This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Show detailsContinuing Education Activity
Necrotizing (malignant) otitis externa (NOE) is a severe infection that affects the external auditory canal, skull base, and temporal bone. This condition can result in significant complications if not promptly diagnosed and treated. This activity provides an overview of the etiology, clinical presentation, potential complications, and treatment options for NOE. Furthermore, this activity also highlights the crucial role of the interprofessional healthcare team in treating patients with NOE.
Objectives:
- Identify the clinical features and risk factors associated with necrotizing otitis externa.
- Implement appropriate diagnostic measures, including imaging studies and microbiological tests, to confirm the diagnosis of necrotizing otitis externa.
- Apply evidence-based treatment strategies, which may include antimicrobial therapy, surgical interventions, and adjunctive measures, to manage necrotizing otitis externa.
- Collaborate with an interprofessional healthcare team, including otolaryngologists, radiologists, and infectious disease specialists, for comprehensive care.
Introduction
Necrotizing (malignant) otitis externa (NOE) is not cancerous, but it can rapidly spread in a patient's body and has been historically associated with a high mortality rate, hence its name.[1][2] Toulmouche reported the initial case of malignant otitis external (MOE) in 1838, and MOE was subsequently introduced by Chandler in 1968 due to the high mortality rate associated with the infection during that period.[3] In recent times, MOE has come to be known as necrotizing otitis externa (NOE), a term that more accurately and distinctly characterizes the aggressive and pathological nature of the condition.[4]
NOE is a severe and potentially life-threatening infection that originates in the external auditory canal (EAC). The most common cause of NOE is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a gram-negative bacterium. Typically, these infections predominantly affect older patients, many of whom have diabetes mellitus.[5] NOE primarily targets the EAC, skull base, and temporal bone, potentially involving the stylomastoid and jugular foramina. Infection and inflammation originating from the EAC can propagate through various anatomical pathways, reaching the mastoid process in the posterior direction, the temporomandibular joint, the parotid gland, and cervicofacial spaces anteriorly, or the skull base medially.[6]
This infection essentially advances from a basic otitis externa, progressing to cellulitis, then chondritis, and ultimately extending to the temporal bone, resulting in periostitis and ultimately culminating in osteomyelitis. NOE can result in serious complications, including the development of cranial neuropathies, brain abscesses, meningitis, and dural venous sinus thromboses.[7] Therefore, healthcare practitioners should maintain a heightened suspicion level for NOE to identify and initiate treatment promptly.[8][9]
Etiology
The predominant causative organism of NOE is the gram-negative bacterium P aeruginosa, which is ubiquitous in water and is particularly prevalent in patients with diabetes mellitus.[5] Other gram-negative bacteria include Proteus spp and Klebsiella spp. Gram-positive bacteria that have been isolated include Staphylococcus aureus, with an increasing presence of methicillin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) strains, and S epidermidis.[5] Fungi, specifically Aspergillus spp and Candida spp, have also been identified as potential culprits for NOE.[10][11][12][13]
Most individuals who develop NOE are older adults, predominantly males, who almost invariably have an underlying medical condition that makes them susceptible to immunosuppression. The primary risk factor for immunosuppression in these patients often involves some form of glucose dysregulation or established diabetes mellitus. Other predisposing risk factors include HIV, malignancies, and chemotherapy.[5] Diabetes mellitus contributes to NOE by inducing small-vessel vasculopathy and immune dysfunction, particularly in cases of poorly controlled glucose levels. Furthermore, the cerumen found in the external ear canal of patients with diabetes mellitus often exhibits an elevated pH and reduced lysozyme concentrations compared to normal, rendering the EAC more susceptible to infection. Although there may not be a difference in the prevalence of NOE between patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, individuals with type 1 diabetes typically experience more adverse outcomes.[14]
Patients with immunosuppression due to HIV or other non-diabetic factors are more likely to develop NOE at a younger age than those with diabetes.[15] Furthermore, individuals with HIV are less prone to Pseudomonas infections but may have a higher risk of fungal infections. In addition, they may not exhibit granulation tissue in the EAC upon physical examination. Generally, these patients experience more unfavorable outcomes than those with diabetes.[16]
Epidemiology
NOE is a relatively rare condition, and its incidence rates are likely underestimated, failing to represent the disease burden accurately. Nevertheless, incidence rates can vary in different local or national publications,[17][18] with a recent systematic review indicating a range between 0.221 and 1.19 cases per 100,000 patients.[5] These statistics are believed to have increased more recently due to the aging population, a higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus, and increased NOE diagnoses.[5][17]
Although NOE has been documented across all age groups, it is most prevalent among individuals older than 60, often coinciding with some form of immunosuppression, which places them at a heightened risk for this condition.[5] The most frequent cause of immunosuppression observed in patients with NOE is diabetes mellitus, followed by other factors such as malignancy, chemotherapy, and HIV infection. Males exhibit a higher likelihood of being affected by NOE than females. However, due to the limited sample sizes reported in studies and substantial variability, it is challenging to determine the precise incidence.[17][19][20] Although the diagnosis of NOE is infrequent in pediatric patients, it can still manifest in young individuals who are neither diabetic nor immunocompromised.[21][22]
Pathophysiology
NOE typically initiates as a simple otitis externa (see Image. Otitis Externa), which is an infection of the soft tissue in the auricle and EAC. From this point, however, NOE subsequently extends through fascial planes and venous sinuses, in contrast to otitis media, which typically follows the pneumatized cavities of the temporal bone. Infectious spread results in bony erosion and the invasion of nearby tissues, potentially leading to the involvement of the skull base, cranial nerves, and intracranial structures as the condition progresses.[23] The infection will commonly spread through the osteocartilaginous junction of the EAC and the fissures of Santorini, which are openings within the cartilage on the lateral aspect of the EAC. Subsequently, the stylomastoid and jugular foramina, as well as hypoglossal canals, become vulnerable.
