This is a work of the US government and distributed under the terms of the Public Domain
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
SUMMARY
Background:
3′Azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT) is the most widely used chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of people with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) or positive for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AZT treatment is also given to prevent transmission of HIV from pregnant mothers to children before or during birth. We tested the effects of AZT on the offspring of female mice (genetically modified to be sensitive to cancer induction) where the mothers were given the drug during pregnancy and the pups were given the drug following birth.
Method:
We exposed groups of haploinsufficient C3B6.129F1-Trp53tm1Brd N12 mice by depositing solutions of AZT in a methylcellulose solvent directly into the animals’ stomachs through a tube five times per week for 30 or 45 weeks following birth; in addition, their mothers were exposed to the drug for seven days during pregnancy. Other sets of mothers and pups received only the methylcellulose solvent and served as the control groups. Tissues from 34 organs were examined for every animal.
Results:
Exposure to AZT caused increases in the rates of liver cancer in the male pups after 45 weeks. In addition, there were occurrences of a few malignant lymphomas in both male and female pups exposed to AZT in the 30-week studies.
Conclusions:
We conclude that AZT caused liver cancers in male pups exposed to AZT before and following birth. Malignant lymphomas in male and female pups may have been related to AZT exposure before and following birth.
ABSTRACT
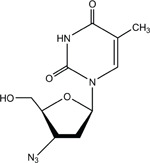
3′-AZIDO-3′-DEOXYTHYMIDINE
CAS No. 30516-87-1
Chemical Formula: C10H13N5O4 Molecular Weight: 267.24
Synonyms: AZT; 3′-azido-2′,3′-dideoxythymidine; azidodeoxythymidine; azidothymidine; 3′-azidothymidine; 3′-deoxy-3′-azidothymidine; 3′-deoxy-(8CI) (9CI); BW A509U; Compound S; ZDV; zidovudine
Trade Name: Retrovir®
Antiviral therapy is essential for treatment and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease in adults and children and to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV during pregnancy and labor. The studies described in this report were designed to determine possible long-term sequelae from 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT) treatment, often used in combination with other antivirals, in preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV. AZT is the most widely used and evaluated chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of persons with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Male and female heterozygous F1 p53+/− mice were exposed, by maternal gavage, to AZT in utero on gestation days (GD) 12 through 18, then administered AZT by gavage from postnatal day (PND) 1 through 30 weeks of age (30-week study), 45 weeks of age (45-week study), or PND 8 (45-week stop-study). Mice in the 0 mg/kg groups received only an aqueous solution containing 0.2% methylcellulose and 0.1% Tween® 80. Mice were dosed once daily until PND 28, then 5 days per week. Genetic toxicology studies were conducted in mouse peripheral blood erythrocytes.
30-Week Study:
Pregnant dams were administered 0 or 240 mg AZT/kg body weight per day on GDs 12 through 18. Groups of 26 or 27 male and 26 or 27 female pups were administered 0 or 120 mg/kg by gavage on PNDs 1 through 10, then 0 or 240 mg/kg until the end of the study. Survival of 240/120/240 mg/kg males was significantly less than that of 0/0/0 mg/kg males. Mean body weights of dosed males and females were less than those of the 0/0/0 mg/kg groups, and absolute kidney weights of dosed males and females were significantly less than those of the 0/0/0 mg/kg groups. Mean cell volume and mean cell hemoglobin in dosed females and mean cell volume in dosed males were significantly increased, suggesting moderately severe macrocytic anemia.
The incidence of malignant lymphoma was increased in male mice administered 240/120/240 mg/kg. The increase was significant when adjusted for litter correlations.
45-Week Study:
Pregnant dams were administered 0, 80, 160, or 240 mg/kg on GDs 12 through 18. Corresponding groups of 27 male and 26 or 27 female pups were administered 0, 40, 80, or 120 mg/kg on PNDs 1 through 10, then 0, 80, 160, or 240 mg/kg until the end of the study. There was no effect of AZT administration on the survival of dosed mice. Mean body weights of dosed males and females were generally less than those of the 0/0/0 mg/kg groups. Absolute brain weights of males and females administered 240/120/240 mg/kg were significantly less than those of the 0/0/0 mg/kg groups. Mean cell volume and mean cell hemoglobin at 160 days were increased in 240/120/240 mg/kg males and females, suggesting moderately severe macrocytic anemia.
