Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
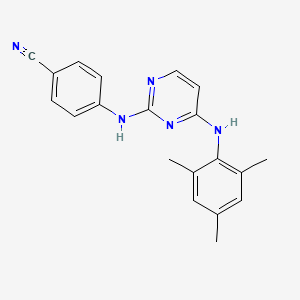
CASRN: 244767-67-7
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Dapivirine is investigational in the United States, but available overseas as a vaginal ring for pre-exposure prophylaxis of HIV infections (PrEP). In this dosage form, it is acceptable to use during breastfeeding.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Sixteen lactating women who had weaned their infants used the dapivirine vaginal ring for 14 days and provided milk, blood and cervicovaginal fluid samples for analysis. Milk samples were obtained on days 0, 1, 7 and 14 during use of the insert and on day 16, two days after its removal. The mean breastmilk concentration was 676 ng/L (range 297 to 1,420 ng/L). This translated to an estimated average infant dosage of 74.3 ng/kg daily. The average half-life in milk was 45.8 hours.[1]
A clinical trial compared the dapivirine vaginal ring 25 mg monthly to emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate as prophylaxis against HIV infection. In women randomized to dapivirine (n = 148), dapivirine concentrations in breastmilk averaged 698.3 ng/L during the first week of use and trended downward to 596.1 ng/L in the third month of use. At 2 weeks after discontinuation, milk dapivirine averaged 50.1 ng/L.[2]
Infant Levels. A clinical trial compared the dapivirine vaginal ring 25 mg monthly to emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate as prophylaxis against HIV infection. In the infants of women randomized to dapivirine (n = 148), dapivirine was detected in 15% of infants’ serum after 2 weeks of use, with an average concentration of 14.5 ng/L. In the third month of use, the drug was detectable in the serum of only 5.1% of infants with an average concentration of 10.7 ng/L. At 2 weeks after drug discontinuation, no infants had detectable dapivirine in their serum.[2]
Effects in Breastfed Infants
A study compared the dapivirine vaginal ring to emtricitabine plus tenofovir for prophylaxis of HIV infections. Of 148 mother-infant pairs who received the dapivirine vaginal ring, no adverse effects in infants were attributed to dapivirine.[3]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Noguchi LM, Hoesley C, Kelly C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of dapivirine transfer into blood plasma, breast milk, and cervicovaginal fluid of lactating women using the dapivirine vaginal ring. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2019;63:e01930-18. [PMC free article: PMC6395928] [PubMed: 30602513]
- 2.
- Owor M, Noguchi L, Horne E, et al. Dapivirine ring safety and drug detection in breastfeeding mother-infant pairs. In Special Issue: Abstracts From CROI 2023 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. Top Antiviral Med 2023;31:314.
- 3.
- Noguchi L, Owor M, Gati B, et al. Phase 3B, randomized, open-label, safety study of dapivirine vaginal ring and oral emtricitabine 200mg/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg tablet in breastfeeding mother-infant pairs. J Int AIDS Soc 2022;25 (Suppl 3):e25935.
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Dapivirine
CAS Registry Number
244767-67-7
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Milk, Human
Anti-Infective Agents
Antiviral Agents
Anti-HIV Agents
Anti-Retroviral Agents
Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of a Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Dapivirine, in Glioblastoma.[J Cancer. 2018]Antitumor Activity and Mechanism of a Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Dapivirine, in Glioblastoma.Liu W, Song XL, Zhao SC, He M, Wang H, Chen Z, Xiang W, Yi G, Qi S, Liu Y. J Cancer. 2018; 9(1):117-128. Epub 2018 Jan 1.
- Dapivirine vaginal ring for HIV prevention: modelling health outcomes, drug resistance and cost-effectiveness.[J Int AIDS Soc. 2019]Dapivirine vaginal ring for HIV prevention: modelling health outcomes, drug resistance and cost-effectiveness.Glaubius R, Ding Y, Penrose KJ, Hood G, Engquist E, Mellors JW, Parikh UM, Abbas UL. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019 May; 22(5):e25282.
- HIV prevention at drug shops: awareness and attitudes among shop dispensers and young women about oral pre-exposure prophylaxis and the dapivirine ring in Shinyanga, Tanzania.[AIDS Res Ther. 2021]HIV prevention at drug shops: awareness and attitudes among shop dispensers and young women about oral pre-exposure prophylaxis and the dapivirine ring in Shinyanga, Tanzania.Tubert J, Packel L, Hunter LA, Mfaume R, Njau P, Ramadhani AA, Liu JX, McCoy SI. AIDS Res Ther. 2021 Apr 26; 18(1):21. Epub 2021 Apr 26.
- Review Etravirine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Etravirine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Rilpivirine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Rilpivirine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Dapivirine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Dapivirine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
