Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
CASRN: 51-06-9
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Maternal doses of procainamide 2 grams daily produced low levels of the drug and its active metabolite in the milk of one mother. Although it would not be expected to cause adverse effects in older breastfed infants, the relative lack of data concerning breastfeeding during maternal procainamide therapy would argue for careful monitoring if this drug is used while breastfeeding a neonate possibly Measurement of infant serum levels could help to rule out toxicity if there is a concern.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. One mother was taking a dose of 500 mg 4 times daily (dosage form not stated, but probably immediate-release). Milk procainamide and N-acetyl procainamide (NAPA) levels were measured on one of the first postpartum days. Procainamide levels averaged 5.4 mg/L (range 2.6 to 10.2 mg/L), and NAPA averaged 3.5 mg/L (range 3.1 to 5 mg/L). Because the mother's serum levels were consistently below the therapeutic range, usual milk levels would probably be higher than reported here. There was no clear correlation between time after the dose and milk levels.[1] Based on data in this case, the average expected dose of procainamide plus NAPA that an infant would receive in breastmilk is less than 5% and the maximum would be less than 7% of the mother's weight-adjusted dosage.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Pittard WB III, Glazier H. Procainamide excretion in human milk. J Pediatr. 1983;102:631-3. [PubMed: 6187910]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
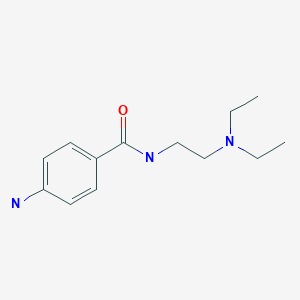
Procainamide
CAS Registry Number
51-06-9
Drug Class
- Breast Feeding
- Antiarrhythmics
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- Review Procaine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Procaine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Dibucaine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Dibucaine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Benzocaine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Benzocaine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Metoclopramide.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Metoclopramide.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Cycloserine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Cycloserine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Procainamide - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Procainamide - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
