From: Selectin-binding analysis of tumor cells
Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 Unported license. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
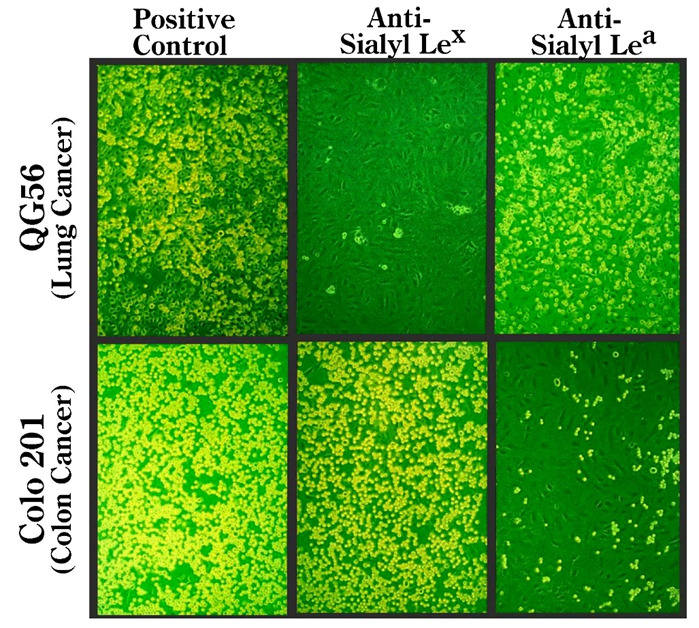
Nonstatic monolayer cell adhesion assay using human cancer cells and recombinant IL-1β-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. QG-56 cells (lung cancer) and Colo201 cells (colon cancer) were treated with anti-sialyl Lewis x (20 μg/mL) or anti-sialyl Lewis a (20 μg/mL) for 30 min before the adhesion experiment. Note that adhesion of QG-56 cells is inhibited by anti-sialyl Lewis x antibody, while that of Colo201 cells is inhibited by anti-sialyl Lewis a antibody.
From: Selectin-binding analysis of tumor cells
Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 Unported license. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...