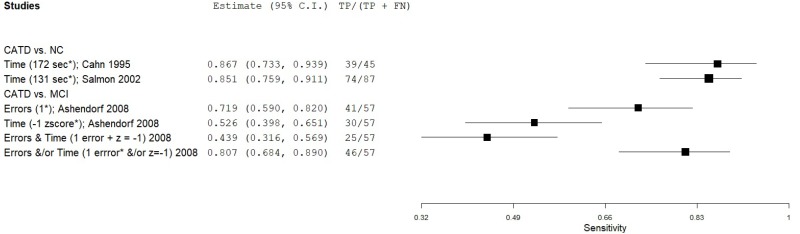
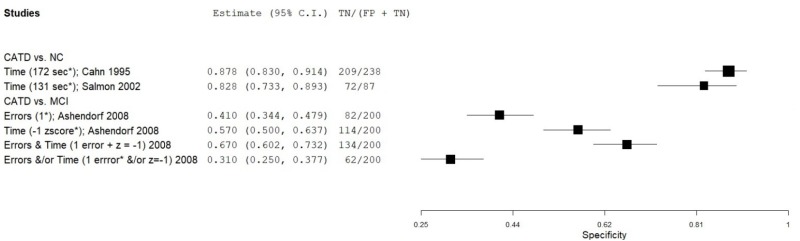
| Trail Making Test (TMT) part B | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Time (sec) | 173* | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.58 | 0.97 | 0.16 |
| Salmon 200254 | 87 | NC | 87 | Time (sec) | 131* | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.50 | |
| Ashendorf 20081 | 57 | MCI | 200 | Time (z score) | -1.0 | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.26 | 0.81 | 0.22 | |
| Ashendorf 20081 | 57 | MCI | 200 | Errors | 1 error* | 0.72 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.84 | 0.22 | |
| Ashendorf 20081 | 57 | MCI | 200 | Errors (1) AND Time (-1.0 z) | 1*, -1 z | 0.44 | 0.67 | 0.27 | 0.81 | 0.22 | |
| Ashendorf 20081 | 57 | MCI | 200 | Errors (1) AND/OR Time (-1.0 z) | 1*, -1 z | 0.81 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.22 | |
| Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised (WAIS-R) Digit Symbol | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Total score | 33 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 0.99 | 0.16 |
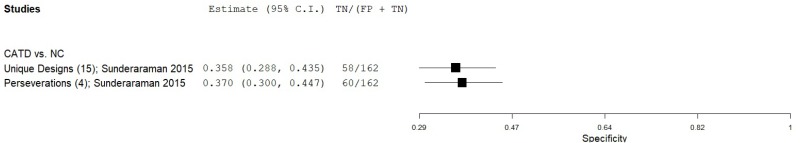
| Graphic Pattern Generation Test (GPGT) | Sunderaraman 201558 | 107 | NC | 162 | Row 1 Unique Designs | 15 | 0.81 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 0.74 | 0.40 |
| Sunderaraman 201558 | 107 | NC | 162 | Row 1 Perseverations | 4 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.70 | 0.40 | |
| Modified Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) | Bondi 19932 | 87 | NC | 75 | Categories | 4 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.54 |
| Bondi 19932 | 23 | NC | 75 | Categories (mild CATD) | 4 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.94 | 0.23 | |
| Bondi 19932 | 87 | NC | 75 | Nonperseverative errors | 16* | 0.58 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 0.54 | |
| Bondi 19932 | 23 | NC | 75 | Nonperseverative errors (mild CATD) | 16* | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.48 | 0.84 | 0.23 | |
| Bondi 19932 | 87 | NC | 75 | Perseverative errors | 6* | 0.76 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.54 | |
| Bondi 19932 | 23 | NC | 75 | Perseverative errors (mild CATD) | 6* | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.23 |
Abbreviations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; Comp=comparator; GPGT=Graphic Pattern Generation Test; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; NC=normal control; NPV=negative predictive value; PPV=positive predictive value; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; TMT=Trail Making Test; WAIR-R=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised; WCST=Wisconsin Card Sorting Test
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cutpoint indicate CATD
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.6Classification accuracy results for language tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Language Test | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semantic (Category) Verbal Fluency (SVF) | Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Animals (mild CATD) | 9 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 0.50 |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Animals (moderate CATD) | 9 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Animals (severe CATD) | 9 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.50 | |
| Connor 200518 | 50 | NC | 50 | Animals | 12 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Animals (DRS 101-105) | 12 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.98 | 0.17 | |
| Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Animals (DRS 106-110) | 12 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.17 | |
| Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Animals (DRS 111-115) | 12 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.17 | |
| Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Animals (DRS 116-120) | 12 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.93 | 0.17 | |
| Connor 200518 | 10 | NC | 50 | Animals (DRS 121-125) | 12 | 0.40 | 0.86 | 0.36 | 0.88 | 0.17 | |
| Monsch 199246 | 89 | NC | 53 | Animals | 13 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.63 | |
| Canning 200411 | 37 | NC | 46 | Animals (mild CATD) | 13 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.45 | |
| Canning 200411 | 98 | NC | 46 | Animals | 14 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.78 | 0.68 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Animals (mild CATD) | 16 | 0.95 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.98 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | First names | 15 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | First names (mild CATD) | 17 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.68 | 0.96 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 43 | NC | 17 | First names (males) | 12 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.70 | 0.72 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 46 | NC | 36 | First names (females) | 16 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.56 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Fruits | 10 | 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Fruits (mild CATD) | 10 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Vegetables | 9 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Vegetables (mild CATD) | 10 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Supermarket | 15 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Supermarket (mild CATD) | 15 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 43 | NC | 17 | Supermarket (males) | 14 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.84 | 0.72 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 46 | NC | 36 | Supermarket (females) | 16 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.56 | |
| Kalbe 200431 | 88 | NC | 97 | Supermarket | ? | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.92 | 0.48 | |
| Cerhan 200212 | 40 | NC | 221 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables) | 28 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.98 | 0.15 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables) | 37 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.63 | |
| Salmon 200254 | 95 | NC | 95 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables) | 37 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables; mild AD) | 37 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 43 | NC | 17 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables; males) | 24 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.72 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 36 | NC | 46 | Total (animals, fruits, vegetables; females) | 37 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.44 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Total Category (unspecified) | 31 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.50 | 0.98 | 0.16 | |
