NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-.
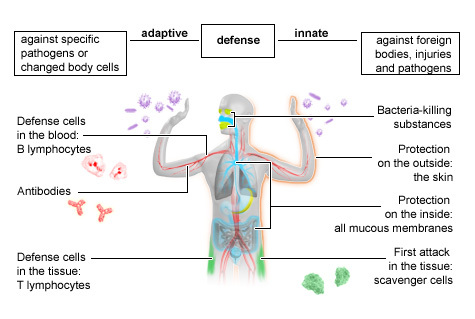
The immune system fights germs on the skin, in the tissues of the body, and in bodily fluids such as blood. It is made up of the innate (general) immune system and the adaptive (specialized) immune system. These two systems work closely together and take on different tasks.
The innate immune system: Fast and general effectiveness
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense against intruders. It responds in the same way to all germs and foreign substances, which is why it is sometimes referred to as the "non-specific" immune system. It acts very quickly – for instance, it makes sure that bacteria that have entered the skin through a small wound are detected and destroyed on the spot within a few hours. But the innate immune system can’t always stop germs from spreading.
The innate immune system provides
- protection offered by the skin and mucous membranes
- protection offered by immune system cells and proteins
Protection offered by the skin and mucous membranes
All outer and inner surfaces of the human body are a key part of the innate immune system. The closed surface of the skin and mucous membranes already forms a physical barrier that stops germs from entering. On top of that, substances like acid, enzymes and mucus prevent bacteria and viruses from growing. Certain movements in the body also stop germs from settling – for example, movements of hair-like structures (cilia) in the lungs or movements of the bowel muscles. Some fluids in the body have a similar effect – including tear fluid, sweat and urine (which flushes the organs of the urinary system).
Protection offered by immune system cells and proteins
If germs get past the skin or mucous membranes and enter the body, the innate immune system fights them using special immune system cells and proteins.
What happens during an inflammation?
If, for example, an area of skin becomes infected, immune system cells spring into action – either by moving to the area or by being activated locally. Certain cells of the immune system release substances to make the blood vessels wider and more “leaky.” This causes the area around the infection to swell, become warm and turn red – visible signs of the inflammation that has developed. A fever may develop too. Then the blood vessels get wider and even more immune system cells arrive to fight the infection.
Certain proteins known as enzymes are also activated to help defend the body (see below).
Phagocytes: Making germs harmless
Bacteria or viruses that enter the body can be stopped right away by phagocytes, also known as scavenger cells. These special white blood cells (leukocytes) enclose germs and "digest" them, making them harmless. The remains of the germs move to the surface of the phagocytes, where they can be detected by the adaptive immune system.
There are also other types of immune system cells that release substances to kill bacteria and other germs. But it’s not only the germs that die – tissue cells and immune system cells die and break down too. Together, their remains form a yellowish fluid called pus.
The role of proteins
Several proteins (enzymes) help the cells of the innate immune system. A total of nine different enzymes activate each other in a kind of chain reaction: One enzyme in the first stage alerts several enzymes in a second stage, each of which activates several enzymes in a third stage, and so on. This allows the immune response to grow stronger very quickly.
The tasks of these enzymes include:
- marking germs as targets for phagocytes,
- attracting other immune system cells from the bloodstream,
- destroying bacteria cell walls to kill the bacteria, and
- fighting viruses by destroying the viral envelope (the outermost layer of a virus) or cells that have been infected with viruses.
Natural killer cells: Searching for body cells that have changed
The natural killer cells are the third major part of the innate immune system. Their main job is to identify cells that have been infected by a virus, as well as abnormal cells that may turn into (or have turned into) tumor cells. To do this, they search for cells with an abnormal surface, and then destroy the cell surface using substances called cytotoxins.
The adaptive immune system: Fighting the germs directly
If the innate (general) immune system fails to destroy the germs, the adaptive (specialized) immune system takes over. The adaptive immune system specifically targets the type of germ that is causing the infection. But to do that, it first needs to recognize the germ as such. This means that it’s slower to respond than the innate immune system, but it’s more accurate when it does respond. It also has the advantage of being able to "remember" germs. So the next time the adaptive immune system faces a germ it has already met, it can start fighting the germ faster.
