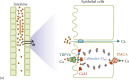
From: Chapter 13, TRPV5 and TRPV6 Calcium-Selective Channels
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.