Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
CASRN: 1744-22-5
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Limited information indicates that maternal doses of riluzole up to 100 mg daily produce low levels in milk and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants, especially if the infant is older than 2 months. Until more data are available, use riluzole with caution, particularly when breastfeeding a newborn.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A woman who was breastfeeding her 18-month-old infant 3 to 4 times a day was diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and started on riluzole 50 mg twice daily by mouth. On the third day of therapy, milk samples were collected before and at 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12 hours after the first dose of the day. The pre-dose sample contained 33.8 mcg/L of riluzole. The peak concentration in milk was 229.5 mcg/L at 2 hours after the dose. The average milk concentration was 94.4 mcg/L over the 12-hour collection time, which would provide the infant with an estimated daily dosage 14.1 mcg/kg. Based on the 12-hour collection period, the maternal weight-adjusted dosage was 0.8%. Riluzole metabolites were not measured.[1]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Datta P, Rewers-Felkins K, Aurora N, et al. Estimation of riluzole levels in human milk and infant exposure during its use in a patient with ALS. J Hum Lact. 2018;34:355–7. [PubMed: 29100479]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
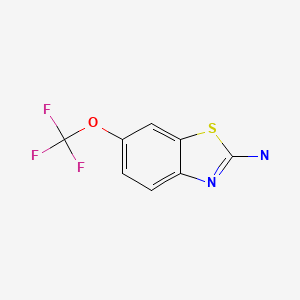
Riluzole
CAS Registry Number
1744-22-5
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists
Neuroprotective Agents
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Teicoplanin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Teicoplanin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Pamidronate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Pamidronate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Iohexol.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Iohexol.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Propafenone.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Propafenone.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Sodium Stibogluconate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Sodium Stibogluconate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Riluzole - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Riluzole - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
- Homo sapiens zinc finger CCHC-type containing 8 (ZCCHC8), transcript variant 3, ...Homo sapiens zinc finger CCHC-type containing 8 (ZCCHC8), transcript variant 3, mRNAgi|1677529708|ref|NM_001350936.2|Nucleotide
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