This memory is also the reason why there are some illnesses you can only get once in your life, because afterwards your body becomes “immune” to them. It may take a few days for the adaptive immune system to respond the first time it comes into contact with the germ, but the next time the body can react immediately. The second infection then usually goes unnoticed, or is at least milder.
The adaptive immune system is made up of:
- T cells in the tissue between the body's cells
- B cells (also in the tissue between the body's cells)
- Antibodies in the blood and other bodily fluids
T cells
T cells (also called T lymphocytes) are made in bone marrow. They travel in the bloodstream to the thymus, where they mature. The "T" in their name comes from "thymus."
T cells have three main jobs:
- They use chemical messengers to activate other cells of the immune system, starting the adaptive immune system response (T helper cells).
- They detect tumor cells or cells that have been infected by viruses and destroy them (cytotoxic T cells).
- Some T helper cells become memory T cells after the infection has cleared up. They "remember" the germ that was fought off, and are then ready to activate the adaptive immune system quickly if the body is infected by the same germ again.
T cells have specific features (receptors) on their surfaces that germs can attach to – like a lock that one particular key will fit. The immune system can make a matching T cell type for each germ within a few days of infection.
Then if a germ attaches to a matching T cell, the T cell starts to multiply – making more T cells that can specifically fight that germ. Because only the cells that match the germ multiply, the immune response is “tailor-made.”
B cells
B cells (B lymphocytes) are made in the bone marrow, where they mature into specialized immune system cells. They take their name from the "B" in "bone marrow." Like the T cells, there are many different types of B cells that match particular germs.
B cells are activated by T helper cells: T helper cells send signals to B cells that match the same germs as they do. This stimulates the B cells to make copies of themselves and turn into plasma cells. The plasma cells quickly make very large amounts of antibodies and release them into the blood. Because the T helper cells only activate the B cells that match the attacking germs, the body only makes the exact antibodies that are needed.
Some of the activated B cells turn into memory cells and become part of the "memory" of the adaptive immune system.
The different cells of the adaptive immune system communicate either directly or through soluble chemical messengers such as cytokines (usually proteins). These chemical messengers are made by various cells in the body.
Antibodies
Antibodies (proteins with sugar groups attached to them) travel around the body in the bloodstream. They are made by the immune system to fight germs and foreign substances. Antibodies can quickly recognize germs and other potentially harmful substances, and then attach to them. This makes the "intruders" harmless and attracts other immune system cells to help. Antibodies are made by B cells. Germs and substances that can trigger the production of antibodies are called "antigens."
An antibody only attaches to an antigen if it matches exactly, like a key in the lock of the antibody. In this way, antibodies recognize matching germs and trigger the fast response of the adaptive immune system.
Antibodies have three main functions:
- They make germs harmless – for example, by directly attaching to the cell surface of viruses or bacteria, or by binding harmful substances made by these germs. This prevents the germs from latching onto normal body cells and infecting them.
- They activate other immune system cells by attaching to their surface. Also, it’s much easier for phagocytes to fight off germs that have a lot of antibodies attached to them.
- They activate proteins that help in the immune system response.
So the antibodies of the adaptive immune system also help the innate immune system to do its job.
Sources
- Brandes R, Lang F, Schmidt R. Physiologie des Menschen: mit Pathophysiologie. Berlin: Springer; 2019.
- Menche N. Biologie Anatomie Physiologie. München: Urban und Fischer; 2023.
- Pschyrembel Online. 2023.
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services.
Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system. The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. informedhealth.org can provide support for talks with doctors and other medical professionals, but cannot replace them. We do not offer individual consultations.
Our information is based on the results of good-quality studies. It is written by a team of health care professionals, scientists and editors, and reviewed by external experts. You can find a detailed description of how our health information is produced and updated in our methods.
- In brief: The innate and adaptive immune systems - InformedHealth.orgIn brief: The innate and adaptive immune systems - InformedHealth.org
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
