Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
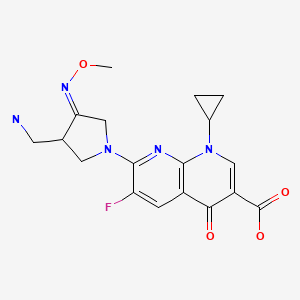
CASRN: 175463-14-6
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
No information is available on the clinical use of gemifloxacin during breastfeeding; however, amounts in breastmilk appear to be low. Fluoroquinolones have traditionally not been used in infants because of concern about adverse effects on the infants' developing joints. However, recent studies indicate little risk.[1,2] The calcium in milk might prevent absorption of the small amounts of fluoroquinolones in milk,[3] but insufficient data exist to prove or disprove this assertion. Use of gemifloxacin is acceptable in nursing mothers. However, it is preferable to use an alternate drug for which safety information is available.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A nursing mother took one tablet of gemifloxacin 320 mg orally. A single breastmilk sample obtained 3 hours after the dose contained approximately 0.9 mg/L.[4]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Gürpinar AN, Balkan E, Kiliç N, et al. The effects of a fluoroquinolone on the growth and development of infants. J Int Med Res. 1997;25:302–6. [PubMed: 9364293]
- 2.
- van den Oever HL, Versteegh FG, Thewessen EA, et al. Ciprofloxacin in preterm neonates: Case report and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr. 1998;157:843–5. [PubMed: 9809826]
- 3.
- Fleiss PM. The effect of maternal medications on breast-feeding infants. J Hum Lact 1992;8:7. Letter. PMID: 1558663. [PubMed: 1558663]
- 4.
- Sagirli O, Demirci S, Onal A. A very simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection for the determination of gemifloxacin in human breast milk. Luminescence. 2015;30:1326–9. [PubMed: 25808579]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Gemifloxacin
CAS Registry Number
175463-14-6
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Enoxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Enoxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Moxifloxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Moxifloxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Norfloxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Norfloxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Delafloxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Delafloxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Sparfloxacin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Sparfloxacin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Gemifloxacin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Gemifloxacin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
