NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Avapritinib is a tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor that targets mutant forms of several genes (KIT, PDGFRA) involved in gastrointestinal stromal tumors which are often found in refractory cases. Serum aminotransferase elevations arise in a small proportion of patients treated with the highest doses of avapritinib, but episodes of clinically apparent liver injury have not been reported with its use.
Background
Avapritinib (a” va prit’ tin ib) is an orally available, tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets activation loop mutants of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA), which are often found in patients with resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) and overexpression of KIT which is often present in systemic mastocytosis. Disregulation of these genes results in constitutive kinase activity and uncontrolled growth and proliferation. Avapritinib has potent specificity against gain of function mutants KIT D816V and PDGRA D842V that are resistant to standard tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as imatinib, sunitinib, and regorafenib, the first-, second-, and third-line therapies of GIST. Avapritinib was granted accelerated approval in the United States in 2020 for adults with unresectable to metastatic GIST with documented PDGFRA alpha exon 18 mutations including D842V, the first drug to be approved for this indication. Indications were subsequently expanded to adults with advanced systemic mastocytosis and indolent systemic mastocytosis. Avapritinib is available in tablets of 25, 50, 100, 200 and 300 mg under the brand name Ayvakit. The recommended oral dose varies by indication, being 300 mg once daily for GIST, 200 mg once daily advanced mastocytosis, but only 25 mg once daily for indolent mastocytosis. Therapy should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Side effects are dose related, but at the highest dose are common, arising in almost all patients. In preregistration clinical trials, dose interruptions or reductions were needed in 57% and permanent discontinuations in 9% of patients being treated with avapritinib for GIST. Common side effects include anemia, neutropenia, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, cognitive impairment, dizziness, headache, rash, hair color changes, alopecia, dyspnea, hyperbilirubinemia, weight loss and insomnia. Uncommon but potentially severe adverse events include major cognitive effects, intracranial hemorrhage, photosensitivity, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Hepatotoxicity
In the prelicensure clinical trials of avapritinib in patients with GIST harboring the PDGFRA D842V mutation, ALT elevations arose in 20% of patients but were usually self-limited and mild. ALT elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were uncommon, being found in 1% to 3% of treated patients. In the open label trials supporting the approval of avapritinib, there were no instances of clinically apparent liver injury, hepatic failure or deaths from liver injury. Avapritinib is associated with frequent elevations in serum bilirubin, but the increases are largely indirect and resolve rapidly with discontinuation.
Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
Mechanism of Injury
The cause of serum aminotransferase elevations from avapritinib is unknown, but the pattern of abnormalities suggests some degree of direct toxicity. Avapritinib is metabolized in the liver via the cytochrome P450 system, largely CYP 3A4, and is susceptible to drug-drug interactions with agents that inhibit or induce the CYP enzyme reactivity.
Outcome and Management
The product label for avapritinib does not recommend regular monitoring of liver tests, but if serum aminotransferase levels above 5 times the upper limit of normal are identified, therapy should be held until levels fall into the normal or near normal range, at which point avapritinib therapy can be resumed at the same or a reduced dose as clinically indicated and with continued monitoring. Cross sensitivity to liver injury is uncommon among the antineoplastic small molecule enzyme and receptor inhibitors, but there is no information on shared adverse event sensitivity of avapritinib with other antineoplastic tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitors.
Drug Class: Antineoplastic Agents, Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Other Drugs for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: Imatinib, Regorafenib, Sunitinib
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Avapritinib – Ayvakit®
DRUG CLASS
Antineoplastic Agents
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avapritinib | 1703793-34-3 | C26-H27-F-N10 |
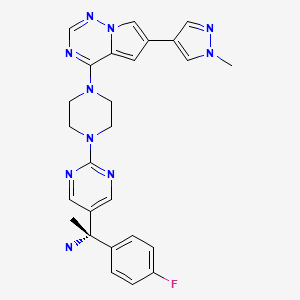
|
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
References updated: 02 September 2023
Abbreviations: GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; KIT, a classical proto-oncogene that encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor that responds to stem cell factor; PDGFRA, platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha.
- Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1999.(Review of hepatotoxicity published in 1999 before the availability of tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitors).