| Clark 201416 | 41 | NC | 44 | Combined correct, perservations, intrusions | NR | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.48 | |
| Clark 201416 | 41 | NC | 44 | Combined correct, perseverations, intrusions, clustering, switching, ICA component scores | NR | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.48 | |
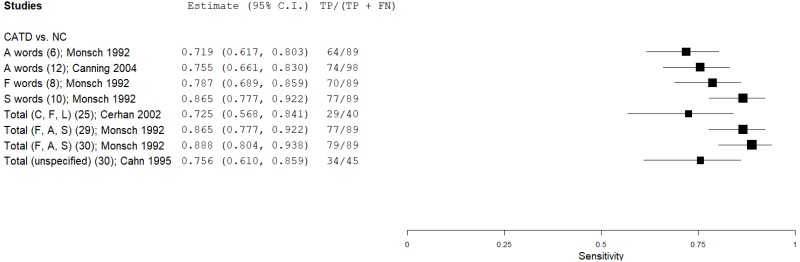
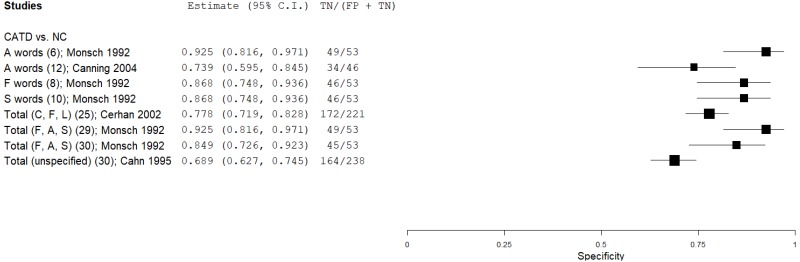
| Phonemic (Letter) Verbal Fluency (PVF) | Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | A words | 6 | 0.72 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.66 | 0.63 |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | A words (mild CATD) | 11 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.91 | 0.28 | |
| Canning 200411 | 98 | NC | 46 | A words | 12 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.68 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | F words | 8 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.71 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | F words (mild CATD) | 8 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | S words | 10 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | S words (mild CATD) | 10 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.28 | |
| Cerhan 200212 | 40 | NC | 221 | Total (C, F, L) | 25 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.37 | 0.94 | 0.15 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Total (F, A, S) | 29 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 89 | NC | 53 | Total (F, A, S) | 30 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.63 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 21 | NC | 53 | Total (F, A, S; mild CATD) | 31 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.28 | |
| Monsch 199245 | 43 | NC | 17 | Total (F, A, S; males) | 27 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.65 | 0.72 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Total Letter (unspecified) | 30 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.32 | 0.94 | 0.16 | |
| Combined Semantic and Phonemic Verbal Fluency | Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Intrusion error proportion | 1* | 0.39 | 0.87 | 0.33 | 0.90 | 0.14 |
| Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Preservative error proportion | 2* | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.14 | |
| Canning 200411 | 98 | NC | 46 | Difference (animal - letter F) | 0 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.49 | 0.68 | |
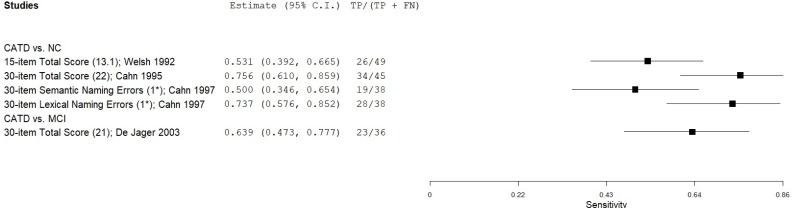
| Boston Naming Test (BNT 15-item) | Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Total score (Mild CATD) | 13 | 0.53 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.50 |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Total score (Moderate CATD) | 13 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 49 | NC | 49 | Total score (Severe CATD) | 13 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.50 | |
| Boston Naming Test (BNT 30-item) | Cahn 19959 | 45 | NC | 238 | Total score | 22 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.49 | 0.95 | 0.16 |
| Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Semantic naming errors | 1* | 0.50 | 0.72 | 0.22 | 0.90 | 0.14 | |
| Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Lexical naming errors | 1* | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 0.14 | |
| De Jager 200319 | 36 | MCI | 27 | Total score | 21 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.63 | 0.57 |
Abbreviations: BNT=Boston Naming Test; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; Comp=comparator; DRS=dementia rating scale; ICA=independent component analysis; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; NC=normal control; NR=not reported; NPV=negative predictive value; PPV=positive predictive value; PVF=phonemic verbal fluency; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; SVF=semantic verbal fluency
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cutpoint indicate CATD
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.7Classification accuracy results for combination cognitive tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Combination Cognitive Test | Author Year | CATD N | Comp Group | Comp N | Score (Subgroup) | Cut Point | SE | SP | PPV+ | NPV+ | CATD Base Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
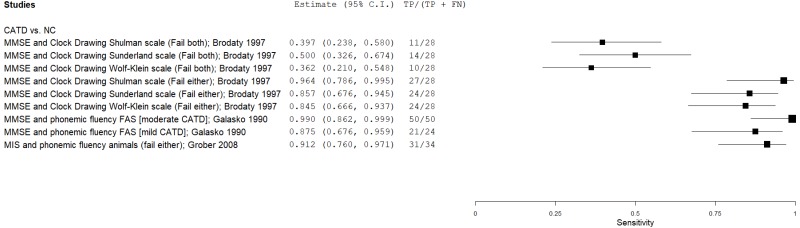
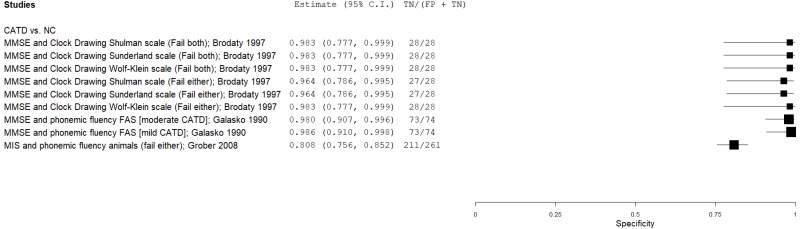
| Supplementing the MMSE | Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Shulman) | Fail both (23, 3*) | 0.40 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.63 | 0.50 |
| Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Sunderland) | Fail both (23, 8) | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.50 | |
| Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Wolf-Klein) | Fail both (23, 8) | 0.36 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 0.50 | |
| Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Shulman) | Fail either (23, 3*) | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.50 | |
| Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Sunderland) | Fail either (23, 8) | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.50 | |
| Brodaty 19975 | 28 | NC | 28 | MMSE, CD (Wolf-Klein) | Fail either (23, 8) | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.50 | |
| Galasko 199023 | 50 | NC | 74 | MMSE, PVF (FAS) | NR | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.40 | |
| Galasko 199023 | 24 | NC | 74 | MMSE, PVF (FAS) | NR | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.24 | |
| Other Test Combinations | Cahn 19978 | 38 | NC | 236 | Errors/intrusions (SVF, PVF, BNT-30, CERAD List) | >0.5 (logistic equation cutoff) | 0.29 | 0.98 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 0.14 |
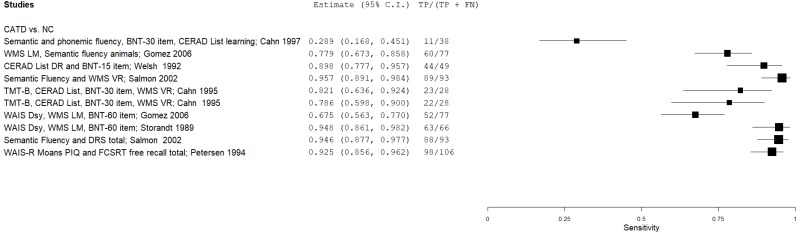
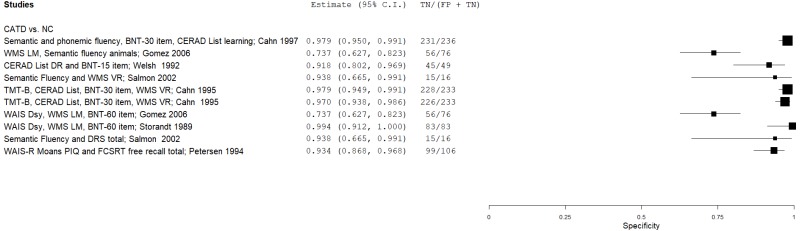
| Cahn 19959 | 28 | NC | 233 | TMT-B, CERAD List, BNT-30, WMS VR | >0.5 (logistic equation cutoff) | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.11 | |
| Cahn 19959 | 28 | NC | 233 | TMT-B, CERAD List, BNT-30, WMS VR (+ age) | >0.5 (logistic equation cutoff) | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.11 | |
| Salmon 200254 | 93 | NC | 16 | SVF, WMS VR | Fail both (39.5, 8.5) | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.85 | |
| Salmon 200254 | 93 | NC | 16 | SVF, DRS total | Fail both (39.5, 132.5) | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.76 | 0.85 | |
| Grober 200827 | 34 | NC | 261 | MIS, SVF animals | Fail either (4, 9) | 0.91 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 0.99 | 0.12 | |
| Storandt 198957 | 66 | NC | 83 | WMS LM, WAIS DSy, BNT 60-item | ≥0 (canonical variate) | 0.95 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.44 | |
| Gomez 200625 | 77 | NC | 76 | WMS LM, WAIS DSy, BNT 60-item | NR | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.50 | |
| Gomez 200625 | 77 | NC | 76 | WMS LM, SVF animals | NR | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.50 | |
