NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Brexpiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic used in the treatment of schizophrenia and major depressive disorders. Brexpiprazole has been associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Background
Brexpiprazole (brex pip' ra zole) is a second generation (atypical) antipsychotic agent that is similar in structure and mechanism of action to aripiprazole. These two agents are believed to act as partial antagonists of dopamine type 2 (D2) and serotonin (5-HT)-2A receptors and partial agonists of serotonin 5-HT-1A receptors. In several randomized controlled trials, therapy with brexpiprazole was associated with a lessening of symptoms of schizophrenia and improvement in depression symptom scores in comparison to placebo treatment. It was approved for use in the United States in 2015 as therapy for schizophrenia and as adjunctive therapy with antidepressants for major depressive disorders. Brexpiprazole is available as tablets of 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3 and 4 mg generically and under the brand name Rexulti. The standard maintenance dose for schizophrenia in adults is 2 to 4 mg daily. The dose for as an adjunctive therapy for major depression is usually less. Common side effects include restlessness (akathisia), sedation, tremor, dizziness, blurred vision, fatigue, headaches, nausea and weight gain. Rare, but potential severe adverse reactions (mentioned in most antipsychotic product labels) include tardive dyskinesia, major neurologic events, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, orthostatic hypotension, seizures and neutropenia. Like many antipsychotic medications, brexpiprazole has a boxed warning for excessive mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis and, like many antidepressants, it also has a boxed warning for increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Hepatotoxicity
Liver test abnormalities were reported to occur in ~1% of patients on long term therapy with brexpiprazole, but similar rates occurred in patients on placebo or with comparator agents. There have been no published reports of clinically apparent acute liver injury due to brexpiprazole and only rare instances have been reported with the much more frequently used aripiprazole. Thus, liver injury due to brexpiprazole must be rare, if it occurs at all.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
Brexpiprazole is extensively metabolized by the liver via the P450 system, largely by CYP 3A4 and 2D6, and liver injury from its use might be caused by a toxic or immunogenic intermediate metabolite. Brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole, is susceptible to drug-drug interactions, strong inducers of CYP 3A4 (such as rifampin) resulting in lower drug levels, and strong inhibitors (such as ketoconazole) resulting in higher levels.
Outcome and Management
The serum aminotransferase elevations that occur with brexpiprazole therapy are usually self-limited and often do not require dose modification or discontinuation. No instances of acute liver failure, chronic hepatitis or vanishing bile duct syndrome have been attributed to brexpiprazole. Cross sensitivity to liver related or other hypersensitivity reactions between brexpiprazole and other antipsychotic agents have not been demonstrated but might be expected to occur with aripiprazole.
Drug Class: Antipsychotic Agents, Atypicals
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Brexpiprazole – Generic, Rexulti®
DRUG CLASS
Antipsychotic Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND STRUCTURES
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NUMBER | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aripiprazole | 129722-12-9 | C23-H27-Cl2-N3-O2 |
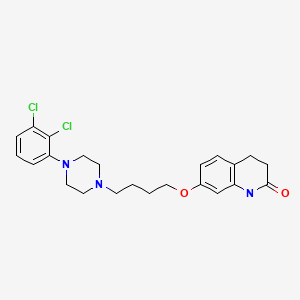
|
| Brexpiprazole | 913611-97-9 | C25-H27-N3-O2-S |
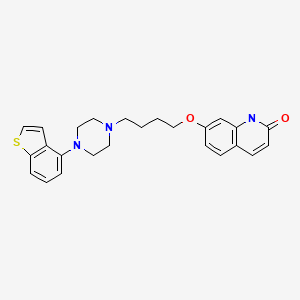
|
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 06 June 2023
- Meyer JM. Pharmacotherapy of psychosis and mania. In, Brunton LL, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2018, pp. 279-302.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- FDA. https://www
.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs /nda/2015/205422Orig1Orig2s000MedR.pdf. (FDA website with product labels and medical review of studies of brexpiprazole in support of its approval; mentions that in preregistration trials of brexpiprazole for schizophrenia, ALT elevations arose in 0.3% of patients on 2 mg daily and 1.4% of those on higher doses versus 0.5% on placebo, and there were no cases of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice). - Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel RR, Li C, Davis JM. Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:31–41. [PubMed: 19058842](Systematic review of efficacy and safety of newer antipsychotic agents including aripiprazole, but not brexpiprazole; no discussion of liver related side effects or ALT elevations).
- Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM., Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2010;52:2065–76. [PMC free article: PMC3992250] [PubMed: 20949552](Among 1198 patients with acute liver failure enrolled in a US prospective study between 1998 and 2007, 133 were attributed to drug induced liver injury including four due to psychotropic agents; one each for quetiapine, nefazodone, fluoxetine and venlafaxine, but none for aripiprazole or brexpiprazole or other second generation antipsychotic agent).
