MedGen Help Documentation
MedGen is NCBI's portal to information about conditions and phenotypes related to Medical Genetics. Terms from the NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR), UMLS, HPO, Orphanet, ClinVar and other sources are aggregated into concepts, each of which is assigned a unique identifier and a preferred name and symbol. The core content of the record may include names, identifiers used by other databases, mode of inheritance, clinical features, and map location of the loci affecting the disorder. The concept identifier (CUI) is used to aggregate information about that concept, similar to the way NCBI Gene serves as a gateway to gene-related information. MedGen provides links to such resources as:
Genetic tests registered in the NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) GeneReviews ClinVar OMIM Related genes Disorders with similar clinical features Medical and research literature Practice guidelines Consumer resources Ontologies such as HPO and ORDO
Links to the GTR, GeneReviews, and Practice Guidelines are based on curation by NCBI staff. Other data feeds are automated, but reviewed by NCBI staff and informed by feedback from the community.
We welcome your comments and suggestions.
MedGen Quick Start
Questions can be entered by entering any term, by selecting from a list of selected terms, or by using the Limits or Advanced functions to ask more complex questions.
Query strategies
| Purpose |
Examples (try the link) |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Find information about a condition by name | achondroplasia | As you type, names of genetic disorders used in the GTR will be provided. If you do not make a selection from the menu that appears under the search box as you type, your query is processed by looking for a match on a word or phrase. * is used as the wild card, and that wild card can be used only at the end of a word. |
| Find information about a condition based on the causative gene | LMNB1[gene] | If you enter a gene symbol followed by [gene], the diseases caused by or with some association to that gene will be retrieved. |
| Find information about a condition based on a clinical feature | short stature[clinical features] | If you enter the name of the feature followed by [clinical features] the diseases with that feature will be retrieved. |
| Find information about a condition based an identifier from another database | 273800 | For most databases, the query can be entered as you see it on the web page. For more detailed examples, see below. |
How to find information
MedGen uses the same type of query interface you may be familiar with if you use PubMed or Gene or the sequence databases. In other words, when you enter a term or phrase of interest in the query box, what you enter will be processed to retrieve records that contain or have some relationship to the word(s) you entered. The information is also organized into information categories or fields, so that queries can be constructed that retrieve records only if the term of interest occurs in that field. If you know the name of the field, you can enter that field name yourself. Otherwise you can use the Limits page or the Advanced page to help you build your query.
Simple queries
Just type your search term, and press enter or click on the Search button to the right of the query box.
Query by database identifier
MedGen is searchable by identifiers established by several resources for disorders or findings. The field in which these identifiers are indexed is "Source ID". Note the hints below.
| Resource | Type of identifier | Note | Sample query |
|---|---|---|---|
| OMIM | disorder | Current MIM numbers are searchable in MedGen. If an integer is entered without field qualifier [mim], then it will be searched both as a MIM number and as an identifier (MedGen UID). | 192600 |
| OMIM | phenotypic series | A phenotypic series ID can be used as a simple query. Phenotypic series data are added MedGen interactively, so the data are not yet complete. | PS192600 |
| HPO | disorders and findings | Current and alternative IDs from HPO are maintained in MedGen. Searching by those alternative ids will direct the users to the current record of that HPO concept. | HP:0012444 |
| Orphanet | disorders and findings | A query for an identifier from Orphanet must be constructed as orphanet_12345, not ORPHA12345. | orphanet_180 |
| MeSH | disorders and findings | Records retrieved based on a query by MeSH identifier are based on relationships supplied by UMLS. | D015211 |
| NCI | disorders | Records retrieved based on a query by NCI identifier are based on relationships supplied by UMLS. | C2910 |
Using Limits
Click on Limits in the grey query bar. There you can make selections to restrict your query by chromosome, relationships to other NCBI databases, types of content, and/or sources of the terms.
Using Advanced/MedGen Advanced Search Builder
Advanced is very useful when you want to construct a query that combines several concepts. The interface allows you browse for terms that may be anywhere in the database (All Fields) or in a particular field (selected from the menu of field names). Each search term can be combined with the others by the choice of AND, OR or NOT provided to the left of the next query term. Documentation of the mechanics of using Advanced Search Builder is provided here.