- DeLeve LD. Kinase inhibitors. Cancer chemotherapy. In, Kaplowitz N, DeLeve LD, eds. Drug-induced liver disease. 3rd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013, p. 556.(Review of hepatotoxicity of cancer chemotherapeutic agents, does not discuss avapritinib).
- Wellstein A, Giaccone G, Atkins MB, Sausville EA. Pathway targeted therapies: monoclonal antibodies, protein kinase inhibitors, and various small molecules. In, Brunton LL Hilal-Dandan R, Knollman BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2018, pp. 1203-36.(Textbook of pharmacology and therapeutics).
- FDA. https://www
.accessdata .fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs /nda/2020/212608Orig1s000MultidisciplineR.pdf (FDA website with initial multidiscipline clinical review of the safety and efficacy of avapritinib; describes the adverse events observed in a pooled safety population of 335 patients that included edema in 74%, bilirubin elevations 65%, fatigue 57%, nausea 56%, cognitive impairment 43%, diarrhea 36%, abdominal pain 32%, anemia 49%, hair color change 22%, rash 20%, dyspnea 15%, and ALT elevations 20% which were above 5 times ULN in only 1% [n=3], and there were no discontinuations for ALT elevations and no instances of clinically apparent liver injury, hepatic failure, or fatalities due to liver injury). - Heinrich MC, Jones RL, von Mehren M, Schöffski P, Serrano C, Kang YK, Cassier PA, et al. Avapritinib in advanced PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (NAVIGATOR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:935-946. [PubMed: 32615108](Among 56 patients with advanced GIST and PDGFRA D842V-mutations treated with avapritinib in a phase 1 open-label trial, the overall response rate was 88% [complete responses in 9%] and almost all patients had adverse events including nausea in 69%, fatigue 41%, anorexia 38%, hair color change e25%, anemia 22%, and neutropenia 19%; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Dhillon S. Avapritinib: first approval. Drugs. 2020;80:433-439. [PubMed: 32100250](Review of the mechanism of action, history of development, pharmacology, clinical efficacy and safety of avapritinib shortly after its approval for use in advanced or metastatic GIST in the U.S.; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- DeAngelo DJ, Radia DH, George TI, Robinson WA, Quiery AT, Drummond MW, Bose P, Heet al. Safety and efficacy of avapritinib in advanced systemic mastocytosis: the phase 1 EXPLORER trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:2183-2191. [PMC free article: PMC8674134] [PubMed: 34873347](Among 86 patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis enrolled in a phase 1 trial of avapritinib, the overall response rate was 75% and complete remission rate 36% while adverse events were common and included intracranial bleeds in 9 patients, largely in those with preexisting thrombocytopenia [n=7]; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Gotlib J, Reiter A, Radia DH, Deininger MW, George TI, Panse J, Vannucchi AM, et al. Efficacy and safety of avapritinib in advanced systemic mastocytosis: interim analysis of the phase 2 PATHFINDER trial. Nat Med. 2021;27:2192-2199. [PMC free article: PMC8674139] [PubMed: 34873345](Among 62 patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis treated in a phase 2 open-label trial excluding those with platelet count below 50,000/uL, the overall response rate was 75% and side effects were common, but there was only one case with intracranial hemorrhage and no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Jones RL, Serrano C, von Mehren M, George S, Heinrich MC, Kang YK, Schöffski P, et al. Avapritinib in unresectable or metastatic PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Long-term efficacy and safety data from the NAVIGATOR phase I trial. Eur J Cancer. 2021;145:132-142. [PMC free article: PMC9518931] [PubMed: 33465704](Among 250 patients [56 with PDGFRA D824V mutant GIST] treated in phase 1 trials of avapritinib, treatment related adverse events occurred in 98% of patients and included cognitive effects in 46%, intracranial bleeding in 3%; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Avapritinib (Ayvakit) for GIST. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2021;63(1617):23-24. [PubMed: 33647006](Concise review of the mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, adverse effects, drug interactions, and costs of avapritinib shortly after its approval in the U.S. mentions that serious adverse effects occur in 52% of patients and include anemia [9%] and intracranial hemorrhage [1%]; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Reiter A, Schwaab J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Deininger MW, Pettit KM, Alvarez-Twose I, et al. Efficacy and safety of avapritinib in previously treated patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis. Blood Adv. 2022;6:5750-5762. [PMC free article: PMC9647833] [PubMed: 35640224](Among 53 patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis treated with avapritinib [200 mg daily] for a median of 15 months, the overall response rate was 71% and adverse events arose in most patients resulting in dose reductions in 57% and including thrombocytopenia [32%], periorbital edema [30%], diarrhea [21%], cognitive disorders [15%], change in hair color [15%], and two instances of subdural hematoma; no mention of ALT elevations or hepatotoxicity).