Infections occurring in these regions can result in cranial neuropathies, presenting with clinical symptoms such as facial weakness, dysphagia, hoarseness, shoulder weakness, and tongue weakness. If the infection progresses medially, it can involve the cavernous sinus, leading to palsy of the trigeminal and abducens nerves. This development indicates a poor prognosis due to the extensive disease involvement required to affect these nerves. The infection spread into the infratemporal fossa results in the invasion of retrocondylar and parapharyngeal fats, the temporomandibular joint, and the muscles responsible for mastication.[24]
The patterns of the NOE spread can be summarized as mentioned below.
Anterior: NOE extends anteriorly toward the muscles of mastication, condylar bone marrow, parotid gland, stylomastoid foramen and facial nerve, temporal fossa, and temporomandibular joint.
Medial: In the medial direction, NOE advances toward the parapharyngeal fat, nasopharyngeal muscle, glossopharyngeal, vagal, and spinal accessory nerves, sphenoid bone, clivus, jugular foramen, and petrous apex.
Intracranial: Intracranial spread is suggested when there is dural enhancement within the intracranial compartment, which may indicate the involvement of the sigmoid sinus, jugular vein, internal carotid artery, jugular fossa, cavernous sinus, or the dura.
Posterior: In the posterior direction, NOE extends to the mastoid process.[25]
Histopathology
The EAC is divided into cartilaginous and bony portions, with the cartilaginous portion comprising the lateral one-third of the canal. Within the cartilaginous portion, a layer of stratified squamous epithelium exists, covering the underlying connective tissue, perichondrium, and cartilage. In the osseous canal, a thick fibrous tissue is found deep within the squamous epithelium.
In patients with NOE, a biopsy of the external auditory canal may reveal ulceration and epithelial loss, with bacteria and inflammation extending into the dense fibrous tissue. In areas where the epithelium remains intact, reactive changes can range from mild hyperplasia to notable pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Both acute and chronic inflammation, including abscess formation, are frequently observed. In biopsy samples taken from the cartilaginous canal, inflammation often extends into the apopilosebaceous units. Although reactive capillary proliferation may be evident within the granulation tissue, notably, chronic inflammation with granuloma formation is not typically associated with NOE.
Microorganisms can be identified by tissue staining or culture; however, in cases where no organism is identified, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing may offer additional diagnostic information.[6] Upon identification of organisms, it is crucial to conduct antimicrobial susceptibility testing to ascertain the effectiveness of specific antimicrobials. This information is critical in determining the appropriate treatment and customizing it based on the susceptibility results. This approach is particularly significant because bacterial resistance to antimicrobials commonly used to treat NOE, such as fluoroquinolones for addressing P aeruginosa, is rising.[26]
Distinguishing very well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma from NOE can be challenging when pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is present. Therefore, identifying NOE should not rule out the possibility of malignancy, as these conditions can coexist.[27]
History and Physical
The prototypical patient with NOE commonly experiences unrelenting otalgia, especially at night, and otorrhea that does not improve with usual topical antimicrobial treatments for otitis externa. Cranial neuropathies can be observed in patients, and facial palsy has been reported in 21% of cases in a recent systematic review.[5] During examination, physical findings typically reveal a painful, erythematous, and edematous auricle, and an EAC often exhibits intense tenderness in the region between the mastoid tip and the mandibular ramus. For patients with Pseudomonas NOE, the presence of granulation tissue at the bony-cartilaginous junction of the external auditory canal is considered pathognomonic. Fever occurrences are rare, and there are few other abnormalities in vital signs.[5]
The diagnosis of NOE can be established using the schema outlined by Cohen and Friedman, which comprises major (obligatory) and minor (occasional) criteria as mentioned below.
