NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-.
Introduction
Many people have digestive problems such as stomach ache, bloating, "gas" and diarrhea after eating or drinking dairy milk or other products that contain lactose. People who have difficulty digesting dairy products may only tolerate small amounts of lactose (a sugar found in milk and other dairy products). This is called lactose intolerance.
But a sensitive reaction to dairy products might actually be due to a different problem. It is important to get the diagnosis right before deciding to make major changes to your diet, especially in children, teenagers and people who need more calcium.
Lactose intolerance is not an allergy. This is an important difference. People who have a milk allergy react to even tiny amounts of milk or other dairy products. Lactose-intolerant people, on the other hand, can eat and drink certain amounts of lactose without developing symptoms.
At a glance
- People who are lactose-intolerant only tolerate small amounts of lactose.
- Eating too many dairy products causes digestive problems.
- It is usually possible to lead a symptom-free life if you change your diet in certain ways.
- Generally speaking, you don't need to cut dairy products out completely.
- It is not clear whether lactase products, prebiotics or probiotics can help.
Symptoms
Lactose intolerance causes symptoms such as:
- A bloated belly
- Feeling full
- Pain in the lower belly
- "Gas"
- Diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Sometimes constipation too
It takes at least half an hour for symptoms to occur after the person has eaten or drunk something containing lactose. The symptoms are at their worst after around 1.5 to 2 hours, but they can last longer.
Causes
Lactose intolerance is usually passed on to children in their parents' genes. In these cases, it's referred to as "primary lactose intolerance."
Babies' digestive systems are designed to survive only on breast milk. In order to digest milk, they make an enzyme called lactase. Lactase breaks down the kind of sugar found in milk (lactose) in the bowel so that the body can process it further.

Normal lactose digestion
When a child is weaned off breast milk, their digestive system gradually adapts to digest and process other foods. Their body then produces less lactase. When this happens, some people don't have enough lactase to break down the lactose in their food. As a result, they don't tolerate lactose-containing foods and drinks as well as other people do.
If an adult consumes more lactose than their body can break down with the available lactase, some lactose is left over in the bowel. It passes on into the large intestine, where it is digested by intestinal bacteria (through fermentation). As a result, more gas and other byproducts are produced in the bowel, and that causes the problems.
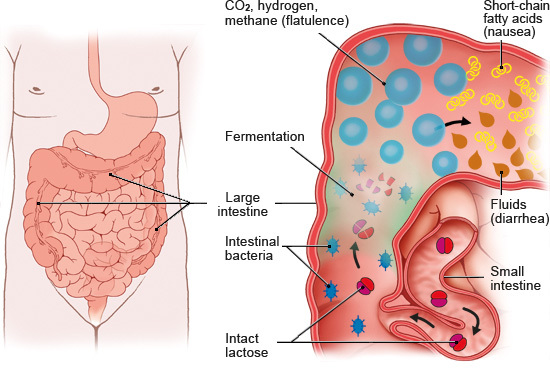
Digestion in a lactose-intolerant person
Lactose intolerance can also develop due to other health problems, including a chronic inflammation (like in Crohn's disease) or injury to the lining of the intestine. This is known as acquired or secondary lactose intolerance. It happens when the small intestine starts producing too little lactase because the lining of the intestine has been damaged.
Prevalence
Lactose intolerance is very rare in children under the age of five. It typically develops in teenagers or adults. Although lactose intolerance is very common all over the world, there are significant differences between regions and populations.
About 5 to 15% of people from Europe are lactose-intolerant. It is least common in Northern Europe. In contrast, it is estimated that between 65% and more than 90% of adults in Africa and East Asia are affected.
These regional differences are probably linked to how long the local milk industry has existed. In many European countries, dairy products have featured heavily in the national diet for a long time. People who tolerated them well had a better chance of surviving.
Diagnosis
If you think you might be lactose-intolerant, you can speak to your family doctor about it. They will then usually refer you to a gastroenterologist for a test. The following tests can be used:
- Hydrogen breath test: This involves measuring the amount of hydrogen in your breath before and after drinking a lactose solution. People with lactose intolerance generally have more hydrogen in their breath afterwards.
- Lactose tolerance test: This test involves measuring your blood sugar levels before and several times after drinking a lactose solution. It shows whether your body is able to break down and absorb the lactose.
- Elimination diet: This involves avoiding lactose-containing foods and drinks for a while and then consuming a certain amount of lactose afterwards to see how your body reacts.
