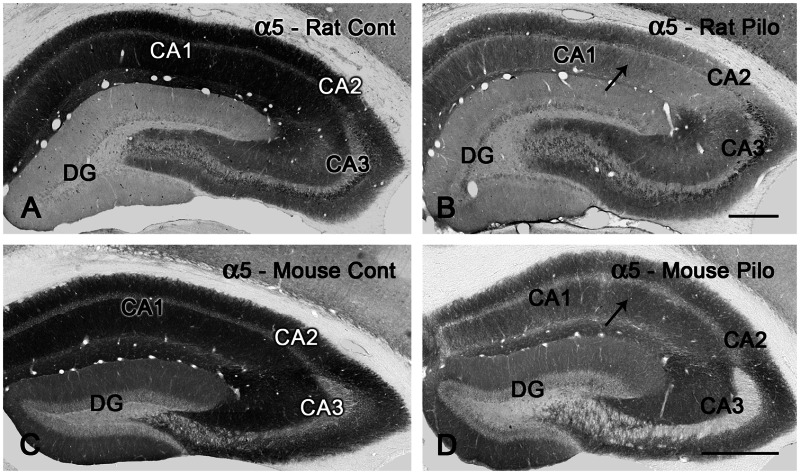
From: Alterations in the Distribution of GABAA Receptors in Epilepsy
All Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies content, except where otherwise noted, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported license, which permits copying, distribution and transmission of the work, provided the original work is properly cited, not used for commercial purposes, nor is altered or transformed.