- Brexpiprazole (Rexulti) for schizophrenia and depression. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2015;57(1475):116–8. [PubMed: 26262883](Brief review of efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole shortly after its approval in the US; frequent side effects are anxiety, headache, nausea, constipation, insomnia, dizziness and somnolence; has little effect on weight; no mention of hepatotoxicity or effect on ALT levels).
- Kane JM, Skuban A, Ouyang J, Hobart M, Pfister S, McQuade RD, Nyilas M, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled phase 3 trial of fixed-dose brexpiprazole for the treatment of adults with acute schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2015;164:127–35. [PubMed: 25682550](Among 674 adults with acute schizophrenia treated with brexpiprazole [1, 2 or 4 mg daily] or placebo for 6 weeks, improvements in symptom scores were greater with brexpiprazole than placebo and side effects included weight gain [1.5 vs 0.35 kg]; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Correll CU, Skuban A, Ouyang J, Hobart M, Pfister S, McQuade RD, Nyilas M, et al. Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole for the treatment of acute schizophrenia: a 6-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2015;172:870–80. [PubMed: 25882325](Among 636 adults with an acute exacerbation of schizophrenia treated with 1 or 3 doses of brexpiprazole [0.25, 2 or 4 mg daily] or placebo for 6 weeks, symptom scores improved more with brexpiprazole, and adverse events included restlessness [akathisia] and weight gain, while discontinuations due to liver test elevations occurred equally with drug and placebo [1.1%]).
- Citrome L. Brexpiprazole: a new dopamine D2 receptor partial agonist for the treatment of schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. Drugs Today (Barc). 2015;51:397–414. [PubMed: 26261843](Systematic review of results of 4 phase III trials and subsequent extension studies of brexpiprazole in schizophrenia and major depressive disorders reported overall improvements in symptom scores with treatment, and an increase in adverse events in comparison to placebo of restlessness [5-10%], weight gain [5-30%]; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Thase ME, Youakim JM, Skuban A, Hobart M, Augustine C, Zhang P, McQuade RD, et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive brexpiprazole 2 mg in major depressive disorder: a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with inadequate response to antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:1224–31. [PubMed: 26301701](Among 353 patients with major depressive disorders on conventional antidepressants who were treated with brexpiprazole [2 mg daily] or placebo for 6 weeks, depression scores improved more with brexpiprazole and adverse events included restlessness [7%] and weight gain [8%]; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Thase ME, Youakim JM, Skuban A, Hobart M, Augustine C, Zhang P, McQuade RD, et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive brexpiprazole 2 mg in major depressive disorder: a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with inadequate response to antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:1224–31. [PubMed: 26301701](Among 353 adults with major depressive disorder with an inadequate response to antidepressants treated with addition of brexpiprazole [2 mg daily] or placebo for 6 weeks, depression symptom scores improved more with brexpiprazole than placebo, while adverse events included weight gain [8% vs 3.1%] and akathisia [7.4% vs 1%], but routine laboratory test results did not differ between the two groups).
- Drugs for psychotic disorders. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2016;58(1510):160–4. [PubMed: 27960194](Concise review of medications available in the US for therapy of psychotic disorders; mentions that olanzapine can cause aminotransferase elevations, and that olanzapine and ziprasidone can cause DRESS syndrome, but does not mention ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity for any of agents discussed, including aripiprazole, brexpiprazole, cariprazine, clozapine, quetiapine, risperidone, asenapine, iloperidone, paliperidone and lurasidone).