- Cavazos K, Eswaran S, Maidlow C, Keklik Karadag F, Idilman R, Idilman I, et al. Liver fibrosis and its response to avapritinib in 2 patients with systemic mastocytosis. Blood Adv. 2022;6:5630-5633. [PMC free article: PMC9647789] [PubMed: 35839085](Two patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis were found to have advanced hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis as shown by elastography and liver biopsy, but had normal liver tests and imaging and tolerated therapy with avapritinib, the hepatic stiffness improving with therapy and without any worsening of liver tests suggesting that avapritinib does not worsen hepatic fibrosis and may improve mastocytosis-associated liver disease).
- Li J, Zhang X, Deng Y, Wu X, Zheng Z, Zhou Y, Cai S, et al. Efficacy and safety of avapritinib in treating unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a phase I/II, open-label, multicenter study. Oncologist. 2023;28:187-e114. [PMC free article: PMC9907038] [PubMed: 36477870](Among 56 Chinese patients with unresectable or metastatic GIST treated with avapritinib [300 mg daily] in phase 1 and 2 clinical trials, the overall response rate was 75% in those with PDGFRA D842V mutations, while adverse events arose in 98% of patients including ALT elevations in 14% which were above 5 times ULN in only 1 patient).
- Pardanani A. Systemic mastocytosis in adults: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2023;98:1097-1116. [PubMed: 37309222](Review of the clinical features, diagnosis, histology, molecular findings, classification and management of systemic mastocytosis including both advanced and indolent forms of the disease condition).
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Circulating tumor DNA analysis of the phase III VOYAGER trial: KIT mutational landscape and outcomes in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with avapritinib or regorafenib.[Ann Oncol. 2023]Circulating tumor DNA analysis of the phase III VOYAGER trial: KIT mutational landscape and outcomes in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor treated with avapritinib or regorafenib.Serrano C, Bauer S, Gómez-Peregrina D, Kang YK, Jones RL, Rutkowski P, Mir O, Heinrich MC, Tap WD, Newberry K, et al. Ann Oncol. 2023 Jul; 34(7):615-625. Epub 2023 Apr 25.
- Clinical efficacy comparison of avapritinib with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors in gastrointestinal stromal tumors with PDGFRA D842V mutation: a retrospective analysis of clinical trial and real-world data.[BMC Cancer. 2021]Clinical efficacy comparison of avapritinib with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors in gastrointestinal stromal tumors with PDGFRA D842V mutation: a retrospective analysis of clinical trial and real-world data.von Mehren M, Heinrich MC, Shi H, Iannazzo S, Mankoski R, Dimitrijević S, Hoehn G, Chiroli S, George S. BMC Cancer. 2021 Mar 19; 21(1):291. Epub 2021 Mar 19.
- Avapritinib in Patients With Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Following at Least Three Prior Lines of Therapy.[Oncologist. 2021]Avapritinib in Patients With Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Following at Least Three Prior Lines of Therapy.George S, Jones RL, Bauer S, Kang YK, Schöffski P, Eskens F, Mir O, Cassier PA, Serrano C, Tap WD, et al. Oncologist. 2021 Apr; 26(4):e639-e649. Epub 2021 Feb 1.
- Review Avapritinib in the treatment of PDGFRA exon 18 mutated gastrointestinal stromal tumors.[Future Oncol. 2020]Review Avapritinib in the treatment of PDGFRA exon 18 mutated gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Smrke A, Gennatas S, Huang P, Jones RL. Future Oncol. 2020 Aug; 16(22):1639-1646. Epub 2020 Jun 10.
- Review Avapritinib: First Approval.[Drugs. 2020]Review Avapritinib: First Approval.Dhillon S. Drugs. 2020 Mar; 80(4):433-439.
- Avapritinib - LiverToxAvapritinib - LiverTox
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...