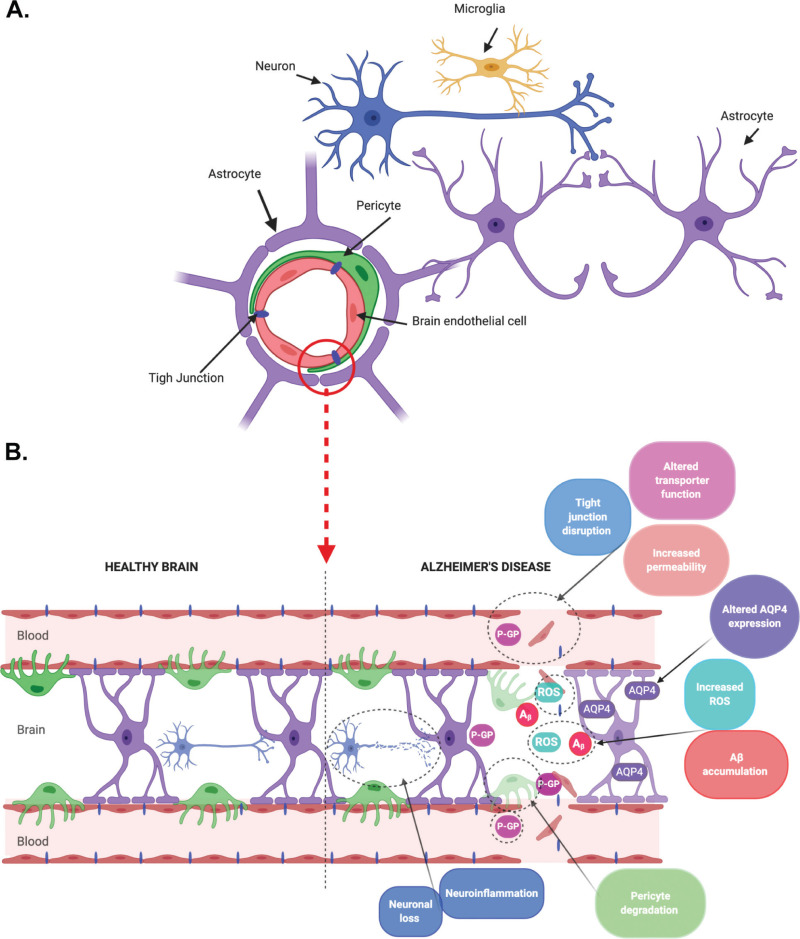
From: Chapter 7, Modeling the Blood–Brain Barrier to Understand Drug Delivery in Alzheimer’s Disease

Licence: This open access article is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.