- Fleischhacker WW, Hobart M, Ouyang J, Forbes A, Pfister S, McQuade RD, Carson WH, et al. Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole (OPC-34712) as maintenance treatment in adults with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;20:11–21. [PMC free article: PMC5412583] [PubMed: 27566723](Among 202 patients with schizophrenia who were stabilized on brexpiprazole for 12 weeks and then continued treatment or were switched to placebo, relapse rates were lower with drug continuation [13.5% vs 38.5%] as were adverse event rates; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Hobart M, Skuban A, Zhang P, Augustine C, Brewer C, Hefting N, Sanchez R, McQuade RD. A Randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of fixed-dose brexpiprazole 2 mg/d as adjunctive treatment of adults with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79:17m12058. [PubMed: 29873953](Among 393 patients with major depressive disorder with inadequate response to antidepressants who were treated with addition of brexpiprazole [2 mg] or placebo daily for 6 weeks, changes in depression rating scores were greater with brexpiprazole, while adverse event rates were higher [60% vs 50%] including weight gain [1.5 vs 0.5 kg], akathisia [8% vs 2%], restlessness [8% vs 2%], insomnia [5% vs 1%], and fatigue [2.6% vs 0.5%], but there were no differences in changes in laboratory test results; no specific mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Forbes A, Hobart M, Ouyang J, Shi L, Pfister S, Hakala M. A long-term, open-label study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of brexpiprazole as maintenance treatment in adults with schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018;21:433–441. [PMC free article: PMC5932477] [PubMed: 29415258](Among 1072 adults with schizophrenia treated with controlled trials of brexpiprazole who were enrolled in a 52 week, open label extension study [flexible dose: 1-4 mg/day], adverse events included relapse of schizophrenia, weight gain [mean +2.1 kg at 52 weeks], headache, agitation, and akathisia; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Hobart M, Zhang P, Skuban A, Brewer C, Hefting N, Sanchez R, McQuade RD. A long-term, open-label study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of brexpiprazole as adjunctive therapy in adults with major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;39:203–209. [PMC free article: PMC6494030] [PubMed: 30946704](Among 2944 patients with major depressive disorder participating in controlled trials of brexpiprazole who were enrolled in a 52 week open label extension study [flexible dose: 0.5 to 3 mg/day], the antidepressant effects were sustained and adverse events included weight gain [2.6 kg at 24 weeks], somnolence, headache, akathisia, increased appetite, and anxiety; no mention of ALT levels or hepatotoxicity).
- Drugs for depression. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020;62(1592):25–32. [PubMed: 32320387](Concise summary of the mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, safety and costs of the drugs approved for depression in the US; mentions that some antipsychotic agents are used to augment the effect of standard antidepressants in patients with major depressive disorders; no discussion of hepatotoxicity).
- Grossberg GT, Kohegyi E, Mergel V, Josiassen MK, Meulien D, Hobart M, Slomkowski M, et al. Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole for the treatment of agitation in Alzheimer's dementia: two 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020;28:383–400. [PubMed: 31708380](Among 703 patients with Alzheimer dementia and agitation treated with brexpiprazole in two 12-week controlled trials, a decrease in agitation was found with higher doses of brexpiprazole [2-4 mg/day]; there were no hepatic serious adverse events or deaths from liver disease; no mention of ALT elevations).
- Zeiss R, Hafner S, Schönfeldt-Lecuona C, Connemann BJ, Gahr M. Drug-associated liver injury related to antipsychotics: exploratory analysis of pharmacovigilance data. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022;42:440–444. [PubMed: 35730552](Review of the VigiBase data base of individual case safety reports on antipsychotics and liver injury found positive hepatic safety signals for olanzapine and clozapine but none for risperidone, quetiapine, ziprasidone, asenapine, aripiprazole, brexpiprazole, and cariprazine).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Brexpiprazole: A review of a new treatment option for schizophrenia and major depressive disorder.[Ment Health Clin. 2017]Review Brexpiprazole: A review of a new treatment option for schizophrenia and major depressive disorder.Diefenderfer LA, Iuppa C. Ment Health Clin. 2017 Sep; 7(5):207-212. Epub 2018 Mar 23.
- Review Brexpiprazole for schizophrenia and as adjunct for major depressive disorder: a systematic review of the efficacy and safety profile for this newly approved antipsychotic - what is the number needed to treat, number needed to harm and likelihood to be helped or harmed?[Int J Clin Pract. 2015]Review Brexpiprazole for schizophrenia and as adjunct for major depressive disorder: a systematic review of the efficacy and safety profile for this newly approved antipsychotic - what is the number needed to treat, number needed to harm and likelihood to be helped or harmed?Citrome L. Int J Clin Pract. 2015 Sep; 69(9):978-97. Epub 2015 Aug 6.
- Medication Adherence, Health Care Utilization, and Costs in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Initiating Adjunctive Atypical Antipsychotic Treatment.[Clin Ther. 2019]Medication Adherence, Health Care Utilization, and Costs in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Initiating Adjunctive Atypical Antipsychotic Treatment.Broder MS, Greene M, Yan T, Chang E, Hartry A, Yermilov I. Clin Ther. 2019 Feb; 41(2):221-232. Epub 2019 Jan 5.
- Health Care Cost in Patients With Schizophrenia Treated With Brexpiprazole Versus Other Oral Atypical Antipsychotic Therapy.[Clin Ther. 2020]Health Care Cost in Patients With Schizophrenia Treated With Brexpiprazole Versus Other Oral Atypical Antipsychotic Therapy.Yan T, Greene M, Chang E, Houle CR, Waters HC, Tarbox MH, Broder MS. Clin Ther. 2020 Jan; 42(1):77-93. Epub 2020 Jan 10.
- Review Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole in acute management of psychiatric disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.[Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020]Review Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole in acute management of psychiatric disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Antoun Reyad A, Girgis E, Mishriky R. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020 May; 35(3):119-128.
- Brexpiprazole - LiverToxBrexpiprazole - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...