Major (Obligatory) Criteria
- Pain, often disproportionate to physical examination
- Edema
- Exudate
- Granulation tissue observed in the EAC
- Microabscess, when surgical intervention is performed
- A positive technetium-99 methylene diphosphate (Tc-99m) bone scan
- Lack of improvement with local treatment for more than 1 week
Minor (Occasional) Criteria
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cranial nerve involvement
- Positive radiograph
- Debilitating condition
- Older age
For a diagnosis of NOE, all major criteria must be met, as the presence of only minor criteria is insufficient for the diagnosis.[28][29]
Healthcare providers should perform a cranial nerve examination, as cranial neuropathies are frequently encountered in NOE cases. The examiner should pay particular attention to assessing the function of the facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, and hypoglossal nerves. The facial nerve is frequently affected among cranial nerves, primarily due to its proximity to the posterior aspect of the bony EAC. More rarely, the abducens and trigeminal nerves may also be affected, which often signifies a poor prognosis.[30] Furthermore, a mental status examination should be conducted, and if abnormalities are detected, it may indicate intracranial involvement.[31]
Evaluation
Laboratory Studies
Blood: Blood tests may reveal a normal or slightly elevated white blood cell count, but a left shift is not a common finding in NOE.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP): Inflammatory markers are typically elevated in these patients and can be utilized to monitor the response to antimicrobial therapy. Mean ESR and CRP values in patients with NOE are 65.5 mm/h and 25.3 mg/dL, respectively.[5] After confirming the diagnosis, monitoring ESR and CRP levels regularly is essential until they have normalized. Typically, ESR starts to decline within 2 weeks of initiating treatment.[32]
Blood glucose: Patients with diabetes should undergo blood glucose testing to assess their baseline, as NOE can affect the baseline glucose intolerance. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain strict glucose control during the treatment of NOE in diabetic patients. Furthermore, individuals without a known history of diabetes should undergo diabetes evaluation after the diagnosis of NOE.[33]
Culture and sensitivities from the EAC: Otorrhea should ideally be cultured before initiating antimicrobial treatment. Tissue sampling has shown significant value in selecting the appropriate antimicrobial treatment, particularly in cases of recurrent otitis externa. Obtaining a biopsy of the EAC is essential for this purpose and to rule out other potential causes, such as malignancy or cholesteatoma.[32]
Imaging Techniques
Computed tomography (CT): CT scanning is advantageous for detecting bony erosions and demineralization, especially in the EAC. CT findings often include the obliteration of fat planes in the subtemporal area and the destruction of the bony cortex of the mastoid.[34]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI surpasses CT in precisely determining the anatomical location and extent of invasion into surrounding soft tissues, especially concerning cranial nerves. Furthermore, MRI more effectively assesses intracranial complications, such as thrombosis and intracranial spread. Monitoring treatment progress and determining prognosis can pose challenges with CT and MRI scans because they may not always effectively distinguish between active inflammation and resolving infection.
Technetium-99 methylene diphosphate (Tc-99m) bone scan: Tc-99m scan is beneficial for the initial evaluation and diagnosis of osteomyelitis. However, this scanning technique is unsuitable for monitoring the progress of resolution because bone remodeling persists for several months after clinical recovery, and thus, the scan will continue yielding positive results. As Tc-99m scanning lacks anatomical precision, combining this radionuclide with single-photon emission CT (SPECT) along with CT or MRI delivers more precise and informative imaging.