| Welsh 199266 | 49 | NC | 49 | CERAD List DR, BNT-15 | NR | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.50 | |
| Petersen 199450 | 106 | NC | 106 | WAIS-R Moans PIQ and FCSRT FR trials total | NR | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.50 |
Abbreviations: BNT=Boston Naming Test; CERAD= Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s-type dementia; CD=clock drawing; Comp=comparator; DR=delayed recall; DRS=dementia rating scale; DSy=Digit Symbol; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; FR=free recall; LM=logical memory; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; MIS=Memory Impairment Screen; MMSE=Mini Mental State Examination; NC=normal control; NR=not reported; NPV=negative predictive value; PIQ=performance intelligence quotient; PPV=positive predictive value; PVF=phonemic verbal fluency; SE=sensitivity; SP=specificity; SVF=semantic verbal fluency; WAIS=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale; VR=visual reproduction; VRT=visual reproduction test
- *
indicates that values equal to or higher than the specified cut point indicate CATD
- +
indicates that some PPV and NPV values were back-calculated
Appendix Table C.8Cognitive studies: Participant characteristics by diagnostic group in eligible cognitive studies with low-medium risk of bias
| Study | N | CATD | NC | MCI | Cognitive Tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashendorf 20081 | 257 | Age (yrs) | 79.7 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 72.5 | TMT B |
| Education (yrs) | 14.6 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 14.6 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 58% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 41% | |||
| Race (% white) | 77% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | 77% (all subjects) | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 24.2 | MMSE | NA | MMSE | 28.1 | |||
| CDR | ≥1.0 | CDR | NA | CDR | NR | |||
| Bondi 19932 | 162 | Age (yrs) | 72.2 | Age (yrs) | 71.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | WCST |
| Education (yrs) | 13.0 | Education (yrs) | 13.7 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 47% | Gender (% male) | 36% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Self-Report | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 20.7 | MMSE | 28.9 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Brodaty 19975 | 56 | Age (yrs) | 73.1 | Age (yrs) | 69.5 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD MMSE & CD |
| Education (yrs) | 8.7 | Education (yrs) | 11.3 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 32% | Gender (% male) | 25% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III-R, NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Unclear | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 19.5 | MMSE | 28.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Brown 20096 | 376 | Age (yrs) | 69 | Age (yrs) | NR (age-matched) | Age (yrs) | NA | TYM |
| Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Medical history | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 22.5 | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Buschke 19997 | 472 | Age (yrs) | 81.1 | Age (yrs) | 79.3 | Age (yrs) | NA | MIS |
| Education (yrs) | 11.3 | Education (yrs) | 12.2 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 36% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 81% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | 81% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III-R, NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Cahn 1995, 1996, 19978–10 | 283 | Age (yrs) | 83.6 | Age (yrs) | 78.4 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD CERAD List WAIS DSy TMT B PVF, SVF Combinations |
| Education (yrs) | 13.8 | Education (yrs) | 13.8 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 60% | Gender (% male) | 41% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Canning 200411 | 144 | Age (yrs) | 73 | Age (yrs) | 70.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | PVF, SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 13.6 | Education (yrs) | 15 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | normal cognitive testing, MRI | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 23 | MMSE | 28.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Cerhan 200212 | 261 | Age (yrs) | 77.3 | Age (yrs) | 76.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | PVF, SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 12.4 | Education (yrs) | 13.7 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 43% | Gender (% male) | 41% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Chandler 200513 | 250 | Age (yrs) | 74.4 | Age (yrs) | 74.2 | Age (yrs) | 72.8 | CERAD TS CERAD List |
| Education (yrs) | 13.6 | Education (yrs) | 15.3 | Education (yrs) | 14.8 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 39% | Gender (% male) | 40% | Gender (% male) | 48% | |||
| Race (% white) | 100% | Race (% white) | 100% | Race (% white) | 100% | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | ||||
| MMSE | 21.1 | MMSE | 28.6 | MMSE | 27.5 | |||
| CDR | 1 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NR | |||
| Chapman 201014 | 133 | Age (yrs) | 75.8 | Age (yrs) | 70.3 | Age (yrs) | NA | MMSE |
| Education (yrs) | 14.3 | Education (yrs) | 15.9 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 56% | Gender (% male) | 40% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV-TR, NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Physician assessment | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 24.3 | MMSE | 28.64 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Clark 201015 | 117 | Age (yrs) | 76.2 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 74.8 | RBANS List RBANS Story |
| Education (yrs) | 12.8 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 13.9 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 37% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 34% | |||
| Race (% white) | 91% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | 91% (all subjects) | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | |||
| MMSE | 21.79 | MMSE | NA | MMSE | 27 | |||
| CDR | 4.4 (sum of boxes) | CDR | NA | CDR | 1.4 (sum of boxes) | |||
| Clark 201416 | 85 | Age (yrs) | 72.5 | Age (yrs) | 70.5 | Age (yrs) | NA | SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | 14.4 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 63% | Gender (% male) | 32% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 24.3 | MMSE | 29.3 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 4.0 (SOB) | CDR | 0.2 (SOB) | CDR | NA | |||
| Connor 200518 | 100 | Age (yrs) | 73.3 | Age (yrs) | 73.7 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 12.6 | Education (yrs) | 13.1 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 21.3 | MMSE | 28.92 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| De Jager 200319 | 84 | Age (yrs) | 77 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 76 | CLOX TPT |
