Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
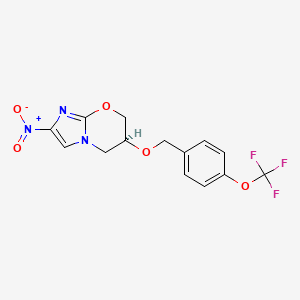
CASRN: 187235-37-6
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
No information is available on the use of pretomanid during breastfeeding, although the estimated dose for a breastfed infant is low. If pretomanid is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but until more data become available, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Using a computed milk-to-plasma ratio of 0.89, one group of authors estimated that a fully breastfed infant would receive a pretomanid dosage of 1.02 mcg/kg daily with a standard maternal dose of 200 mg daily.[1] However, the authors used a nonstandard milk volume in their calculation. Using the standard 150 mL/kg daily, the estimated infant dosage would be 0.83 mcg/kg daily.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Algharably EA, Kreutz R, Gundert-Remy U. Infant exposure to antituberculosis drugs via breast milk and assessment of potential adverse effects in breastfed infants: Critical review of data. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15:1228. [PMC free article: PMC10143885] [PubMed: 37111713]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Pretomanid
CAS Registry Number
187235-37-6
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Structure-activity relationships for amide-, carbamate-, and urea-linked analogues of the tuberculosis drug (6S)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine (PA-824).[J Med Chem. 2012]Structure-activity relationships for amide-, carbamate-, and urea-linked analogues of the tuberculosis drug (6S)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine (PA-824).Blaser A, Palmer BD, Sutherland HS, Kmentova I, Franzblau SG, Wan B, Wang Y, Ma Z, Thompson AM, Denny WA. J Med Chem. 2012 Jan 12; 55(1):312-26. Epub 2011 Dec 29.
- 3D QSAR, Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulations and MM-GBSA studies of Extended Side Chain of the Antitubercular Drug (6S) 2-Nitro-6- {[4-(trifluoromethoxy) benzyl] oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b] [1,3] oxazine.[Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019]3D QSAR, Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulations and MM-GBSA studies of Extended Side Chain of the Antitubercular Drug (6S) 2-Nitro-6- {[4-(trifluoromethoxy) benzyl] oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b] [1,3] oxazine.Chaudhari HK, Pahelkar A. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019; 19(2):145-166.
- Synthesis and structure-activity relationships for extended side chain analogues of the antitubercular drug (6S)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine (PA-824).[J Med Chem. 2015]Synthesis and structure-activity relationships for extended side chain analogues of the antitubercular drug (6S)-2-nitro-6-{[4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzyl]oxy}-6,7-dihydro-5H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine (PA-824).Palmer BD, Sutherland HS, Blaser A, Kmentova I, Franzblau SG, Wan B, Wang Y, Ma Z, Denny WA, Thompson AM. J Med Chem. 2015 Apr 9; 58(7):3036-59. Epub 2015 Mar 27.
- Review Zafirlukast.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Zafirlukast.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Daridorexant.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Daridorexant.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Pretomanid - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Pretomanid - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