Gallium-67 (Ga-67) citrate leukocyte scan: Ga-67 is a valuable method for monitoring the resolution of NOE because it labels white blood cells, providing a more detailed tracking of inflammatory processes than Tc-99m. Visual confirmation of reduced Ga-67 uptake typically signifies resolving infection. However, a lesion-to-non-lesion ratio of approximately 1.0 may indicate the resolution of NOE, even if there appears to be increased Ga-67 uptake.[35] Similar to Tc-99m, using Ga-67 for SPECT scanning may improve the accuracy of assessing the progress of NOE resolution.[36]
Indium-111 leukocyte scan (In-III): In-111 is an alternative to Ga-67 scanning, and it uses labeled white blood cells to monitor inflammation and, consequently, the progress of disease resolution. Similar to Ga-67, In-111 may yield false-positive results if inflammation persists after the resolution of the infection. Enhanced diagnostic accuracy can be achieved by combining In-111 and Tc-99m in a single scan.[37]
Positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT): Scanning with 18-fluorodeoxyglucose combined with CT allows for detecting metabolically active tissues, making it an ideal test for identifying and monitoring malignancies or localized infections. Due to its widespread use in oncological surveillance, PET/CT is readily available at many hospitals, and most radiologists are experienced in interpreting these studies. Although no extensive studies have directly compared PET/CT to Tc-99m or Ga-67 scintigraphy for diagnosing or monitoring NOE, its inherent advantages may allow it to supplant these older nuclear medicine scanning techniques.[38]
Treatment / Management
Treatment Overview
- Treatment for NOE is multimodal and can include systemic and local antimicrobial therapy, meticulous glucose control, aural hygiene, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.[39][40][41] Surgery is considered when non-surgical treatments have proven ineffective and typically involves procedures such as local debridement, abscess drainage, or removal of a bony sequestrum.
Antimicrobial Therapy
- Topical antibiotic drops, including ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone, and polymyxin B/neomycin/hydrocortisone, are commonly used to treat uncomplicated otitis externa. However, they are typically inadequate for managing NOE and may not offer additional benefits when used alongside systemic antibiotics.
- Before initiating antimicrobial therapy, gathering microbiological and tissue samples for bacterial and fungal cultures is crucial to identify the specific organism causing the infection. Furthermore, requesting antimicrobial susceptibility testing is essential to inform and customize antimicrobial therapy as needed.
- Oral ciprofloxacin can be prescribed in outpatient settings for cases that lack complications, such as cranial nerve involvement, diabetes, or the necessity for admission to manage pain. However, in cases where complications arise and swallowing pills becomes challenging, a switch to intravenous ciprofloxacin may be necessary.
- Patients admitted to the hospital with more severe disease or requiring parenteral therapy may initiate treatment with intravenous ciprofloxacin. They can later switch to oral administration upon hospital discharge. Alternatively, the patients may receive intravenous antibiotics through a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) as outpatient care.
- Systemic antimicrobials are the recommended treatment approach for NOE. When selecting initial empirical therapy, it is advisable to use antimicrobials with antipseudomonal activity, as P aeruginosa is the predominant cause of NOE. Typically, fluoroquinolones are preferred due to their excellent tissue penetration and the convenience of oral administration, which is particularly beneficial in outpatient settings.
- The effectiveness of fluoroquinolones may be compromised by the increasing antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas spp to this class of antimicrobials, primarily driven by their widespread global use. Therefore, it is essential to consider the presence of resistant organisms when deciding on the empirical treatment for NOE.
- Other antipseudomonal antimicrobials may be considered in situations with known resistance to fluoroquinolones.[19][26] When fluoroquinolone resistance is detected, empirical antimicrobial options with activity against Pseudomonas spp include ceftazidime, aztreonam, or ticarcillin/clavulanate, either alone or in combination with an aminoglycoside such as gentamicin or tobramycin. In such cases, empirical treatment should be initiated, and therapy should be tailored based on microbiological culture and susceptibility results to improve outcomes and prevent delays.[26]
- Although P aeruginosa is the most common causative organism in NOE, other pathogens have also been identified. Antibiotic selection should be based on the specific organism identified through culture. In cases where empirical therapy is necessary, a broader-spectrum antimicrobial regimen may be required to cover a range of bacteria, such as gram-negative and gram-positive, and fungal pathogens. For fungal infections, the primary treatment is usually amphotericin B. However, itraconazole and voriconazole are also effective alternatives with fewer adverse effects.[42]
- The duration of treatment will depend on the response to therapy. Patients should be reevaluated every 4 to 6 weeks during treatment using a Ga-67 scan. Even after the infection has resolved, patients at high risk should undergo periodic reassessment for up to a year, as recurrence can occur.
- Systemic antibiotic treatment should be discontinued one week after a normal Ga-67 scan, provided that inflammatory markers have also normalized.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Surgical Therapy
- Surgical management is reserved for patients whose medical therapy has failed to cure the disease. Surgical therapy includes local debridement, removal of bony sequestra, and abscess drainage. Facial nerve decompression is not indicated when patients have facial paralysis in NOE. Although surgery has not been shown to improve outcomes, it is generally utilized in patients with more severe diseases.[43][44]
Differential Diagnosis
NOE can be misdiagnosed as several other conditions, including, but not limited to, the following conditions:
- Localized otitis externa
- Acute diffuse otitis externa
- Chronic otitis externa
- Carcinoma of the ear canal
- Aspergillus skull-base osteomyelitis [33]
Staging
In 2007, Peleg et al published a stratification schema categorizing NOE patients into severe and non-severe cases. Severe cases are assigned 3 to 4 points, whereas non-severe cases receive scores ranging from 0 to 2.[14] Severe cases are more likely to have prolonged or complicated clinical courses.
