Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
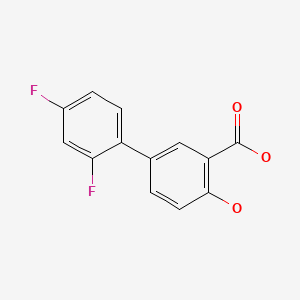
CASRN: 22494-42-4
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
The small amounts of diflunisal in milk do not appear to pose a serious risk to breastfeeding infants. However, a shorter-acting agent having more published information may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Review articles report that milk levels are 2 to 7% of simultaneous maternal serum levels after 7 days of administration of 125 or 250 mg twice daily; however, no study details are provide.[1,2] This would represent milk levels ranging from 0.3 to 0.9 mg/L with a dose of 125 mg daily and 0.8 to 2.7 mg/L with a dose of 250 mg daily.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
Acetaminophen, Flurbiprofen, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Naproxen, Piroxicam
References
- 1.
- Steelman SL, Breault GO, Tocco D, et al. Pharmacokinetics of MK-647, a novel salicylate. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975;17:245. Abstract.
- 2.
- Tempero KF, Cirillo VJ, Steelman SL. Diflunisal: chemistry, toxicology, experimental and human pharmacology. In, Diflunisal: new perspectives in analgesia. Royal Soc Med Int'l Con Sym Ser Huskisson EC, Caldwell, ADS, eds 1979;6:3-4.
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Diflunisal
CAS Registry Number
22494-42-4
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- Review Piroxicam.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Piroxicam.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Oxaprozin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Oxaprozin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Amoxapine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Amoxapine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Norfloxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Norfloxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Salsalate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Salsalate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Diflunisal - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Diflunisal - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
