Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
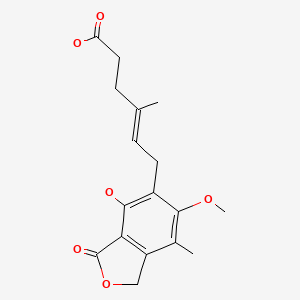
CASRN: 24280-93-1
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Information from 3 patients on the excretion of mycophenolate into milk is inconsistent. A few infants have reportedly been breastfed during mycophenolate therapy, with no adverse effects reported. Because little information is available on the use of mycophenolate during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. A woman was treated for lupus nephritis with delayed-release mycophenolate (Myfortic) in a dose of 720 mg in the morning and evening and 360 mg midday for a total of 21.6 mg/kg daily. Steady-state milk samples before and at 2 and 4 hours after a morning dose of 720 mg contained 35 mg/L, 80 mg/L, and 28 mg/L, respectively.[1,2] An exact relative infant dosage cannot be calculated from these data points, but the value lies between 19% and 56% (probably closer to 19%) of the mother’s weight-adjusted dosage using the standard milk intake of 150 mL/kg daily.
One woman with lupus nephritis was receiving mycophenolate mofetil 500 mg twice daily, which was increased to 1000 mg twice daily. A second woman with a kidney transplant was receiving enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium 720 mg twice daily. Milk samples were obtained at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 hours from the women. In the first woman, the average milk concentrations were 16.3 and 38.7 mcg/L at the 500 mg and 1000 mg dosages, respectively. These translated into a relative infant dosage of 0.02% at both dosages. In the second woman, the drug was undetectable (<60 ng/L) in milk at any time. Interactions with concurrent medications sevelamer and pantoprazole could have decreased the serum and hence milk levels, but patient nonadherence and other factors could have played a role.[3]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
The National Transplantation Pregnancy Registry (renamed Transplant Pregnancy Registry International) collected information on 6 mothers (5 kidney and 2 heart transplants) who breastfed 7 infants while taking a mycophenolate product. The maximum time that any of the infants was breastfed was 14 months. None of the infants had any reported adverse reactions.[4] Another case series from the Transplant Pregnancy Registry International reported women who received heart transplants reported that 3 women breastfed their infants while taking mycophenolate. Durations of breastfeeding and infant outcomes were not reported.[5] It is possible that some of these women were the same as those in the case series above.
In case series of 77 patients from the UK who received either a liver or cardiothoracic transplant, 9 took mycophenolate mofetil throughout pregnancy. Overall, 60% breastfed their infants, although the exact number who breastfed with mycophenolate or their outcomes were not reported.[6]
An Australian case series reported 3 women with heart transplants who had a total of 5 infants, all of whom were breastfed (extent not stated). Two of the women took mycophenolate mofetil postpartum, one in a dosage of 720 mg twice daily and the other woman in a dosage of 1 gram twice daily. No adverse infant effects were reported up to the times of hospital discharge.[7]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Huerta A, Caballero Bermejo AF, de Villa LF, et al. Measurement of the passage of mycophenolic acid into breast milk in a patient with lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 2021;100:711. [PubMed: 34420668]
- 2.
- Ruiz‐Antorán B. Personal communication. August 26 & 30, 2021.
- 3.
- Krutsch K, Burkham J, Datta P, Hale TW. Transfer of mycophenolic acid into human milk. J Nephrol 2023;36:1715-7. [PubMed: 37285005]
- 4.
- Constantinescu S, Pai A, Coscia LA, et al. Breast-feeding after transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2014;28:1163-73. [PubMed: 25271063]
- 5.
- Punnoose LR, Coscia LA, Armenti DP, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in heart transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant 2020;39:473-80. [PubMed: 32201090]
- 6.
- Mohamed-Ahmed O, Nelson-Piercy C, Bramham K, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in liver and cardiothoracic transplant recipients: A UK national cohort study. PLoS One 2014;9:e89151. [PMC free article: PMC3929648] [PubMed: 24586554]
- 7.
- Boyle S, Sung-Him Mew T, Lust K, et al. Pregnancy following heart transplantation: A single centre case series and review of the literature. Heart Lung Circ 2021;30:144-53. [PubMed: 33162367]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Mycophenolate
CAS Registry Number
128794-94-5; 24280-93-1
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Nalidixic Acid.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Nalidixic Acid.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Etidronate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Etidronate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Risedronate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Risedronate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Meclofenamate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Meclofenamate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Lovastatin.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Lovastatin.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Mycophenolate - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Mycophenolate - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