Peleg Stratification
In this schema, 1 point is provided for each of the following criteria:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Temporal bone involvement on CT scan
- Skull base involvement on CT scan
- Temporomandibular joint involvement on CT scan
The Carney Clinicopathological Staging System
This system provides greater detail and complexity than the Peleg schema and more closely resembles the various stages of malignancy, as mentioned below.[12]
- Stage 1: Clinical evidence of NOE with inflammation of soft tissues extending beyond the external auditory meatus and a normal Tc-99m bone scan.
- Stage 2: Clinical evidence of NOE with inflammation of soft tissues extending beyond the external auditory meatus and a positive Tc-99m bone scan.
- Stage 3: Clinical evidence of NOE with inflammation of soft tissues extending beyond the external auditory meatus, a positive Tc-99m bone scan, and cranial nerve involvement.
- Stage 3a: Single cranial nerve palsy.
- Stage 3b: Multiple cranial nerve palsies.
- Stage 4: Meningitis, dural venous sinus thrombosis, empyema, and brain abscess.
Prognosis
Several factors can influence the duration and prognosis of NOE. In diabetic patients, it is crucial to consider the duration of the patient's diabetes and the level of diabetes control. Laboratory values, such as elevated ESR and CRP levels, along with significant imaging findings, can indicate a more unfavorable prognosis for NOE.[44] Older patients are at a greater risk of developing complications and experiencing higher mortality rates than younger patients.[45]
Patients who exhibit any of the following factors have poorer prognoses of NOE than those who do not:[46]
- Facial nerve involvement
- Additional cranial nerve involvement
- Non-cranial nerve neurological involvement
- Extensive granulation or edema in the EAC
- Bilateral symptoms
- Aspergillus species as the causative organism
Recurrence
Notably, the recurrence rate of NOE is exceptionally high, reaching from 15% to 20%. Recurrence should be suspected if there is a rise in the ESR.[31] As NOE can recur up to 1 year after treatment, patients should be monitored regularly for up to 1 year before being considered cured.[22]
Mortality
Due to contemporary diagnostic and treatment modalities, the mortality rate for NOE has decreased significantly from a historical range of 50% to 60% to the current range of 10% to 20%.[47]
Complications
Complications of NOE occur due to the invasion of surrounding structures, primarily cranial nerves. Although the facial nerve is the most frequently affected, other nerves can also be involved, including the glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, hypoglossal, trigeminal, and abducens nerves.[30] Skull base osteomyelitis occurs when the infection extends beyond the temporal bone and spreads to the sphenoid bone, occipital bone, or clivus.[24] Intracranial involvement may manifest with a range of symptoms—from mild confusion to more severe conditions, including meningitis, venous sinus thrombosis, or even death.[31]
Consultations
NOE is typically managed by an otolaryngologist or head and neck surgeon, regardless of whether surgical intervention is needed. Infectious disease specialists should also be consulted to assist in selecting the appropriate antibiotic treatment, particularly due to the rising incidence of antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas spp and other bacteria, which can render empirical treatment ineffective.[5][19] Internal medicine consultation may also be essential, especially for achieving tight glycemic control and managing comorbidities in older or less healthy patients.[44]
Deterrence and Patient Education
Patients should be educated about the implications of NOE and how to address the risk factors that could predispose them to developing or prolonging this infection. Maintaining tight glycemic control is an effective measure for reducing the risk of developing NOE and lessening the severity of the disease.[44] Patients should refrain from engaging in activities and being in environments that can harbor contact with pathogenic bacteria, such as Pseudomonas spp. For example, precautions should be taken to avoid the proliferation of bacteria in otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, especially in hot and humid environments.[9]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
NOE is a rapidly progressing infection that can result in numerous severe complications. Therefore, a team-based approach should be utilized when caring for these patients to manage the infection and enhance patient outcomes effectively. An interprofessional team of healthcare providers, including an otolaryngologist, radiologist, infectious disease specialist, microbiologist, primary care physician, and endocrinologist, should collaborate in caring for patients with NOE. This collaborative approach can enhance patient outcomes by effectively addressing both the infection and the patient's coexisting health conditions, enabling the correct and prompt management of the infection and mitigating the risk factors that make patients susceptible to this condition.[36][19][44][48][21]
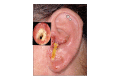
Figure
Otitis Externa. This image shows an inflamed external auditory canal with serous fluid on the tragus, auricular lobule, and antitragus, and purulent material within the canal. Courtesy of S Bhimji, MD
References
- 1.