| Education (yrs) | 12 (all subjects) | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 12 (all subjects) | |||
| Gender (% male) | 55% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 41% | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | NR | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 21 | MMSE | NA | MMSE | 28 | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NA | CDR | NR | |||
| Elamin 201620 | 59 | Age (yrs) | 62.6 | Age (yrs) | 66.6 | Age (yrs) | NA | ACE-III |
| Education (yrs) | 46.7%<16, 26.7% 16-18, 16.7%>18 | Education (yrs) | 53.6%<16, 42.9% 16-18, 3.6%>18 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 48.4% | Gender (% male) | 57.1% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | Full diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NR | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Esteban-Santillas 199821 | 80 | Age (yrs) | 72 | Age (yrs) | 72 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD |
| Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | ~50% | Gender (% male) | ~50% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Screening test and staging | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 1 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Galasko 199023 | 148 | Age (yrs) | 71.3 | Age (yrs) | 69.7 | Age (yrs) | NA | MMSE & PVF |
| Education (yrs) | 14.2 | Education (yrs) | 14.5 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 47% | Gender (% male) | 37% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 20.47 | MMSE | 29 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Gavett 200924 | 153 | Age (yrs) | 80.6 | Age (yrs) | 71.5 | Age (yrs) | 76.1 | NAB List |
| Education (yrs) | 14.7 | Education (yrs) | 16.5 | Education (yrs) | 14.7 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 58% | Gender (% male) | 67% | Gender (% male) | 45% | |||
| Race (% white) | 89% | Race (% white) | 83% | Race (% white) | 83% | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | |||
| MMSE | 23.1 | MMSE | 29.6 | MMSE | 28 | |||
| CDR | 1.21 | CDR | 0.0 | CDR | 0.3 | |||
| Gomez 200625 | 153 | Age (yrs) | 76.8 | Age (yrs) | 77 | Age (yrs) | NA | Combination (WMS LM, WAIS digit symbol, BNT) Combination (WMS LM, SVF) |
| Education (yrs) | 14.3 | Education (yrs) | 14.9 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 47% | Gender (% male) | 42% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 93% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | 93% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA, DSM III-R | Dx Criteria | CDR | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.5 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Grober 2008}26 | 318 | Age (yrs) | 65+ | Age (yrs) | 65+ | Age (yrs) | NA | FCSRT free recall, FCSRT total recall |
| Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | African American and Caucasian patients | Race (% white) | African American and Caucasian patients | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV, neurologist dx | Dx Criteria | Neuropsychological evaluation | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 18+ | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | Most 0.5 | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Grober 200827 | 295 | Age (yrs) | NR for CATD | Age (yrs) | 78.2 | Age (yrs) | NA | Combination (MIS or SVF) |
| Education (yrs) | NR for CATD | Education (yrs) | 12.9 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR for CATD | Gender (% male) | 18% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | African American and Caucasian patients | Race (% white) | African American and Caucasian patients | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV and NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic battery, informant responses | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 18+ | MMSE | 27.4 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR for CATD | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Hollocks 201829 | 102 | Age (yrs) | 73.4 | Age (yrs) | 73.3 | Age (yrs) | NA | BMET |
| Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 49% | Gender (% male) | 49% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV and ICD-10 | Dx Criteria | Medical history | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 22.0 | MMSE | 28.3 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Johnson 200330 | 242 | Age (yrs) | 74.3 (both cohorts) | Age (yrs) | 76.7 (both cohorts) | Age (yrs) | NA | WMS LM |
| Education (yrs) | 12.9 (both cohorts) | Education (yrs) | 14.1 (both cohorts) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 45% (cohort 1) | Gender (% male) | 28% (cohort 1) | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV (cohort 1); DSM-III-R and NINCDS-ADRDA (cohort 2) | Dx Criteria | Neuro exam (both cohorts) | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.5 (both cohorts) | CDR | 0.0 (both cohorts) | CDR | NA | |||
| Kalbe 200431 | 185 | Age (yrs) | 73.3 | Age (yrs) | 70.2 | Age (yrs) | NA | DemTect List SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 9.8 | Education (yrs) | 11.4 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 40% | Gender (% male) | 28% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 24.1 | MMSE | 28.5 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 1.0-2.0 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Knopman 198932 | 83 | Age (yrs) | 74 | Age (yrs) | 73.5 | Age (yrs) | NA | DWR List |
| Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | 12 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 36% | Gender (% male) | 45.5% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Self-Report | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 23.4 | MMSE | 28.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Kuslansky 200233 | 240 | Age (yrs) | 77.2 | Age (yrs) | 78.9 | Age (yrs) | NA | MIS |
| Education (yrs) | 11.6 | Education (yrs) | 12.6 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 43% | Gender (% male) | 35% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 61% | Race (% white) | 73% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III-R, NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 1.2 | CDR | 0.2 | CDR | NA | |||
| Kuslansky 200434 | 380 | Age (yrs) | 81.7 | Age (yrs) | 78.6 | Age (yrs) | NA | HVLT List |
| Education (yrs) | 11.8 | Education (yrs) | 12.9 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 40% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 65% | Race (% white) | 65% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Self-report | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 22.4 | MMSE | 26.1 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Lange 200635 | 68 | Age (yrs) | 73 | Age (yrs) | 72.9 | Age (yrs) | NA | WMS-III GMI, WMS-III IMI, WMS-III DMI, WAIS-III GAI |
| Education (yrs) | 14.5 | Education (yrs) | 14.2 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 55.9% | Gender (% male) | 55.9% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 91.2% | Race (% white) | 91.2% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 18-23 (or >95 DRS) | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Lee 199636 | 60 | Age (yrs) | 72.4 | Age (yrs) | 67.7 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD |
| Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 36% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Self-Report | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 20.9 | MMSE | 27.9 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.98 | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Loewenstein 200138 | 412 | Age (yrs) | 77.7 | Age (yrs) | 73.8 | Age (yrs) | NA | FOME |
| Education (yrs) | 12.1 | Education (yrs) | 14.1 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 35% | Gender (% male) | 38% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | >18 | MMSE | ≥24 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Logsdon 198937 | 98 | Age (yrs) | 70 | Age (yrs) | 68 | Age (yrs) | NA | WAIS-R Fuld Profile |
| Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 53% | Gender (% male) | 43% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA, DSM III | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 23 | MMSE | 30 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Maruff 201340 | 710 | Age (yrs) | 79.3 | Age (yrs) | 69.5 | Age (yrs) | NA | CBB |
| Education (yrs) | Median 12 | Education (yrs) | Median 12 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 49% | Gender (% male) | 42% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Neuropsych testing | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 19.8 | MMSE | 28.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 5.9 (sum of boxes) | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Mendez 199242 | 72 | Age (yrs) | 70.7 | Age (yrs) | 69.3 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD |
| Education (yrs) | 12 | Education (yrs) | 12.1 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 39% | Gender (% male) | 38% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Medical history, cognitive screening | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 13-23 | MMSE | ≥28 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Mendiondo 200343 | 1,534 | Age (yrs) | 72.8 (CERAD) 62.1 (UK-ADRC) | Age (yrs) | 68.6 (CERAD) 73.1 (UK-ADRC) | Age (yrs) | NA | BAS |
| Education (yrs) | 13.4 (CERAD) 12.9 (UK-ADRC) | Education (yrs) | 13.8 (CERAD) 15.8 (UK-ADRC) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 41% (CERAD) 28.4% (UK-ADRC) | Gender (% male) | 34% (CERAD) 36.6% (UK-ADRC) | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 87% (CERAD) 98.4% (UK-ADRC) | Race (% white) | 94% (CERAD) 98.9% (UK-ADRC) | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | (CERAD) NR (UK-ADRC) | Dx Criteria | No dementia dx, screen, no other neurological conditions (CERAD) Diagnostic workup (UK-ADRC) | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 22.6 (CERAD) NR (UK-ADRC) | MMSE | 28.9 (CERAD) NR (UK-ADRC) | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.5 or 1.0 (UKADRC) | CDR | NR (UK-ADRC) | CDR | NA | |||
| Millar 201744 | 583 | Age (yrs) | 75.0 | Age (yrs) | 68.9 | Age (yrs) | NA | PDP memory task, FCSRT, WMS LM II |
| Education (yrs) | 15.1 | Education (yrs) | 15.6 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 58% | Gender (% male) | 38% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | CDR | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 26.2 | MMSE | 29 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.5 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Monsch 199245 | 142 | Age (yrs) | 72.1 | Age (yrs) | 71.2 | Age (yrs) | NA | PVF, SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 13.5 | Education (yrs) | 13.6 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 48% | Gender (% male) | 32% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 98% | Race (% white) | 98% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III and NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Medical history | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 18 | MMSE | 28.8 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Monsch 199546 | 641 | Age (yrs) | 74.2 (both cohorts) | Age (yrs) | 75.9 (both cohorts) | Age (yrs) | NA | DRS |
| Education (yrs) | 13.2 (both cohorts) | Education (yrs) | 14.2 (both cohorts) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 50% (both cohorts) | Gender (% male) | 41% (both cohorts) | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | majority white (cohort 1) | Race (% white) | Majority white (cohort 1) | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III and NINCDS-ADRDA (both cohorts) | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup (both cohorts) | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Morgan 201048 | 238 | Age (yrs) | 77.8 | Age (yrs) | 76.5 | Age (yrs) | 76.5 | RBANS |
| Education (yrs) | 3.5* (3=12 years; 4=13-15 years) | Education (yrs) | 3.8* (3=12 years; 4=13-15 years) | Education (yrs) | 3.4* (3=12 years; 4=13-15 years) | |||
| Gender (% male) | 37% | Gender (% male) | 37% | Gender (% male) | 37% | |||
| Race (% white) | 87% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | 87% (all subjects) | Race (% white) | 87% (all subjects) | |||
| Dx Criteria | Cognitive scores | Dx Criteria | Self-Report | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 22.9 | MMSE | NR | MMSE | 26.2 | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NR | |||
| Parsey 201149 | 66 | Age (yrs) | 74.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 70.5 | CLOX |
| Education (yrs) | 15.7 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 16.2 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 61% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 39% | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | NR | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | MMSE | NR | |||
| CDR | 1.0 | CDR | NA | CDR | 0.5 | |||
| Petersen 199450 | 212 | Age (yrs) | 80.7 | Age (yrs) | 80.2 | Age (yrs) | NA | Brief Battery (WIAS-R PIQ and FCSRT trials total free recall) |
| Education (yrs) | 11.8 | Education (yrs) | 12.6 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NR | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA, DSM III-R | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 20.9 | MMSE | 28.5 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Quarmley 201751 | 496 | Age (yrs) | NA (subsample data reported) | Age (yrs) | NA (subsample data reported) | Age (yrs) | NA (subsample data reported) | MoCA |
| Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | NA | MMSE | NA | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NA | CDR | NA | CDR | NA | |||
| Roalf 201753 | 587 | Age (yrs) | 75.9 | Age (yrs) | 70.3 | Age (yrs) | 73 | MoCA, MMSE |
| Education (yrs) | 13.4 | Education (yrs) | 17 | Education (yrs) | 14.7 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 35% | Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 48 | |||