As an example of using the MedGen Advanced Search Builder, try the following steps to identify disorders that have been coded to have the clinical features of cleft palate and learning disability.
- Click on Advanced in the query bar at the top of the page.
- In the menu labeled All Fields, scroll down and select Clinical Features.
- Enter cleft in the box at the right, and click on Show index list to review the terms indexed in the clinical features field that start with cleft
- Select cleft palate. You may have to scroll down. The terms are listed alphabetically.
- In the next open line, make certain AND is displayed in the first menu.
- In the menu labeled All Fields, scroll down and select Clinical Features.
- Enter learning in the box at the right, and click on Show index list to review the terms indexed in the clinical features field that start with learning.
- Process your query by clicking on Search.
Note: If you want to combine several terms for a search, and some are alternative terms (connected by OR) the order in which you enter terms does make a difference. For example, "cleft palate"[Clinical Features] AND "learning disability"[Clinical Features] OR "developmental delay"[Clinical Features] is processed differently from "learning disability"[Clinical Features] OR "developmental delay"[Clinical Features] AND "cleft palate"[Clinical Features] . See the general documentation about how to use the Edit or History function on the Advanced page to control your search.
| Name | Abbreviation | Scope and explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosome |
[chr] [chromosome] |
The chromosome(s) contributing to the disorder, based on the genes or alleles that have been identified. A search including a term like 5[chr] will restrict results to conditions mapping to chromosome 5. |
| Clinical features |
[clinfeat] [clinical features] |
Clinical features associated with a disorder. These are built from annotation data supplied by the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO), or features from OMIM as processed by UMLS. Images from Elements of Morphology mapped to HPO terms are displayed as available. |
| Definition |
[defn] [definition] |
Terms occurring in the definition of the disorder. Definitions are provided from vocabularies registered in UMLS, from GeneReviews, CPIC, Medical Genetics Summaries, or more... |
| Exact title | [exact title] | The preferred name of any record. This field is used to improve retrieval based on the full name of any record. If the name is made of more than one word, performance is improved by surrounding the query in quotes, e.g. "ectodermal dysplasia" |
| Filter |
[sb] [filter] |
Terms in this field can be used to find records that fall into certain categories, such as all records for which a gene relationship has been reported. |
| Gene Full Name | [gene full name] | Full names of genes that have some relationship to a phenotype. The full names used to support this search are limited to current official names from the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). |
| Gene Name | [gene] | Gene symbols that have some relationship to a phenotype. The symbols used to support this search are limited to current or previous official symbols from the HGNC. If there is no official symbol from the HGNC, then NCBI Gene's preferred symbol is used. The data supporting the gene-phenotype relationship is built primarily from OMIM, GTR, NHGRI GWAS catalog, etc. |
| Guideline title | [Guideline title] | Titles of guidelines associated with a record in MedGen. Both the full title and terms in the title are represented in the index. This field is useful to find records associated with a practice guideline, position statement, or recommendation based on the title of that document. |
| Keyword | [keyword] | For a limited number of records, a key word may be added to the indexed terms to facilitate retrieval. |
| MIM | [mim] | The MIM (Mendelian Inheritance in Man) number associated with a record. See OMIM. |
| Mode of inheritance | [mode of inheritance] | The mode of inheritance for records that are heritable disorders. |
| Modification date | [moddate] | The date any element in the record was last modified. |
| Properties |
[prop] [property] |
Terms in the property field are standards used to categorize records in MedGen. The full list of properties, and their definitions, are provided in this document. |
| SNOMED CT CUI | [SNOMED CT CUI] | The concept identifier(s) (CUI) used by SNOMED CT for terms associated with the MedGen record. |
| Source ID | [Source ID] |
The identifier used by the source of the term in MedGen, e.g. MeSH, OMIM, SNOMED CT. This field also includes the concept identifiers (CUI) from UMLS and identifiers created by NCBI (format CN + 6 digits) when no CUI was associated. If a CUI is established, the previous NCBI identifier is retained in this field for indexing. |
| Text word | [text] | Any word in a MedGen record. |
| Title | [title] | Any word in the title of a MedGen record. |
| UID | [uid] | The integer identifer that corresponds to the CUI. This integer and the CUI exist in a 1:1 relationship, i.e. if a CUI for a concept is updated for any reason, the UID will change as well. A partial history of CUI modifications is provided on ClinVar's FTP site. |
| Vocabulary |
[vocab] [vocabulary] |
Abbreviations of the vocabularies used explicitly in MedGen. gtr: GTR, hpo: Human Phenotype Ontology, msh: MeSH, nci: NIH National Cancer Institute, omim: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, snomedct: SNOMED CT |
Application programming interface (API)
Data from MedGen can be retrieved programmatically via several application programming interfaces (API). These include:
E-utilities and Entrez Direct
As part of NCBI's Entrez system, MedGen can be accessed by E-utilities, both via web services and a UNIX command line as Entrez Direct. Documentation for these utilities is available from NCBI's BookShelf. To apply the general cases in the documentation to the specifics of MedGen, please note that MedGen currently supports only esearch and esummary.