- Dabholkar JP, Sheth A. Malignant otitis externa. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001 Jan;53(1):55-6. [PMC free article: PMC3450864] [PubMed: 23119754]
- 2.
- Treviño González JL, Reyes Suárez LL, Hernández de León JE. Malignant otitis externa: An updated review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021 Mar-Apr;42(2):102894. [PubMed: 33429178]
- 3.
- Su N, Syed I, Garth R. Skull based osteomyelitis due to postsurgery malignant otitis externa presenting as stroke. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 May 24;2011 [PMC free article: PMC3105569] [PubMed: 22696765]
- 4.
- Hasnaoui M, Ben Mabrouk A, Chelli J, Larbi Ammari F, Lahmar R, Toumi A, Mighri K. Necrotising otitis externa: A single centre experience. J Otol. 2021 Jan;16(1):22-26. [PMC free article: PMC7814081] [PubMed: 33505446]
- 5.
- Takata J, Hopkins M, Alexander V, Bannister O, Dalton L, Harrison L, Groves E, Kanona H, Jones GL, Mohammed H, Andersson MI, Hodgson SH. Systematic review of the diagnosis and management of necrotising otitis externa: Highlighting the need for high-quality research. Clin Otolaryngol. 2023 May;48(3):381-394. [PubMed: 36759416]
- 6.
- Magliocca KR, Vivas EX, Griffith CC. Idiopathic, Infectious and Reactive Lesions of the Ear and Temporal Bone. Head Neck Pathol. 2018 Sep;12(3):328-349. [PMC free article: PMC6081288] [PubMed: 30069844]
- 7.
- Handzel O, Halperin D. Necrotizing (malignant) external otitis. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Jul 15;68(2):309-12. [PubMed: 12892351]
- 8.
- Karaman E, Yilmaz M, Ibrahimov M, Haciyev Y, Enver O. Malignant otitis externa. J Craniofac Surg. 2012 Nov;23(6):1748-51. [PubMed: 23147298]
- 9.
- Nadol JB. Histopathology of Pseudomonas osteomyelitis of the temporal bone starting as malignant external otitis. Am J Otolaryngol. 1980 Nov;1(5):359-71. [PubMed: 7457757]
- 10.
- Chaudhary HA, Ibrahim WH, Yousaf Z, Abubeker IY, Kartha A. Fungal Malignant Otitis Externa Involves a Cascade of Complications Culminating in Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Maxillary Artery: A Case Report. Am J Case Rep. 2019 Apr 21;20:562-566. [PMC free article: PMC6489412] [PubMed: 31005959]
- 11.
- Mion M, Bovo R, Marchese-Ragona R, Martini A. Outcome predictors of treatment effectiveness for fungal malignant external otitis: a systematic review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2015 Oct;35(5):307-13. [PMC free article: PMC4720925] [PubMed: 26824911]
- 12.
- Tsilivigkos C, Avramidis K, Ferekidis E, Doupis J. Malignant External Otitis: What the Diabetes Specialist Should Know-A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2023 Apr;14(4):629-638. [PMC free article: PMC10064349] [PubMed: 36897495]
- 13.
- McCarty Walsh E, Hanson MB. Fungal Infections of the External Auditory Canal and Emerging Pathogens. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2023 Oct;56(5):909-918. [PubMed: 37553272]
- 14.
- Peleg U, Perez R, Raveh D, Berelowitz D, Cohen D. Stratification for malignant external otitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007 Aug;137(2):301-5. [PubMed: 17666260]
- 15.
- Martel J, Duclos JY, Darrouzet V, Guyot M, Bébéar JP. [Malignant or necrotizing otitis externa: experience in 22 cases]. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 2000 Nov;117(5):291. [PubMed: 11084403]
- 16.
- Walton J, Coulson C. Fungal malignant otitis externa with facial nerve palsy: tissue biopsy AIDS diagnosis. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2014;2014:192318. [PMC free article: PMC3933303] [PubMed: 24649388]
- 17.
- Chawdhary G, Liow N, Democratis J, Whiteside O. Necrotising (malignant) otitis externa in the UK: a growing problem. Review of five cases and analysis of national Hospital Episode Statistics trends. J Laryngol Otol. 2015 Jun;129(6):600-3. [PubMed: 25990028]
- 18.