The incidences of hepatocellular adenoma occurred with a positive trend in males, and the incidence in the 240/120/240 mg/kg group was significantly increased. In females, there was a positive trend in the incidences of malignant lymphoma, and the increased incidence in the 240/120/240 mg/kg group was significant when adjusted for litter correlations.
45-Week Stop-Study:
Pregnant dams were administered 0 or 240 mg/kg on GDs 12 through 18. Groups of 24 or 25 male and 26 female pups were administered 0 or 40 mg/kg on PNDs 1 through 8; pups were then maintained on study until 45 weeks of age without dosing. There was no effect of AZT administration on the survival of dosed mice. Mean body weights of dosed males were generally less than those of the 0/0 mg/kg group. Absolute, but not relative, brain weights of dosed males and females were significantly less than those of the 0/0 mg/kg groups.
The incidences of hepatocellular adenoma and hepato-cellular adenoma or carcinoma (combined) were slightly increased in 240/40 mg/kg males.
Genetic Toxicology:
Micronucleated normochromatic erythrocyte and reticulocyte frequencies were generally significantly increased relative to the corresponding 0, 0/0, or 0/0/0 mg/kg group values in 1-day-old pups exposed to AZT in utero at 160 or 240 mg/kg, in 10-day-old pups administered 80/40, 160/80, or 240/120 mg/kg, in 28-day-old pups administered 80/40/80, 160/80/160, or 240/120/240 mg/kg, and in 30-week-old mice administered 240/120/240 mg/kg.
Conclusions:
Under the conditions of these gavage studies, there was clear evidence of carcinogenic activity* of AZT in male heterozygous F1 p53+/− mice based on the occurrence of hepatocellular neoplasms (predominantly adenomas) after 45 weeks of administration. The occurrence of malignant lymphoma may have been related to AZT administration for 30 weeks. There was equivocal evidence of carcinogenic activity of AZT in female heterozygous F1 p53+/− mice based on the occurrence of malignant lymphoma after 45 weeks of administration.
Summary of the In Utero/Postnatal Gavage Studies of AZT in C3B6.129F1-Trp53tm1Brd N12 Haploinsufficient Mice
| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Doses in aqueous methylcellulose/Tween® 80 by gavage | ||
| 30-Week Study a | F0: 0 or 240 mg/kg per day | F0: 0 or 240 mg/kg per day |
| F1: 0 or 120/240 mg/kg per day | F1: 0 or 120/240 mg/kg per day | |
| 45-Week Study a | F0: 0, 80, 160, or 240 mg/kg per day | F0: 0, 80, 160, or 240 mg/kg per day |
| F1: 0, 40/80, 80/160, | F1: 0, 40/80, 80/160, | |
| or 120/240 mg/kg per day | or 120/240 mg/kg per day | |
| 45-Week Stop-Study | F0: 0 or 240 mg/kg per day | F0: 0 or 240 mg/kg per day |
| F1: 0 or 40 mg/kg per day postnatal days 1-8 | F1: 0 or 40 mg/kg per day postnatal days 1-8 | |
| Body weights | Dosed groups less than 0 mg/kg groups | Dosed groups less than 0 mg/kg groups, except in 45-week stop-study |
| Survival rates | ||
| 30-Week Study | 27/27, 21/26 | 24/27, 26/26 |
| 45-Week Study | 24/27, 21/27, 27/27, 22/27 | 23/26, 23/27, 24/27, 21/27 |
| 45-Week Stop-Study | 23/24, 22/25 | 25/26, 23/26 |
| Nonneoplastic effects | ||
| 30-Week Study | None | None |
| 45-Week Study | None | None |
| 45-Week Stop-Study | None | None |
| Neoplastic effects | ||
| 30-Week Study | None | None |
| 45-Week Study | Liver: hepatocellular adenoma (3/26, 2/27, 6/27, 9/27) | None |
| 45-Week Stop-Study | Liver: hepatocelluar adenoma (3/24, 5/25); hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma (3/24, 7/25) | None |
| Equivocal findings | ||
| 30-Week Study | Malignant lymphoma: (0/27, 3/26) | None |
| 45-Week Study | None | Malignant lymphoma: (0/26, 0/27, 1/27, 3/27) |
| 45-Week Stop-Study | None | None |
| Level of evidence of carcinogenic activity | Clear evidence | Equivocal evidence |
| Genetic toxicology | ||
| Micronucleated normochromatic erythrocytes and reticulocytes | ||
| 30-Week Study | Positive in males and females at 30 weeks of age | |
| 45-Week Study | Positive in males and females at PND 1, PND 10, and PND 28 | |
- a
Pups in the 30- and 45-week studies were administered AZT doses that were half that of the maternal dose on post natal days 1 through 10. Pup doses were the same as maternal doses from post natal day 11 until the end of the studies.
