NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Levorphanol is a synthetic opioid which is used as a narcotic analgesic for moderate-to-severe pain or as a preoperative medication. Levorphanol has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to clinically apparent liver injury.
Background
Levorphanol (lee vor’ fa nol) is a fully synthetic opioid that has full agonist activity to the µ type opiate receptors which are found in the central nervous system, but also in the heart, lungs, intestine and skin. Levorphanol also has activity against the κ and δ opioid receptors. Engagement of the opiate receptors results in inhibition of intracellular adenylate cyclase, decrease in calcium influx, and hyperpolarization of neurons with suppression of action potentials. These actions lead to typical analgesic effects of the opioids. Levorphanol is similar to morphine in effect, but is 4 to 8 times as potent and somewhat longer acting. Levorphanol is the levo-rotatory version of morphinan, the parent drug and prototype of many opioids and inhibitors of the NMDA receptor (morphinans). Levorphanol was first approved for use in the United States in 1953. Indications are for moderate-to-severe pain that is that is not responsive to nonnarcotic analgesia and for perioperative sedation and analgesia. It is available in tablets of 2 mg and as a solution for intravenous or intramuscular injection in concentrations of 2 mg/mL generically and under the brand name Levo-dromoran. Typical doses are 2 mg orally every 6 to 8 hours and 1 to 2 mg parenterally every 3 to 6 hours, as needed. Side effects include sedation, respiratory depression, confusion, euphoria, agitation, itching, sweating, abdominal bloating, nausea, vomiting and constipation, adverse effects which are typical of the opioids. Levorphanol is a controlled substance and is classified as a Schedule II drug, indicating that it has medical usefulness, but also a high potential for physical and psychological dependency and abuse.
Hepatotoxicity
Like most opioid analgesics, levorphanol has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to instances of idiosyncratic, clinically apparent liver injury.
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of levorphanol are given in the 0verview section of the Opioids, last updated April 2019.
Drug Class: Opioids
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Levorphanol – Generic, Levo-Dromoran®
DRUG CLASS
Opioids
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Levorphanol | 77-07-6 | C17-H23-N-O |
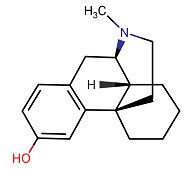 |
- Review Opioids.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Opioids.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Levorphanol use: past, present and future.[Postgrad Med. 2016]Review Levorphanol use: past, present and future.Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Postgrad Med. 2016 Jan; 128(1):46-53. Epub 2015 Dec 27.
- Review Butorphanol.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Butorphanol.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Levorphanol: pharmacokinetics and steady-state plasma concentrations in patients with pain.[Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmac...]Levorphanol: pharmacokinetics and steady-state plasma concentrations in patients with pain.Dixon R, Crews T, Inturrisi C, Foley K. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1983 Jul; 41(1):3-17.
- Pharmacological Characterization of Levorphanol, a G-Protein Biased Opioid Analgesic.[Anesth Analg. 2019]Pharmacological Characterization of Levorphanol, a G-Protein Biased Opioid Analgesic.Le Rouzic V, Narayan A, Hunkle A, Marrone GF, Lu Z, Majumdar S, Xu J, Pan YX, Pasternak GW. Anesth Analg. 2019 Feb; 128(2):365-373.
- Levorphanol - LiverToxLevorphanol - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...