From: Other signaling pathways that contribute to lymphocyte behavior

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
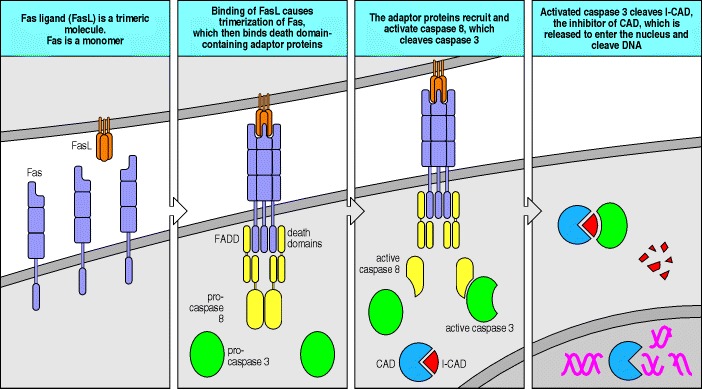
The Fas ligand (FasL) recognized by Fas is a homotrimer, and when it binds it induces the trimerization of Fas. This brings the death domains in the Fas cytoplasmic tails together. A number of adaptor proteins containing death domains bind to the death domains of Fas, in particular the protein FADD, which in turn interacts through a second death domain with the protease caspase 8. Clustered caspase 8 can transactivate, cleaving caspase 8 itself to release an active caspase domain that in turn can activate other caspases. The ensuing caspase cascade culminates in the activation of the caspase-activatable DNase (CAD), which is present in all cells in an inactive cytoplasmic form bound to an inhibitory protein called I-CAD. When I-CAD is broken down by caspases, CAD can enter the nucleus where it cleaves DNA into the 200-base-pair fragments that are characteristic of apoptosis.
From: Other signaling pathways that contribute to lymphocyte behavior

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.