The content of MedGen's document summary is the same as the XML displayed by selecting XML as a Display Setting. Please note that to conform to the requirements of NCBI's Entrez system, there are many elements in the ConceptMeta element, with element tags represented as the ASCII transform so the complex structure can be processed as a text string. Thus, depending on how you access the data, you may want to consider a global replacement of these encoded values.
| Function | Example |
|---|---|
| Use esearch to find unique identifiers of records of interest | http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/esearch.fcgi?db=medgen&term=charcot&retmax=500 |
| Use esummary to retrieve the document summary of one of the identifiers retrieved in the previous query | http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/esummary.fcgi?db=medgen&id= |
Accessing MedGen by URL
Data in MedGen can be accessed by URLs. The result may be a single record, or a set of records that satisfy the query. These examples are a sample only; any field or property listed in the previous section can be used to build a URL by combining the base URL with the term and its field qualifier.
The base url is: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/
which also takes you to MedGen's home page.
Add the value in the Qualifier column in the table below to construct the final URL.
| Type | Qualifier | Example |
|---|---|---|
| CUI | C0010674 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/C0010674 |
| Clinical feature | Hypoplasia of the ulna[clinical features] | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/?term=%22Hypoplasia+of+the+ulna%22%5BClinical+Features%5D |
| Symbol of the gene that contributes to the phenotype | FGFR3[gene] | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/?term=fgfr3%5Bgene%5D |
| Identifier used by a source, e.g. OMIM 188400 | 188400[sourceid] | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/?term=188400%5Bsourceid%5D |
| Preferred name | cystic fibrosis[exacttitle] | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/?term=cystic+fibrosis%5Bexacttitle%5D |
| Pharmacogenetic phenotypes | pharmacogenetic[keyword] | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen?term=%22pharmacogenetic%22%5BKeyword%5D |
Using the query results
MedGen search results are provided in the Summary format, in order of relevance and with 20 items per page. You can change the display format as well as the number of the items per page by opening the Display Settings menu at the upper left and resetting the values.
Options for Display Settings
| Format option | Description |
|---|---|
| Summary |
The default summary display. Includes the title, a brief description /definition when available, a report of the UID, the ConceptID, and the type of record, and links to GTR, Genes, OMIM, and GeneReviews when available. The source of the definition is indicated in square brackets at the end. Details about each source are provided here. |
| Summary (text) | The text of the summary (no links). Includes the title, a brief description /definition when available, the (semantic) type of record, the identifier for that semantic type, the Concept ID, and the integer ID. |
| UI List | The list of integer IDs for the records returned by a query. |
| XML | The document summary with elements of ConceptId, Title, Definition, SemanticId, SemanticType, Suppressed, ConceptMeta, ModificationDate, and Merged. ConceptMeta contains structured information about related identifers and terms. |
To display the full record of an item, click on the title of the summary (available only from the Summary display option).
Using the full report page
The full report page provides descriptive information defining a record, and links to sites with related information. This page may be divided into several sections; not all records will have content in all sections and each section can be collapsed or expanded for ease of navigation.