| Race (% white) | 71% | Race (% white) | 79% | Race (% white) | 78% | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-IV-TR | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 20 | MMSE | 29 | MMSE | 26 | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NR | |||
| Salmon 200254 | 196 | Age (yrs) | 71.6 | Age (yrs) | AD Match (2 years) | Age (yrs) | NA | TMT B SVF Combinations |
| Education (yrs) | 14.2 | Education (yrs) | AD Match (3years) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 49% | Gender (% male) | AD Match | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | AD Match | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III/DSM-III-R, NINCDS-ADRDA, pathological or clinical verification | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 25.6 | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Solomon 199870 | 120 | Age (yrs) | 77.6 | Age (yrs) | 77.5 | Age (yrs) | NA | 7MS |
| Education (yrs) | 13.3 | Education (yrs) | 14.4 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 35% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Medical history, functionally independent | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 21 | MMSE | 28.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Springate 201456 | 147 | Age (yrs) | 73.9 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 72.9 | DRS |
| Education (yrs) | 12.5 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 13.3 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 43% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 43% | |||
| Race (% white) | 94% | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | 98% | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | |||
| MMSE | 23.1 | MMSE | NA | MMSE | 26.8 | |||
| CDR | 0.9 | CDR | NA | CDR | 0.5 | |||
| Storandt 198957 | 149 | Age (yrs) | 72.2 | Age (yrs) | 71.6 | Age (yrs) | NA | Combination (WMS LM, WAIS DSy, BNT) |
| Education (yrs) | 12.8 (all subjects) | Education (yrs) | 12.8 (all subjects) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 44% | Gender (% male) | 39% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 100% | Race (% white) | 100% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | CDR and physician diagnosis | Dx Criteria | CDR | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 1.0 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Sunderaraman 201558 | 269 | Age (yrs) | 77.6 | Age (yrs) | 75.7 | Age (yrs) | NA | GPGT |
| Education (yrs) | 15.4 | Education (yrs) | 16.0 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 43% | Gender (% male) | 34% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Interview, cognitive screen | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | ≥17 | MMSE | ≥27 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Thompson 201159 | 183 | Age (yrs) | 73.5 | Age (yrs) | 73.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | Cogstate ISLT |
| Education (yrs) | 11.7 | Education (yrs) | 12.1 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 58% | Gender (% male) | 53% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Cognitive testing, neuro exam | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 22.3 | MMSE | 29.1 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 4.9 (sum of boxes) | CDR | 0 (sum of boxes) | CDR | NA | |||
| Tremont 201160 | 150 | Age (yrs) | 74.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 72.9 | MCAS |
| Education (yrs) | 12.5 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 13.3 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 42% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 42% | |||
| Race (% white) | 94% | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | 98% | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 0.5-1.0 | CDR | NA | CDR | 0.5 | |||
| Troster 199361 | 127 | Age (yrs) | 72.9 | Age (yrs) | 74.4 | Age (yrs) | NA | WMS LM & VR |
| Education (yrs) | 13.2 | Education (yrs) | 13.5 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 47% | Gender (% male) | 41% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Medical history | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | NR | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Trzepacz 201562 | 399 | Age (yrs) | 77.6 | Age (yrs) | NA | Age (yrs) | 74.2 | MoCA |
| Education (yrs) | 15.8 | Education (yrs) | NA | Education (yrs) | 16.2 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 67% | Gender (% male) | NA | Gender (% male) | 61% | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | Race (% white) | NR | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | NA | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 20.3 | MMSE | NA | MMSE | 27.8 | |||
| CDR | 0.5-1.0 | CDR | NA | CDR | 0.5 | |||
| Tuokko 199263 | 120 | Age (yrs) | 70.6 | Age (yrs) | 71.3 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD |
| Education (yrs) | 10.7 | Education (yrs) | 13.1 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 33% | Gender (% male) | 40% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III-R and NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Interview, medical questionnaire | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 15.5 | MMSE | NR | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Uhlmann 199164 | 209 | Age (yrs) | 76 (all subjects) | Age (yrs) | 76 (all subjects) | Age (yrs) | NA | MMSE |
| Education (yrs) | 19% middle, 30% HS, 38% college, 13% graduate (all subjects) | Education (yrs) | 19% middle, 30% HS, 38% college, 13% graduate (all subjects) | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 42% (all subjects) | Gender (% male) | 42% (all subjects) | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | 97% | Race (% white) | 95% | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | DSM-III, NINCDS/ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Unclear | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 19 | MMSE | 27 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Welsh 1991, 199265, 66 | 196 | Age (yrs) | 71.1 | Age (yrs) | 71.1 | Age (yrs) | NA | CERAD List SVF |
| Education (yrs) | 13.8 | Education (yrs) | 14 | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 51% | Gender (% male) | 51% | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup, free of cognitive impairment | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 20.0 | MMSE | 28.9 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | 1.3 | CDR | 0 | CDR | NA | |||
| Wolf-Klein 198967 | 251 | Age (yrs) | 79 | Age (yrs) | 77 | Age (yrs) | NA | CD |
| Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NR | Education (yrs) | NA | |||
| Gender (% male) | 30% (all subjects) | Gender (% male) | 30% (all subjects) | Gender (% male) | NA | |||
| Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NR | Race (% white) | NA | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Diagnostic Workup | Dx Criteria | NA | |||
| MMSE | 12.8 | MMSE | 27.7 | MMSE | NA | |||
| CDR | NR | CDR | NR | CDR | NA | |||
| Zainal 201668 | 269 | Age (yrs) | 72.2 | Age (yrs) | 61.8 | Age (yrs) | 66.4 | ADAS-Cog List |
| Education (yrs) | 6.0 | Education (yrs) | 11.7 | Education (yrs) | 10.9 | |||
