Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
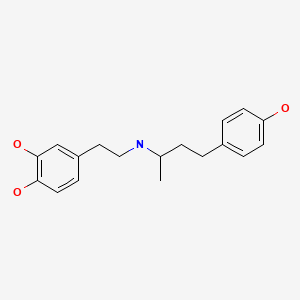
CASRN: 34368-04-2
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
No information is available on the use of dobutamine during breastfeeding. Because of its poor oral bioavailability and short half-life, any dobutamine in milk is unlikely to affect the infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. Unlike dopamine, dobutamine infusion does not affect serum prolactin concentration in infants and in adult males.[1,2] The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed.
References
- 1.
- Filippi L, Pezzati M, Poggi C, et al. Dopamine versus dobutamine in very low birthweight infants: Endocrine effects. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007;92:F367–71. [PMC free article: PMC2675359] [PubMed: 17329276]
- 2.
- Schilling T, Grundling M, Strang CM, et al. Effects of dopexamine, dobutamine or dopamine on prolactin and thyreotropin serum concentrations in high-risk surgical patients. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:1127–33. [PubMed: 15138671]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Dobutamine
CAS Registry Number
34368-04-2
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Adrenergic beta-Agonists
Cardiotonic Agents
Catecholamines
Sympathomimetics
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Dopamine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Dopamine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Epinephrine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Epinephrine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Norepinephrine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Norepinephrine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Sevoflurane.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Sevoflurane.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Riluzole.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Riluzole.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Dobutamine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Dobutamine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
- Benzocaine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Benzocaine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