Names and identifiers
This section summarizes names and identifiers associated with the record. If the record is a disorder with a known genetic basis, the gene or genes are reported, along with mode of inheritance and cytogenetic location (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The preferred name and its preferred acronym (in parentheses) are provided at the top of the page. Under that are the identifiers assigned to the record, namely the MedGen integer identifier and the alphanumeric Concept ID. Please note that the MedGen integer identifier and the alphanumeric Concept ID are maintained on a 1:1 basis, so there is no avantage to storing one over the other.
When the concept ID has an integer at the second position, as in this example, then the identifier is provided by UMLS. If starting with CN, the concept is not from the current release of UMLS but generated from NCBI. With a new release of UMLS, the CN identifier may be replaced with a concept identifier from UMLS. The history of these changes as they relate to GTR and ClinVar is provided for ftp at ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/clinvar/ConceptID_history.txt.
Of all the terms available for a Concept ID, MedGen selects the preferred one based on preferred names from these sources, listed in order of precedence:
Curatorially reviewable by the NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) and ClinVar Preferred name from the Human Phenotype Ontology NCI thesaurus for cancer-related terms (semantic type of Neoplastic Process) SNOMEDCT_US (which is used as a first priority for names from UMLS when available) Orphanet UMLS
Synonyms
Alternate terms are derived from the vocabularies being used in MedGen that belong to the same concept.
Modes of inheritance
Report of one or more modes of inheritance for this disorder. These data are integrated from Orphanet or association files from the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO). The values that may be reported are documented here.
SNOMED CT
Terms from SNOMED CT for this concept, and their identifiers. In this example, the identifiers are all the same, but in some cases UMLS will include terms from different SNOMED CT concepts within the same UMLS concept; thus providing the identifers from SNOMED CT will make it clear when that has occurred.
Gene
The symbols of genes reported to contribute to a disorder. Each symbol anchors a link to the record in NCBI's Gene database. The complete list of Gene-MedGen relationships is provided from Gene's FTP site
Cytogenetic location
Cytogenetic locations associated with a disorder. There are based on the location of each gene with a reported relationship to the disorder.
OMIM
The MIM condition number corresponding to this record.
HPO
The HPO number corresponding to this record.
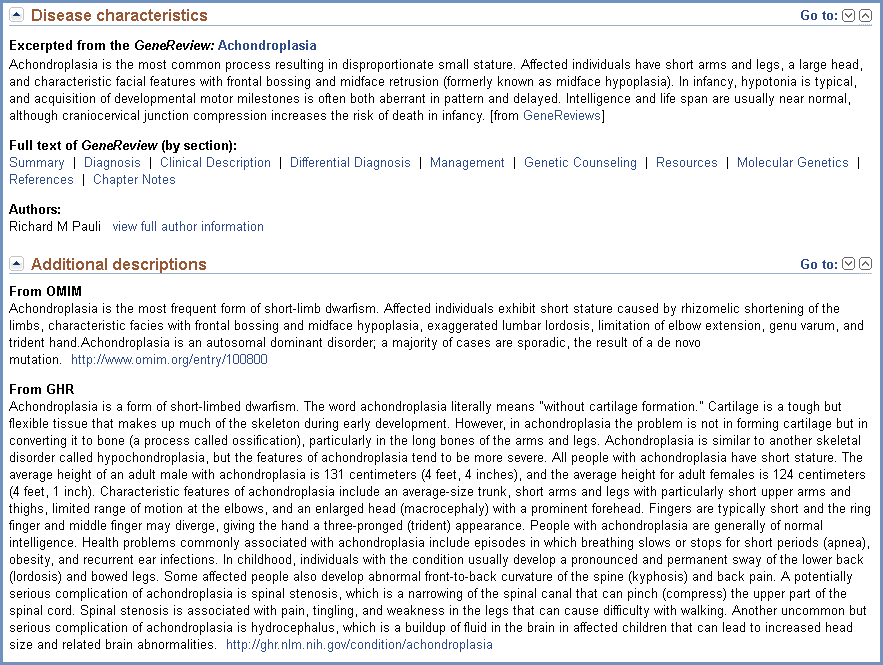
Disease characteristics and additional descriptions
This section of the full report provides a brief description or definition of the concept, along with attribution for the primary source of that description. More details about each source are provided here. If, as in this example (Figure 2), content is provided from a GeneReviews, the section also provides links to explicit sections of the GeneReviews and the list of authors.
