NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-.

LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet].
Show detailsOVERVIEW
Introduction
Morphine is one of the natural plant alkaloids found in opium and is the prototype opiate, against which other derivatives are measured in terms of analgesic effects and side effects. Morphine has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations during therapy or to clinically apparent liver injury.
Background
Morphine is a natural alkaloid that is derived from resin extracts from the seeds of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. Morphine has potent and profound analgesic effects and has been used in clinical medicine for almost two hundred years. Morphine acts by engagement in cell surface opiate receptors (predominant µ type receptors) that are found in the central nervous system, but also heart, lung, vascular and intestinal cells. Current indications are for severe pain, pre- and postoperative analgesia, control of pain from angina pectoris or acute myocardial infarction and therapy of pulmonary edema. Morphine is available in multiple formulations, including oral tablets and syrups, suppositories, and solutions for injection in multiple concentrations. The typical dose of morphine for analgesia in adults is 10 mg every 3 to 4 hours by the subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous route. Morphine is well absorbed orally, but has extensive and variable first pass metabolism, so that its effect orally is somewhat variable. Side effects of opiates are many and include sedation, respiratory depression, confusion, euphoria, agitation, itching, abdominal bloating, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Severe adverse events include life-threatening respiratory depression, addiction, abuse, opioid withdrawal, biliary spasm, serotonin syndrome (when used with serotonergic agents) and adrenal insufficiency. Morphine is a controlled substance and classified as a Schedule II drug, indicating that it has medical usefulness, but also a high potential for physical and psychological dependency and abuse.
Hepatotoxicity
Therapy with morphine has not been linked to serum enzyme elevations. Hepatitis B and C are common among persons with opiate addiction and illicit injection drug use, but the opiates themselves appear to have little hepatotoxic potential. There have been no convincing cases of idiosyncratic acute, clinically apparent liver injury attributed to morphine. Morphine has little hepatic metabolism and is generally excreted unchanged in the urine, perhaps accounting for their relative lack of hepatotoxicity.
Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury).
References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of morphine are given in the Overview section of the Opioids.
Drug Class: Opioids
PRODUCT INFORMATION
REPRESENTATIVE TRADE NAMES
Morphine – Generic, Duramorph®
DRUG CLASS
Opioids
Product labeling at DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, NIH
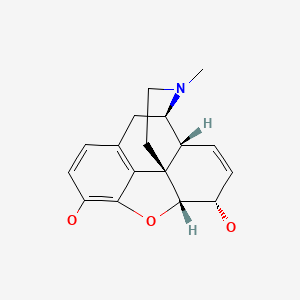
CHEMICAL FORMULA AND STRUCTURE
| DRUG | CAS REGISTRY NO. | MOLECULAR FORMULA | STRUCTURE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphine | 57-27-2 | C17-H19-N-O3 |
|
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- [The influence of the minor alkaloids in opium on the analgesic effect of Morphine].[Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp ...][The influence of the minor alkaloids in opium on the analgesic effect of Morphine].ALBERTY J. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1949; 208(2-3):179.
- [Application of paper chromatography to some opium alkaloids and morphine derivatives].[Arch Pharm Ber Dtsch Pharm Ges...][Application of paper chromatography to some opium alkaloids and morphine derivatives].ABDEL-RAHMAN AA. Arch Pharm Ber Dtsch Pharm Ges. 1957 Jul; 290/62(7):321-5.
- [QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF OPIUM ALKALOIDS IN WASTE PRODUCTS FROM THE PREPARATION OF MORPHINE FROM OPIUM].[Med Prom SSSR. 1964][QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF OPIUM ALKALOIDS IN WASTE PRODUCTS FROM THE PREPARATION OF MORPHINE FROM OPIUM].BRUTKO LI. Med Prom SSSR. 1964 May; 18:42-4.
- Review Codeine.[LiverTox: Clinical and Researc...]Review Codeine.. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. 2012
- Review Opium alkaloids, biosynthesis, pharmacology and association with cancer occurrence.[Open Biol. 2023]Review Opium alkaloids, biosynthesis, pharmacology and association with cancer occurrence.Vadhel A, Bashir S, Mir AH, Girdhar M, Kumar D, Kumar A, Mohan A, Malik T, Mohan A. Open Biol. 2023 May; 13(5):220355. Epub 2023 May 3.
- Morphine - LiverToxMorphine - LiverTox
- 597380[uid] (1)Taxonomy
- 197409[uid] (1)Taxonomy
- Screening for Speech and Language Delay in Preschool ChildrenScreening for Speech and Language Delay in Preschool Children
- Oncostemum neriifolium voucher CAS:P. Fritsch 1727 atpB-rbcL intergenic spacer, ...Oncostemum neriifolium voucher CAS:P. Fritsch 1727 atpB-rbcL intergenic spacer, partial sequence; chloroplastgi|357540849|gb|JN813468.1|Nucleotide
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...