Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
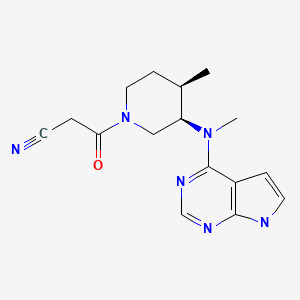
CASRN: 477600-75-2
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
The manufacturer and an expert panel recommend that breastfeeding be discontinued during tofacitinib therapy and for 18 hours after the last dose of the immediate-release product or 36 hours after the last dose of the sustained-release product.[1] Data from 2 mothers indicate that the amount in milk is relatively low and no adverse effects were seen in 2 infants who were exclusively breastfed during maternal tofacitinib use. Until more data become available, tofacitinib should be used with caution during breastfeeding, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A woman with treatment-refractory ulcerative proctitis was started on tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily. She was nursing her 30-month-old daughter once daily. She stopped breastfeeding when tofacitinib was started, but collected 37 timed milk samples over 14 hours after a dose 25 days after stopping breastfeeding while she was still producing milk. The highest tofacitinib milk concentration of 54.5 mcg/L occurred 4 hours after the dose and the lowest milk concentration of 2 mcg/L occurred 14 hours after the dose. Based on the highest milk concentration, the infant would receive 3.4% of the mother’s weight-adjusted dosage.[2]
One nursing mother taking tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily donated 18 prenursing milk samples on days 20 to 22 postpartum. The median level was 7.8 mcg/L (range 1.8 to 32.8 mcg/L). The highest milk concentration of 32.8 mcg/L occurred 3.5 hours after a maternal dose of tofacitinib. The lowest concentration of 1.8 mcg/L occurred 11.3 hours after the previous tofacitinib dose. Based on the highest milk level, the worst-case daily infant dosage was 4.9 mcg/kg, equating to a weight-adjusted relative infant dose of 3.4%.[3]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Two mothers took tofacitinib during pregnancy while exclusively breastfeeding. One infant whose mother was taking a dose of 5 mg twice daily was breastfed for 14 weeks. The other infant whose mother was taking a dose of 10 mg twice daily was breastfed for 6 weeks. These infants were followed up at 3.5 ad 14 months of age, respectively. They had normal growth and psychomotor development at the time of follow-up and no negative safety signal was seen. Both received the mandatory non-live vaccinations without complications.[3]
A woman was taking tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily for ulcerative proctocolitis. She reduced the dose to 5 mg twice daily at week 23 of pregnancy and continued it for the rest of her pregnancy and while breastfeeding (extent not stated). At 12 weeks of age, the infant underwent a thorough immunologic evaluation that was normal. The infant was given two doses of the live rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix, GlaxoSmithKline) at weeks 13 and 20 of age. No adverse events were reported following immunization, including severe vomiting, diarrhea or intussusception, with active and passive surveillance. The infant was healthy at 12 months of age.[4]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
(Rheumatoid Arthritis) Adalimumab, Certolizumab Pegol, Etanercept, Infliximab, Tocilizumab
References
- 1.
- Mahadevan U, Robinson C, Bernasko N, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease in pregnancy clinical care pathway: A report from the American Gastroenterological Association IBD Parenthood Project Working Group. Gastroenterology 2019;156:1508-24. [PubMed: 30658060]
- 2.
- Julsgaard M, Mahadevan U, Vestergaard T, et al. Tofacitinib concentrations in plasma and breastmilk of a lactating woman with ulcerative colitis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;8:695-7. [PubMed: 37269871]
- 3.
- Mitrova K, Julsgaard M, Augustijns P, et al. Tofacitinib in pregnancy: Assessing pregnancy and infant outcomes, cord blood and breast milk concentrations. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2024. [PubMed: 38309493]
- 4.
- Ernest-Suarez K, Murguía-Favela LE, Novak KL, et al. Normal infant immunologic assessment and uneventful live rotavirus vaccination despite continuous tofacitinib exposure in utero and during breastfeeding. Crohns Colitis 360 2024;6:otae006. [PMC free article: PMC10841763] [PubMed: 38317692]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Tofacitinib
CAS Registry Number
477600-75-2
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Milk, Human
Antirheumatic Agents
Enzyme Inhibitors
Janus Kinase Inhibitors
JAK Inhibitors
Signal Transduction Inhibitors
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Baricitinib.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Baricitinib.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Nilotinib.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Nilotinib.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Development of selective inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: (R)-3-(3-(Methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-oxopropanenitrile as a JAK1-selective inhibitor.[Bioorg Med Chem. 2018]Development of selective inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: (R)-3-(3-(Methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-oxopropanenitrile as a JAK1-selective inhibitor.Chough C, Joung M, Lee S, Lee J, Kim JH, Kim BM. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 1; 26(8):1495-1510. Epub 2018 Feb 3.
- Review Abrocitinib.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Abrocitinib.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Ruxolitinib.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Ruxolitinib.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Tofacitinib - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Tofacitinib - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