- *
Explanation of Levels of Evidence of Carcinogenic Activity is on page 10. A summary of the Peer Review Panel comments and the public discussion on this Report appears on page 12.
Contents
- FOREWORD
- CONTRIBUTORS
- EXPLANATION OF LEVELS OF EVIDENCE OF CARCINOGENIC ACTIVITY
- NATIONAL TOXICOLOGY PROGRAM TECHNICAL REPORTS PEER REVIEW PANEL
- SUMMARY OF PEER REVIEW PANEL COMMENTS
- INTRODUCTION
- MATERIALS AND METHODS
- RESULTS
- DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS
- REFERENCES
- APPENDIX A. SUMMARY OF LESIONS IN HETEROZYGOUS F1 p53+/− MICE IN THE IN UTERO/POSTNATAL GAVAGE STUDIES OF AZT
- APPENDIX B. GENETIC TOXICOLOGY
- APPENDIX C. CLINICAL PATHOLOGY RESULTS
- APPENDIX D. BODY WEIGHT ANALYSES
- APPENDIX E. ORGAN WEIGHTS AND ORGAN-WEIGHT-TO-BODY-WEIGHT RATIOS
- APPENDIX F. CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND DOSE FORMULATION STUDIES
- APPENDIX G. LITTER EFFECTS ON SURVIVAL, BODY WEIGHT, AND PATHOLOGY
- APPENDIX H. LITTER SUCCESS AND SURVIVAL
- APPENDIX I. HISTORICAL CONTROL INCIDENCES
About the Series
- NLM CatalogRelated NLM Catalog Entries
- Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Mixtures of 3'-Azido-3'-Deoxythymidine (AZT), Lamivudine (3TC), and Nevirapine (NVP) (CAS Nos. 30516-87-1, 134678-17-4, 129618-40-2) in Genetically Modified C3B6.129F1-Trp53(tm1Brd) N12 Haploinsufficient Mice (in utero and postnatal gavage studies).[Natl Toxicol Program Genet Mod...]Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Mixtures of 3'-Azido-3'-Deoxythymidine (AZT), Lamivudine (3TC), and Nevirapine (NVP) (CAS Nos. 30516-87-1, 134678-17-4, 129618-40-2) in Genetically Modified C3B6.129F1-Trp53(tm1Brd) N12 Haploinsufficient Mice (in utero and postnatal gavage studies).National Toxicology Program. Natl Toxicol Program Genet Modif Model Rep. 2013 Oct; (16):1-236.
- NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of AZT (CAS No. 30516-87-1) and AZT/alpha-Interferon A/D B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).[Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep ...]NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of AZT (CAS No. 30516-87-1) and AZT/alpha-Interferon A/D B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).National Toxicology Program. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1999 Feb; 469:1-361.
- Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of transplacental AZT (Cas No. 30516-87-1) in Swiss (CD-1®) mice (in utero studies).[Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep ...]Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of transplacental AZT (Cas No. 30516-87-1) in Swiss (CD-1®) mice (in utero studies).National Toxicology Program. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2006 Jun; (522):1-184.
- Review Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).[Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep ...]Review Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010 Sep; (560):1, 7-31,33-171 passim.
- Review NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Modified One-Generation Study of 2-Ethylhexyl p-Methoxycinnamate (CASRN 5466-77-3) Administered in Feed to Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley(®) SD(®)) Rats with Prenatal, Reproductive Performance, and Subchronic Assessments in F(1) Offspring: DART Report 06[ 2022]Review NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Modified One-Generation Study of 2-Ethylhexyl p-Methoxycinnamate (CASRN 5466-77-3) Administered in Feed to Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley(®) SD(®)) Rats with Prenatal, Reproductive Performance, and Subchronic Assessments in F(1) Offspring: DART Report 06National Toxicology Program. 2022 Jun
- NTP Genetically Modified Model Report on the Toxicology and Carcinogenicity Stud...NTP Genetically Modified Model Report on the Toxicology and Carcinogenicity Studies of 3’-Azido-3’-Deoxythymidine (CASRN 30516-87-1) in Genetically Modified C3B6.129F1-Trp53tm1Brd N12 Haploinsufficient Mice (In Utero and Postnatal Gavage Study)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