Figure 2
Clinical features
A record about a condition may include a section describing the features of the condition. These data are provided from either the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) or OMIM. The first five features are displayed, with an option to view the full list.
Figure 3
If you hover over any term in the list, a pop-up (Figure 4) will display the definition of that term, and provide links to either the full report in MedGen for that feature (Feature record), or other conditions reported to have that feature (Search on this feature).
Figure 4

Images depicting clinical features are displayed, as available from Elements of Morphology e.g., Crumpled ear.
Term hierarchy
The hierarchies (Figure 5) are constructed based on relationships reported for each concept as direct or indirect links between terms from vocabulary sources. Concepts in GTR hierarchy (Figure 5- A) are displayed alongside any available links to Clinical tests, Research tests, OMIM, or GeneReviews. Each term is linked to the full report for that concept.
Figure 5

Practice Guidelines
This section (Figure 6- A) is provided via curation by staff at NCBI. If we have missed any, please contact us to provide the information.
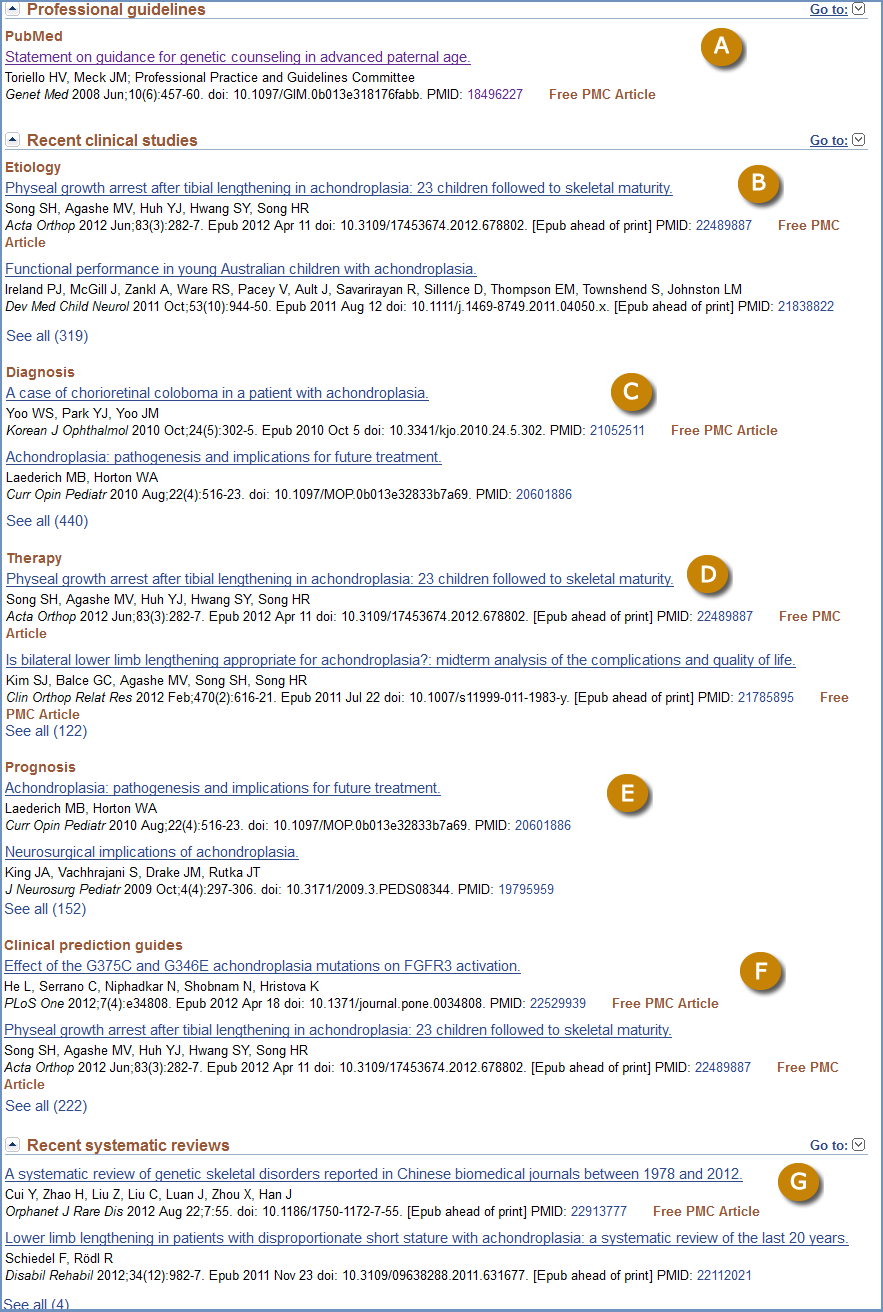
Recent clinical studies
This section (Figure 6) is generated at the time of display of the web page. It uses the title of the record as a query and processes that title as if it had been submitted as a clinical query to PubMed (PubMed Clinical Queries), with display of the results in the Clinical Study Categories section, selecting Diagnosis with broad scope. Additional filters are applied, namely English language and human, and not comment publication types nor letter publication types. The results are presented in 5 subsections of Etiology (B), Diagnosis (C), Therapy (D), Prognosis (E), and Clinical prediction guides (F).
Figure 6
Recent systematic reviews
This section (Figure 6- G) is generated at the time of display of the web page. It uses the title of the record as a query and processes that title as if it had been submitted as a clinical query to PubMed (PubMed Clinical Queries), with display of the results in the Systemic Reviews section. Additional filters are applied, namely English language and human, and not comment publication types nor letter publication types.