But lactose intolerance can't be diagnosed based only on the readings measured in tests. It is only possible to say with certainty whether you're lactose-intolerant if typical symptoms occur during the test(s).
You don't have to do all of these tests. In Germany and other countries, the standard test is the breath test.
Treatment
Before starting the treatment, it's important to find out whether your lactose intolerance is genetic or acquired. If it's acquired, the symptoms are caused by a different disease. If that disease is treated and the lining of the bowel recovers, the symptoms will disappear too.
People with genetic lactose intolerance can lead a symptom-free life if they make some changes to their diet. Research findings show that the best known way to reduce the symptoms is to eat and drink small amounts of lactose and to only ever drink dairy milk together with other foods. There is no treatment that can "cure" lactose intolerance.
To prevent the symptoms, some people take tablets or capsules containing commercially made lactase. The aim is to help break down the lactose in the bowel, allowing people to tolerate more lactose. But no good-quality studies have proven that they can relieve the typical symptoms. It is also not clear whether prebiotic or probiotic products can help.
Everyday life
Dairy products aren't essential for a balanced diet, but you do need to make sure you get enough calcium. Good sources of calcium include green vegetables such as spinach and kale, and calcium-rich mineral water. Aged cheeses such as parmesan or mature gouda also contain a lot of calcium and hardly any lactose. Lactose-intolerant people tend to tolerate them well.
You don't usually need to cut lactose-containing foods out of your diet completely. The following amounts are normally well tolerated – especially if consumed together with a meal or other foods:
- Up to 12 g of lactose at once (for example, 250 ml of milk)
- Up to 24 g of lactose over the course of the day (for example, 500 ml of milk)
Further information
When people are ill or need medical advice, they usually go to see their family doctor first. In our "Health care in Germany" topic you can read about how to find the right doctor – and our list of questions can help you to prepare for your appointment.
Sources
- Halpert A, Drossman DA. Irritable bowel syndrome. In: McDonald J, Burroughs AK, Feagan BG (Ed). Evidence-based Gastroenterology and Child Health. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2004. S. 265-283.
- Ledochowski M, Bair H, Fuchs D. Laktoseintoleranz. Ernährungsmed 2003; 5(1): 7-14.
- Marklund B, Ahlstedt S, Nordstrom G. Food hypersensitivity and quality of life. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 7(3): 279-287. [PubMed: 17489049]
- Marklund B, Wilde-Larsson B, Ahlstedt S et al. Adolescents' experiences of being food-hypersensitive: a qualitative study. BMC Nurs 2007; 6: 8. [PMC free article: PMC2104527] [PubMed: 17922926]
- Marton A, Xue X, Szilagyi A. Meta-analysis: the diagnostic accuracy of lactose breath hydrogen or lactose tolerance tests for predicting the North European lactase polymorphism C/T-13910. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012; 35(4): 429-440. [PubMed: 22211845]
- Misselwitz B, Pohl D, Fruhauf H et al. Lactose malabsorption and intolerance: pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. United European Gastroenterol J 2013; 1(3): 151-159. [PMC free article: PMC4040760] [PubMed: 24917953]
- Sahi T. Genetics and epidemiology of adult-type hypolactasia with emphasis on the situation in Europe. Scand J Nutr Näringsforskning 2001; 45(1): 161-162.
- Shaukat A, Levitt MD, Taylor BC et al. Systematic review: effective management strategies for lactose intolerance. Ann Intern Med 2010; 152(12): 797-803. [PubMed: 20404262]
- Wilt TJ, Shaukat A, Shamliyan T et al. Lactose intolerance and health. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 2010; (192): 1-410. [PMC free article: PMC4781456] [PubMed: 20629478]
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services.
Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system. The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. informedhealth.org can provide support for talks with doctors and other medical professionals, but cannot replace them. We do not offer individual consultations.
Our information is based on the results of good-quality studies. It is written by a team of health care professionals, scientists and editors, and reviewed by external experts. You can find a detailed description of how our health information is produced and updated in our methods.
- Overview: Lactose intolerance - InformedHealth.orgOverview: Lactose intolerance - InformedHealth.org
- G patch domain-containing protein 2 isoform X7 [Homo sapiens]G patch domain-containing protein 2 isoform X7 [Homo sapiens]gi|767909701|ref|XP_011507996.1|Protein
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