- Hutson KH, Watson GJ. Malignant otitis externa, an increasing burden in the twenty-first century: review of cases in a UK teaching hospital, with a proposed algorithm for diagnosis and management. J Laryngol Otol. 2019 May;133(5):356-362. [PubMed: 30975233]
- 19.
- Rubin Grandis J, Branstetter BF, Yu VL. The changing face of malignant (necrotising) external otitis: clinical, radiological, and anatomic correlations. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004 Jan;4(1):34-9. [PubMed: 14720566]
- 20.
- Mills R. Malignant otitis externa. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986 Feb 15;292(6518):429-30. [PMC free article: PMC1339416] [PubMed: 3081109]
- 21.
- Chen JC, Yeh CF, Shiao AS, Tu TY. Temporal bone osteomyelitis: the relationship with malignant otitis externa, the diagnostic dilemma, and changing trends. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:591714. [PMC free article: PMC4052568] [PubMed: 24963511]
- 22.
- Wiegand S, Berner R, Schneider A, Lundershausen E, Dietz A. Otitis Externa. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Mar 29;116(13):224-234. [PMC free article: PMC6522672] [PubMed: 31064650]
- 23.
- Sreepada GS, Kwartler JA. Skull base osteomyelitis secondary to malignant otitis externa. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003 Oct;11(5):316-23. [PubMed: 14502060]
- 24.
- van Kroonenburgh AMJL, van der Meer WL, Bothof RJP, van Tilburg M, van Tongeren J, Postma AA. Advanced Imaging Techniques in Skull Base Osteomyelitis Due to Malignant Otitis Externa. Curr Radiol Rep. 2018;6(1):3. [PMC free article: PMC5778178] [PubMed: 29416952]
- 25.
- Kwon BJ, Han MH, Oh SH, Song JJ, Chang KH. MRI findings and spreading patterns of necrotizing external otitis: is a poor outcome predictable? Clin Radiol. 2006 Jun;61(6):495-504. [PubMed: 16713420]
- 26.
- Tamma PD, Aitken SL, Bonomo RA, Mathers AJ, van Duin D, Clancy CJ. Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 18; [PubMed: 37463564]
- 27.
- Mattucci KF, Setzen M, Galantich P. Necrotizing otitis externa occurring concurrently with epidermoid carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 1986 Mar;96(3):264-6. [PubMed: 3951301]
- 28.
- Cohen D, Friedman P. The diagnostic criteria of malignant external otitis. J Laryngol Otol. 1987 Mar;101(3):216-21. [PubMed: 3106547]
- 29.
- Illing E, Zolotar M, Ross E, Olaleye O, Molony N. Malignant otitis externa with skull base osteomyelitis. J Surg Case Rep. 2011 May 01;2011(5):6. [PMC free article: PMC3649245] [PubMed: 24950586]
- 30.
- Mani N, Sudhoff H, Rajagopal S, Moffat D, Axon PR. Cranial nerve involvement in malignant external otitis: implications for clinical outcome. Laryngoscope. 2007 May;117(5):907-10. [PubMed: 17473694]
- 31.
- Manso MC, Rodeia SC, Rodrigues S, Cavilhas P, Domingos R. Malignant Otitis Externa and Stroke. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2016;3(4):000387. [PMC free article: PMC6346865] [PubMed: 30755871]
- 32.
- McLaren O, Potter C. Scedosporium apiospermum: a rare cause of malignant otitis externa. BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Sep 09;2016 [PMC free article: PMC5020719] [PubMed: 27613266]
- 33.
- Leahy TW, Sader C. A rare case of bilateral malignant otitis externa and osteomyelitis with lower cranial nerve sequelae. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 May 12;2011 [PMC free article: PMC3094778] [PubMed: 22696730]
- 34.
- Curtin HD, Wolfe P, May M. Malignant external otitis: CT evaluation. Radiology. 1982 Nov;145(2):383-8. [PubMed: 7134442]
- 35.
- Stokkel MP, Takes RP, van Eck-Smit BL, Baatenburg de Jong RJ. The value of quantitative gallium-67 single-photon emission tomography in the clinical management of malignant external otitis. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997 Nov;24(11):1429-32. [PubMed: 9371879]
- 36.
- Okpala NC, Siraj QH, Nilssen E, Pringle M. Radiological and radionuclide investigation of malignant otitis externa. J Laryngol Otol. 2005 Jan;119(1):71-5. [PubMed: 15807974]
- 37.