| Gender (% male) | 63% | Gender (% male) | 31% | Gender (% male) | 50% | |||
| Race (% white) | 77% Chinese | Race (% white) | 90% Chinese | Race (% white) | 89% Chinese | |||
| Dx Criteria | NINCDS-ADRDA | Dx Criteria | Staging | Dx Criteria | Petersen criteria | |||
| MMSE | 22.3 | MMSE | 29.1 | MMSE | 27.4 | |||
| CDR | 0.5-1.0 | CDR | 0 | CDR | 0.5 |
Abbreviations: ACE=Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination; ADAS-Cog=Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale; BAS=Brief Alzheimer’s Screen; BMET=Brief Memory and Executive Test; BNT=Boston Naming Test; CATD=clinical Alzheimer-type dementia; CBB=Cogstate Brief Battery; CD=Clock drawing; CDR=Clinical Dementia Rating; CERAD=Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease neuropsychological battery; DMI=Delayed Memory Index; DRS=Dementia Rating Scale; DSM=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; DSy=Digit Symbol; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; FOME=Fuld Object Memory Evaluation; GAI=General Ability Index; GMI=General Memory Index; GPGT=Graphic Pattern Generation Test; HS=high school; HVLT=Hopkins Verbal Learning Test; IMI=Immediate Memory Index; ISLT=International Shopping List Test; LM=Logical Memory; MCAS=Minnesota Cognitive Acuity Screen; MCI=Mild Cognitive Impairment; MIS=Memory Impairment Screen; MMSE=Mini-Mental State Examination; MoCA=Montreal Cognitive Assessment; NA=not applicable; NAB=Neuropsychological Assessment Battery; NC=normal cognition; NINCDS-ADRDA=National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke and Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders; NR=not reported; PDP=Process Dissociation Procedure; PIQ=Performance Intelligent Quotient; PVF=phonemic verbal fluency; RBANS=Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status; SVF=semantic verbal fluency; TMT B=Trail Making Test Part B; TPT=The Placing Test; TYM=Test Your Memory; VR=visual reproduction; WAIS=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; WCST=Wisconsin Card Sorting Test; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale
Appendix Table C.9Brief cognitive tests and scores represented in extracted studies with low-moderate risk of bias
| Test, estimated administration time | Score | Range* | Better performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Minute Screen (7MS), 5-10 min | Total score | 0-no ceiling | Higher |
| Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Exam (ACE), 15-20 min | Total score | 0-100 | Higher |
| Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive (ADAS-Cog), 30 min | 11-item total score | 0-70 | Lower |
| 12-item total score | 0-80 | Lower | |
| 12-item list learning score | 0-32 | Lower | |
| Boston Naming Test (BNT) | 15-item total score, 5-10 min | 0-15 | Higher |
| 30-item total score, 15 min | 0-30 | Higher | |
| 30-item semantic errors | 0-30 | Lower | |
| 30-item lexical errors | 0-30 | Lower | |
| Brief Alzheimer’s Screen (BAS), < 5 min | Total score | 0-no ceiling | Higher |
| Brief Memory and Executive Test (BMET), 10 min | Total score | 0-16 | Higher |
| Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD) neuropsychological battery, 30 min | CERAD total score, 20 min | 0-100 | Higher |
| List learning delayed recall | 0-10 | Higher | |
| List learning % retention (savings) | 0-100 | Higher | |
| List learning recognition scores | Varies | Higher | |
| List learning intrusion scores | Varies | Lower | |
| Clock Drawing, multiple versions, 5 min | Rouleau quantitative scale | 10 | Higher |
| Sunderland | 10 | Higher | |
| Mendez | 20 | Higher | |
| Shulman | 5 | Higher | |
| Tuokko | -- | Lower | |
| Watson | 0-7 | Lower | |
| Wolf-Klein | 10 | Higher | |
| CLOX 1 (draw) | 15 | Higher | |
| CLOX 2 (copy) | 15 | Higher | |
| Cogstate Brief Battery (CBB), 15 min | Learning & Working Memory composite | M 100 ±10 | Higher |
| Attention & Psychomotor composite | M 100 ±10 | Higher | |
| Cogstate International Shopping List Test (ISLT), 20-25 min | Trials total | 0-36 | Higher |
| Delayed recall | 0-12 | Higher | |
| Dementia Rating Scale (DRS), multiple versions, 30 min | Total score | 0-144 | Higher |
| Attention | 0-37 | Higher | |
| Initiation/Perseveration | 0-37 | Higher | |
| Construction | 0-6 | Higher | |
| Conceptualization | 0-39 | Higher | |
| Memory | 0-25 | Higher | |
| Delayed Word Recall (DWR), 5-10 min | Total score | 0-10 | Higher |
| DemTect, 8-10 min | Delayed recall | 0-18 | Higher |
| Free and Cued Selective Reminding (FCSR), 15 min | Free recall | 0-48 | Higher |
| Total recall | 0-48 | Higher | |
| Fuld Object Memory Evaluation (OME), 15 min | 3 trials total | 0-30 | Higher |
| Graphic Pattern Generation (GPG) | Row 1 perseverations | 0-9 | Lower |
| Row 1 unique designs | 0-10 | Higher | |
| Hopkins Verbal Learning Test (HVLT), multiple versions, 30+ min | Trials total, 10-15 min | 0-36 | Higher |
| Memory Impairment Screen (MIS), < 5 min | Total score | 0-8 | Higher |
| Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), 5-10 min | Total score | 0-30 | Higher |
| Minnesota Cognitive Acuity Screen (MCAS), 15 min | Total score | 0-no ceiling | Higher |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), 10 min | Total score | 0-30 | Higher |
| Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (NAB) List Learning subtest, 20-25 min | List A immediate recall | M 50 ±10 | Higher |
| List B immediate recall | M 50 ±10 | Higher | |
| List A short delayed recall | M 50 ±10 | Higher | |
| List A long delayed recall | M 50 ±10 | Higher | |
| Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS), 30 min | Verbal index | M 100 ±15 | Higher |
| Visual index | M 100 ±15 | Higher | |
| % Retention scores (savings) | 0-100 | Higher | |
| Test Your Memory (TYM), < 5 min (scoring time) | Total score | 0-50 | Higher |
| Trail Making Test (TMT), part B, 5 min | TMT B time (seconds) | 0-300 | Lower |
| TMT B errors | 0-5 | Lower | |
| Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), multiple versions | Fuld profile, 30 min | Yes/No | -- |
| Digit Symbol total, < 5 min | Varies | Higher | |
| Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS), multiple versions, 30-40 min | General Memory index | M 100 ±15 | Higher |
| Immediate Memory index | M 100 ±15 | Higher | |
| Delayed Memory index | M 100 ±15 | Higher | |
| Logical Memory I & II | Varies | Higher | |
| Visual Reproduction I & II | Varies | Higher | |
| % Retention scores (savings) | 0-100 | Higher | |
| Intrusion error scores | 0-no ceiling | Lower | |
| Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), 20-30 min | Categories achieved | 0-6 | Higher |
| Perseverative errors | count or % | Lower | |
| Non-perseverative errors | count or % | Lower | |
| The Placing Test, 6 min | Total score | 0-20 | Higher |
| Objects | 0-10 | Higher | |
| Faces | 0-10 | Higher | |
| Verbal fluency, < 5 min | Semantic (category) | 0-no ceiling | Higher |
| Phonemic (letter) | 0-no ceiling | Higher |
- *
Scores presented as M ±SD indicate a normed score with a known distribution (Standard score, T score, etc.)