Discovery panel at the right
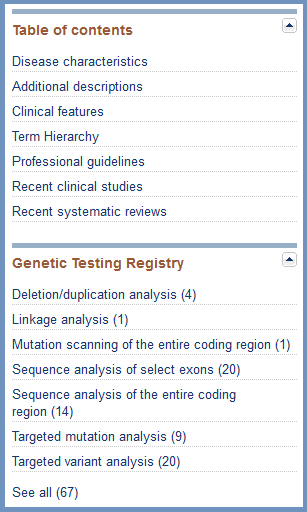
Table of contents and page navigation
The table of contents (Figure 7) summarizes the sections that are available in the record being displayed. Each term is hyperlinked to support quick navigation to that section. When you are within the page, the Go to link at the top of any section header (e.g. Figure 2) provides a pull down menu with quick links to other sections.
NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR)
The NIH Genetic Testing Registry section (Figure 7) lists the types of genetic tests that are reported in the GTR for the condition or phenotype, according to the primary method being used. The section provides links to all tests, or tests using the method category being listed.
Figure 7
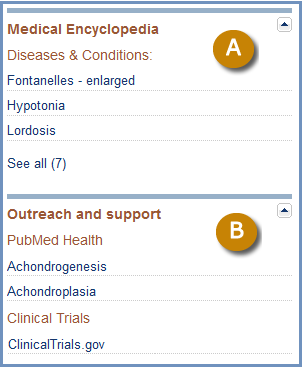
Outreach and support
This section enumerates and provides links to several sources that may provide information for consumers.
Figure 8
Reviews
The Reviews section (Figure 9- A) provides links based on curation by NCBI staff.
Figure 9
Related information
These links (Figure 9- B) point to other NCBI databases, and are computed by NCBI's query retrieval system.
Recent activity
A list of your recent queries and retrieval sets. This function is provided by many NCBI databases.
Display settings
On the full report page, three format options are provided.
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| Full report | The default full display |
| Full report (text) | This title is misleading. The text is rather the text of the document summary for this report. |
| XML | The XML for the document summary for this report. |
Building the database
MedGen is built by aggregating data from multiple resources. The primary foundation is concepts provided from UMLS without restriction, with updates according the UMLS' release cycle (May and November). Other sources also provide terms as summarized in the Data Sources table below.