- Weber PC, Seabold JE, Graham SM, Hoffmann HH, Simonson TM, Thompson BH. Evaluation of temporal and facial osteomyelitis by simultaneous In-WBC/Tc-99m-MDP bone SPECT scintigraphy and computed tomography scan. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995 Jul;113(1):36-41. [PubMed: 7603719]
- 38.
- Sturm JJ, Stern Shavit S, Lalwani AK. What is the Best Test for Diagnosis and Monitoring Treatment Response in Malignant Otitis Externa? Laryngoscope. 2020 Nov;130(11):2516-2517. [PubMed: 32159853]
- 39.
- Phillips JS, Jones SE. Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjuvant treatment for malignant otitis externa. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD004617. [PubMed: 15846724]
- 40.
- Phillips JS, Jones SE. Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjuvant treatment for malignant otitis externa. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD004617. [PMC free article: PMC7389256] [PubMed: 23728650]
- 41.
- Byun YJ, Patel J, Nguyen SA, Lambert PR. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in malignant otitis externa: A systematic review of the literature. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 Oct;7(4):296-302. [PMC free article: PMC8486695] [PubMed: 34632343]
- 42.
- Walsh TJ, Anaissie EJ, Denning DW, Herbrecht R, Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Morrison VA, Segal BH, Steinbach WJ, Stevens DA, van Burik JA, Wingard JR, Patterson TF., Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of aspergillosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008 Feb 01;46(3):327-60. [PubMed: 18177225]
- 43.
- Raines JM, Schindler RA. The surgical management of recalcitrant malignant external otitis. Laryngoscope. 1980 Mar;90(3):369-78. [PubMed: 7359959]
- 44.
- Lee SK, Lee SA, Seon SW, Jung JH, Lee JD, Choi JY, Kim BG. Analysis of Prognostic Factors in Malignant External Otitis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Sep;10(3):228-235. [PMC free article: PMC5545692] [PubMed: 27671716]
- 45.
- Sylvester MJ, Sanghvi S, Patel VM, Eloy JA, Ying YM. Malignant otitis externa hospitalizations: Analysis of patient characteristics. Laryngoscope. 2017 Oct;127(10):2328-2336. [PubMed: 27882553]
- 46.
- Eveleigh MO, Hall CE, Baldwin DL. Prognostic scoring in necrotising otitis externa. J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Oct;123(10):1097-102. [PubMed: 19586581]
- 47.
- Bhandary S, Karki P, Sinha BK. Malignant otitis externa: a review. Pac Health Dialog. 2002 Mar;9(1):64-7. [PubMed: 12737420]
- 48.
- Rubin J, Yu VL. Malignant external otitis: insights into pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and therapy. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):391-8. [PubMed: 3046354]
Disclosure: Mahmoud Al Aaraj declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Cecylia Kelley declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Review An emergency medicine-focused review of malignant otitis externa.[Am J Emerg Med. 2020]Review An emergency medicine-focused review of malignant otitis externa.Long DA, Koyfman A, Long B. Am J Emerg Med. 2020 Aug; 38(8):1671-1678. Epub 2020 Apr 29.
- CT findings in temporal bone sites in skull base osteomyelitis from malignant otitis externa.[Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023]CT findings in temporal bone sites in skull base osteomyelitis from malignant otitis externa.Brenner A, Cavel O, Shendler G, Dekel M, Handzel O, Abu Eta R, Oron Y, Muhanna N, Ungar OJ. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Jun; 280(6):2687-2694. Epub 2022 Nov 22.
- Complicated necrotizing otitis externa.[Am J Otolaryngol. 2013]Complicated necrotizing otitis externa.Nawas MT, Daruwalla VJ, Spirer D, Micco AG, Nemeth AJ. Am J Otolaryngol. 2013 Nov-Dec; 34(6):706-9. Epub 2013 Aug 5.
- Exploring Suspected Diagnoses in Elderly Patients: A Case Study of Potential Necrotizing Otitis Externa.[Cureus. 2023]Exploring Suspected Diagnoses in Elderly Patients: A Case Study of Potential Necrotizing Otitis Externa.Rocha LA, Costa T, Silva L, Veríssimo R. Cureus. 2023 Dec; 15(12):e49801. Epub 2023 Dec 1.
- Review The diagnostic conundrum in necrotizing otitis externa.[World J Otorhinolaryngol Head ...]Review The diagnostic conundrum in necrotizing otitis externa.Ahmed AA, Rashid S, Gupta VK, Molony NC, Gupta KK. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Mar; 10(1):59-65. Epub 2023 Jun 28.
- Necrotizing (Malignant) Otitis Externa - StatPearlsNecrotizing (Malignant) Otitis Externa - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...