Figure C.1Sensitivity results of MMSE in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.2Specificity results of MMSE in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.3Sensitivity results of MIS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.4Specificity results of MIS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.5Sensitivity results of MoCA in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.6Specificity results of MoCA in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.7Sensitivity results of 7MS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; 7MS=7 Minute Screen
Figure C.8Specificity results of 7MS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; 7MS=7 Minute Screen
Figure C.9Sensitivity results of MCAS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.10Specificity results of MCAS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.11Sensitivity results of BAS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: BAS=Brief Alzheimer Screen; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.12Specificity results of BAS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: BAS=Brief Alzheimer Screen; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.13Sensitivity results of clock drawing tests (Rouleau scoring) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.14Specificity results of clock drawing tests (Rouleau scoring) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.15Sensitivity results of clock drawing tests (Shulman scale) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.16Specificity results of clock drawing tests (Shulman scale) in eligible and low-moderate risk of bias studies
Figure C.17Sensitivity results of clock drawing tests (Sunderland scale) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.18Specificity results of clock drawing tests (Sunderland scale) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.19Sensitivity results of other clock drawing tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.20Specificity results of other clock drawing tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.21Sensitivity results of CLOX in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.22Specificity results of CLOX in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.23Sensitivity results of DRS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.24Specificity results of DRS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.25Sensitivity results of ADAS-Cog in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.26Specificity results of ADAS-Cog in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.27Sensitivity results of CSBB in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; CSBB=Cogstate Brief Battery; NC=normal control
Figure C.28Specificity results of CSBB in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; CSBB=Cogstate Brief Battery; NC=normal control
Figure C.29Sensitivity results of CERAD in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.30Specificity results of CERAD in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.31Sensitivity results of RBANS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.32Specificity results of RBANS in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.33Sensitivity results of ADAS-Cog Combined Scores in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.34Specificity results of ADAS-Cog Combined Scores in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.35Sensitivity results of WMS Indices in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.36Specificity results of WMS Indices in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.37Sensitivity results of CogState ISLT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.38Specificity results of CogState ISLT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.39Sensitivity results of FCSRT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.40Specificity results of FCSRT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.41Sensitivity results of RBANS (% retention) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.42Specificity results of RBANS (% retention) in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.43Sensitivity results of WMS logical memory in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.44Specificity results of WMS logical memory in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.45Sensitivity results of figure recall in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.46Specificity results of figure recall in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.47Sensitivity results of NAB list learning in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.48Specificity results of NAB list learning in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.49Sensitivity results of TPT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.50Specificity results of TPT in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.51Sensitivity results of Trail Making Test part B in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.52Specificity results of Trail Making Test part B in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.53Sensitivity results of Graphic Pattern Generation test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.54Specificity results of Graphic Pattern Generation test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.55Sensitivity results of Wisconsin Card Sorting test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.56Specificity results of Wisconsin Card Sorting test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.57Sensitivity results of semantic fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.58Specificity results of semantic fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score
Figure C.59Sensitivity results of phonemic fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.60Specificity results of phonemic fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.61Sensitivity results of mixed fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.62Specificity results of mixed fluency in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; NC=normal control
Figure C.63Sensitivity results of Boston Naming Test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.64Specificity results of Boston Naming Test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.65Sensitivity results of brief stand-alone test + another cognitive test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.66Specificity results of brief stand-alone test + another cognitive test in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Figure C.67Sensitivity results of other combination tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: BNT=Boston Naming Test; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; CERAD=Constortium to Establish Registry for Alzheimer’s Diease; DR=Delayed Recall; DRS=Dementia Rating Scale; Dsy=Digit Symbol; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; LM=Logical Memory; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; MMSE=Mini Mental State Examination; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score; PIQ=Performance Intelligence Quotient; TMT-B=Trail Making Test part B; VR=visual reproduction; WAIS=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale
Figure C.68Specificity results of other combination tests in eligible studies with low-moderate risk of bias
Abbrevations: BNT=Boston Naming Test; CATD=Clinical Alzheimer’s type dementia; CERAD=Constortium to Establish Registry for Alzheimer’s Diease; DR=Delayed Recall; DRS=Dementia Rating Scale; Dsy=Digit Symbol; FCSRT=Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test; LM=Logical Memory; MCI=mild cognitive impairment; MMSE=Mini Mental State Examination; NC=normal control; OS=optimal score; PIQ=Performance Intelligence Quotient; TMT-B=Trail Making Test part B; VR=visual reproduction; WAIS=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale
- Key Question 1: Accuracy, Comparative Accuracy, and Harms of Cognitive Tests for...Key Question 1: Accuracy, Comparative Accuracy, and Harms of Cognitive Tests for Identifying CATD - Diagnosis and Treatment of Clinical Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia: A Systematic Review
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...