The data model of MedGen is patterned on that of UMLS, namely sets of terms thought to be equivalent are grouped by a concept unique identifier (CUI). That equivalency depends on the term and its definition, and the type of concept it represents. For example, the same term may be the name of disorder and a description of a clinical feature. Because those are different types of terms, they may be assigned different CUI values.
Terms from sources not in scope for UMLS may be integrated into concepts already created by UMLS, or new 'concepts' may be created. You can tell the difference because concepts from UMLS begin with the letter C followed by numerals. Concepts from MedGen's processing start with CN.
Note: Identifiers generated by MedGen may be retired if UMLS generates a concept that corresponds to one initiated by MedGen. The history of those changes is reported as MedGen_CUI_history.txt.
The automated aggregation of terms in MedGen can be reviewed by staff of GTR and ClinVar. If staff members or external user question a mapping, or identify a gap, curators will review data sources and the data flow to identify a solution. In some cases, staff members may establish records to seed the automated processing.
Data Sources for terms
Representation from UMLS is not comprehensive, but is selected for MedGen based both on vocabulary source (to ensure coverage and requests from you, our user community) , and categories of terms within that vocabulary source (semantic type). In other words, even though MedGen includes terms from MeSH, it does not include terms from such categories as Subheadings or Technology and Food and Beverages. Vocabulary sources used from UMLS include MeSH, NCI, OMIM and SNOMED CT US.
Selected sources with frequency of update
MedGen is updated daily, but not all data sources update that often. Updates may include adding terms, or adding connections to related concepts in other databases.
| Source | Frequency | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| ClinVar | Daily | A subset of terms provided by submitters to ClinVar. Terms are reviewed by NCBI staff before releasing to MedGen. Thus there may be condition reported to ClinVar that is not represented in MedGen. |
| GeneReviews | Daily | Terms may be reviewed by GTR staff. Definitions are added based on the MIM number relationship. |
| GTR | Daily | Terms provided by those registering tests in the NIH Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) |
| Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) | Within a month of any release from HPO | A primary source for clinical features of Mendelian disorders. MedGen uses the mapping of preferred terms from HPO to CUI provided by UMLS. Until one is available, MedGen assigns a CUI starting with CN. Thus CUI used in MedGen for HPO-specific data may change with updates from UMLS. |
| Medical Genetics Summaries | When published to the NCBI BookShelf | Definitions are submitted based on CUI. |
| Mondo | Monthly (by release from Mondo) | Terms used by Mondo, their identifiers, their definitions, and their mappings between Mondo IDs and IDs from GARD, OMIM Phenotypic Series and Orphanet. |
| OMIM | Daily | Terms from OMIM are processed from both UMLS (which releases information twice a year), and daily updates directly from OMIM. The direct updates from OMIM are also used as a foundation of reporting gene-disease relationships. CUI assigned to records defined by MIM numbers may change with updates from UMLS, i.e. when MedGen-generated CUI is replaced with one from UMLS. |
| OMIM phenotypic series | Releases from Mondo | Concepts represented by OMIM's phenotypic series are integrated into MedGen as part of releases from Mondo. |
| ORDO | Releases from ORDO and Mondo | Terms and definitions from the Orphanet Rare Disease ontology (ORDO) are processed into MedGen automatically based on mappings establshed by Mondo. Concepts include the modes of inheritance characteristic of any disorder. |
| UMLS | twice a year |
Representation of terms from UMLS is restricted to a subset of vocabulary sources, and categories of terms (semantic types). Vocabulary sources included in the UMLS data flow include
|
| Elements of Morphology | unscheduled | Images from Elements of Morphology: Human Malformation Terminology mapped to HPO terms are displayed on Clinical feature records, as available. |
Sources of definitions
For a complete listing of the sources of definitions used by MedGen, please refer to the Sources of definitions page.
Sources of relationships between disorders and their clinical features
OMIM, based on data from UMLS, represented as 'has_manifestation' in the relationships file (MGREL).
Human Phenotype Ontology, based on data from HPO and UMLS, represented as 'has_manifestation' in the relationships file (MGREL).