Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
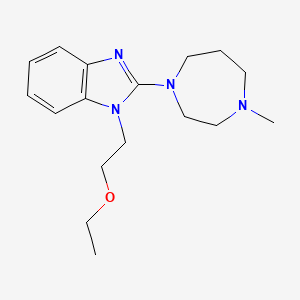
CASRN: 87233-61-2
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Emedastine is an antihistamine that is not approved for marketing in the United States by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, but is available in other countries. Preliminary data indicate that oral administration of 2 mg daily produces low levels in milk and does not affect the breastfed infant.
When used as an eye drop, emedastine would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A woman was prescribed emedastine difumarate 2 mg once daily and pranlukast hydrate 112.5 mg twice daily during pregnancy and postpartum. Emedastine concentration in milk were measured on days 1 to 4 postpartum. Emedastine concentrations at 9.3 and 12.3 hours after a dose were 0.44 and 0.13 mcg/L, respectively. At 20.3, 22.5, and 23.3 hours after a dose, milk concentrations were 0.09, 0.07, and 0.06 mcg/L, respectively.[1]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
A woman was prescribed emedastine difumarate 2 mg once daily and pranlukast hydrate 112.5 mg twice daily during pregnancy and postpartum. Her infant was breastfed and no adverse effects were noted.[1]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
(Oral) Desloratadine, Fexofenadine, Loratadine
References
- 1.
- Saito J, Yakuwa N, Sasaki A, et al. Emedastine during pregnancy and lactation: Emedastine levels in maternal serum, cord blood, breast milk, and neonatal serum. Breastfeed Med. 2020;15:809–12. [PubMed: 33035080]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Emedastine
CAS Registry Number
87233-61-2
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- [Cross-reactivities of active metabolites in the radioreceptor assay of an antiallergic agent, 1-(2-ethoxyethyl)-2-(hexahydro-4-methyl-1H-1,4-diazepin-1-yl)- 1H-benzimidazole difumarate (KG-2413)].[Yakugaku Zasshi. 1989][Cross-reactivities of active metabolites in the radioreceptor assay of an antiallergic agent, 1-(2-ethoxyethyl)-2-(hexahydro-4-methyl-1H-1,4-diazepin-1-yl)- 1H-benzimidazole difumarate (KG-2413)].Hamada T, Kawashima T, Awata N. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1989 Jul; 109(7):474-9.
- Review Mianserin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Mianserin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Teicoplanin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Teicoplanin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Azelastine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Azelastine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Tolazamide.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Tolazamide.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Emedastine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Emedastine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
