NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
National Collaborating Centre for Cancer (UK). Neutropenic Sepsis: Prevention and Management of Neutropenic Sepsis in Cancer Patients. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE); 2012 Sep. (NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 151.)

Neutropenic Sepsis: Prevention and Management of Neutropenic Sepsis in Cancer Patients.
Show details
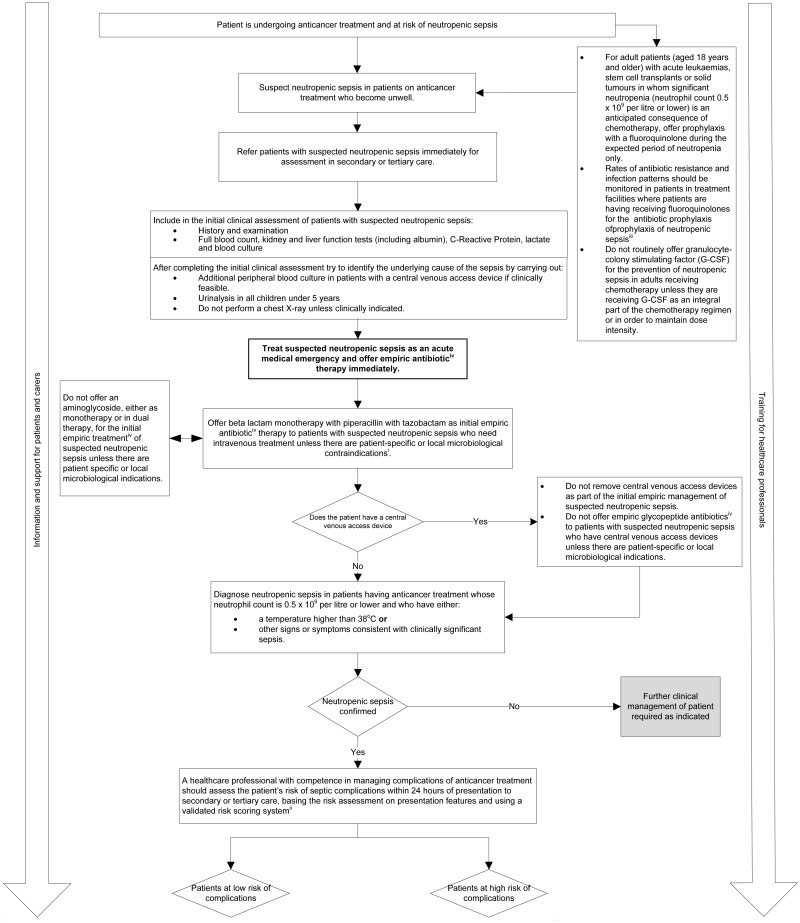
- i
At the time of publication (September 2012) piperacillin with tazobactam did not have a UK marketing authorisation for use in children aged under 2 years. The prescriber should follow relevant professional guidance, taking full responsibility for the decision. The child's parent or carer should provide informed consent, which should be documented. See the GMC's Good practice in prescribing medicines – guidance for doctors and the prescribing advice provided by the Joint Standing Committee on Medicines (a joint committee of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health and the Neonatal and Paediatric Pharmacists Group) for further information.
- ii
Examples of risk scoring systems include The Multinational Association for Supportive Care in Cancer risk index: a multinational scoring system for identifying low-risk febrile neutropenic cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;18:3038–51. [PubMed: 10944139] and the modified Alexander rule for children (aged under 18). European Journal of Cancer. 2009;45:2843–9. [PubMed: 19616427].
- iii
For more information see the Department of Health's Updated guidance on the diagnosis and reporting of Clostridium difficile and guidance from the Health Protection Agency and the Department of Health on Clostridium difficile infection: how to deal with the problem..
- iv
An empiric antibiotic is given to a person before a specific microorganism or source of the potential infection is known. It is usually a broad-spectrum antibiotic and the treatment may change if the microorganism or source is confirmed.
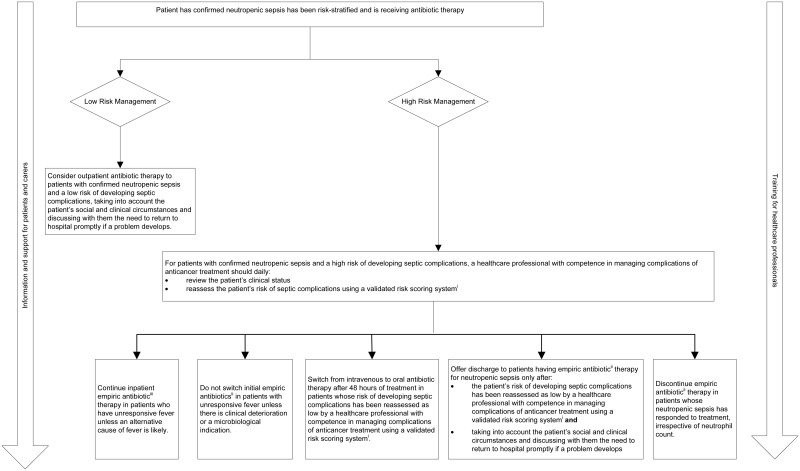
Overview of low and high risk management
- i
Examples of risk scoring systems include The Multinational Association for Supportive Care in Cancer risk index: a multinational scoring system for identifying low-risk febrile neutropenic cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;18:3038–51. [PubMed: 10944139] and the modified Alexander rule for children (aged under 18). European Journal of Cancer. 2009;45:2843–9. [PubMed: 19616427].
- ii
An empiric antibiotic is given to a person before a specific microorganism or source of the potential infection is known. It is usually a broad-spectrum antibiotic and the treatment may change if the microorganism or source is confirmed.
- Algorithm: Summary of recommendations - Neutropenic Sepsis: Prevention and Manag...Algorithm: Summary of recommendations - Neutropenic Sepsis: Prevention and Management of Neutropenic Sepsis in Cancer Patients
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...