Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
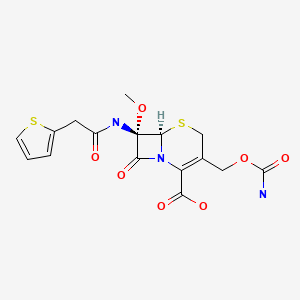
CASRN: 35607-66-0
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Substantial information indicates that cefoxitin produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Combined use of cefoxitin and cefuroxime can alter the milk flora and infant fecal flora.[1] Occasionally, diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Cefoxitin is acceptable in nursing mothers.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. After a 1 gram dose of cefoxitin in one woman, the cefoxitin level in milk 2 hours after the dose was 5.6 mg/L.[2,3]
Four postpartum women received 1 gram of cefoxitin three times a day. Only 8 of 50 breastmilk samples had measurable cefoxitin levels of 0.8 to 1 mg/L. Other samples had unmeasurable (<0.8 mg/L) cefoxitin levels.[4]
Fifteen nursing others received a single intramuscular dose of cefoxitin 1 gram. Cefoxitin was not detected (<0.5 mg/L) in any milk samples taken up to 24 hours after the dose.[5]
After a single 2 gram intramuscular dose of cefoxitin in 5 women, peak milk levels of 0.31 to 0.65 mg/L occurred 1 to 5 hours after the dose.[6]
Cefoxitin was not measurable in breastmilk at any time up to 6 hours after a single 1 gram intravenous dose of cefoxitin in 2 women.[7]
Eighteen women undergoing cesarean section were given either a single 2 gram dose of cefoxitin or 2 g followed by two 1 gram doses (route unspecified). Cefoxitin was detected (detection limit 0.5 mg/L) in the milk of only one woman at a concentration of 0.9 mg/L 19 hours after the third dose of cefoxitin.[8]
Fifteen women were given a single 1 gram dose of cefoxitin intravenously at about 1 month after delivery. The average milk level 2 hours after the dose was 0.05 mg/L.[[9]
Five women were who had been receiving intravenous cefoxitin 1 gram twice daily for 2 days following cesarean section each donated a milk sample. The highest milk concentration was 1.71 mg/L at 1 hour after the dose in one woman. Drug concentrations in samples taken at 1.5 or 2 hours after the dose in 3 women ranged from 0.71 to 0.94 mg/L. A fifth woman who donated a milk sample at 2.5 hours after the dose had a milk cefoxitin concentration of 0.57 mg/L.[10]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
References
- 1.
- Ji C, Zhang G, Xu S, et al. Antibiotic treatments to mothers during the perinatal period leaving hidden trouble on infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2022;181:3459–71. [PMC free article: PMC9395442] [PubMed: 35680662]
- 2.
- Geddes AM, Schnurr LP, Ball AP, et al. Cefoxitin: A hospital study. Br Med J. 1977;1:1126–8. [PMC free article: PMC1606712] [PubMed: 861496]
- 3.
- Geddes AM, McGhie D, Ball AP, et al. Studies with cefuroxime and cefoxitin. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;13:78–81. [PubMed: 308260]
- 4.
- Santo GH, Huch A. Ubergang von cefoxitin in muttermilch. Infection. 1979;7 Suppl 1:S90–S91.
- 5.
- Dubois M, Delapierre D, Chanteux L, et al. A study of the transplacental transfer and the mammary excretion of cefoxitin in humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21:477–83. [PubMed: 7334140]
- 6.
- Dresse A, Lambotte R, Dubois M, et al. Transmammary passage of cefoxitin: Additional results. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;23:438–40. [PubMed: 6643697]
- 7.
- Matsuda S. Transfer of antibiotics into maternal milk. Biol Res Pregnancy Perinatol. 1984;5:57–60. [PubMed: 6743732]
- 8.
- Roex AJ, van Loenen AC, Puyenbroek JI, et al. Secretion of cefoxitin in breast milk following short-term prophylactic adminstration in caesarean secretion. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1987;25:299–302. [PubMed: 3653494]
- 9.
- Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Xu Z. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 1997;32:288–92. [Tissue and body fluid distribution of antibacterial agents in pregnant and lactating women] [PubMed: 9596854]
- 10.
- Kiriazopoulos E, Zaharaki S, Vonaparti A, et al. Quantification of three beta-lactam antibiotics in breast milk and human plasma by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/positive-ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal. 2017;9:1062–72. [PubMed: 27714984]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Cefoxitin
CAS Registry Number
35607-66-0
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Milk, Human
Anti-Infective Agents
Antibacterial Agents
Cephalosporins
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Cefoxitin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Cefoxitin - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
