Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
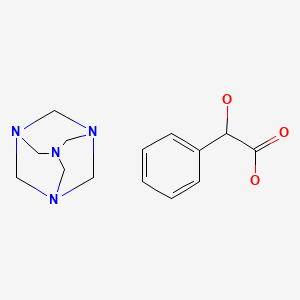
CASRN: 587-23-5
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Both methenamine and mandelic acid pass into milk in small quantities. Methenamine mandelate appears acceptable to use, even while nursing a newborn.
Drug Levels
Maternal Levels. Six mothers nursing newborn infants were given methenamine hippurate 1 gram orally. Five hours after the dose, a mean methenamine concentration of 7 mg/L was found in milk. In two other women, milk concentrations averaged 9.1 mg/L at 2 to 3 hours after a 1 gram dose of methenamine hippurate orally and 4.3 mg/L at 6 to 7 hours after the dose. Based on the amount of milk ingested, the authors calculated the dose the infants received to be 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg, which is about 1% of the adult dose.[1]
Six mothers were given mandelic acid 3 grams orally 4 times daily, a dose far in excess of that contained in a typical dose of methenamine mandelate. The authors estimated that their exclusively breastfed infants received an average 273 mg of mandelic acid daily in breastmilk. This amounted to an average daily dosage of 86 mg/kg in the 6 infants, which is about 48% of the adult dosage.[2]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Four newborn infants were allowed to breastfeed in one study after a maternal dose of 1 gram of methenamine hippurate. No adverse effects were reported.[1]
Six infants were allowed to nurse during maternal ingestion of the large daily dosage of 12 grams of mandelic acid. There was no clinical or laboratory evidence of harm to the infants.[2]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Allgén LG, Holmberg G, Persson B, et al. Biological fate of methenamine in man. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1979;58:287–93. [PubMed: 484222]
- 2.
- Berger H. Excretion of mandelic acid in breast milk. Am J Dis Child. 1941;61:256–61.
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Methenamine Mandelate
CAS Registry Number
587-23-5
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Methenamine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Methenamine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Methenamine Hippurate.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Methenamine Hippurate.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- The treatment of urinary infections with mandelamine (methenamine mandelate); a clinical study of 200 cases.[J Urol. 1946]The treatment of urinary infections with mandelamine (methenamine mandelate); a clinical study of 200 cases.CARROLL G, ALLEN HN. J Urol. 1946 Jun; 55:674-81.
- Sterilization of neurogenic bladder by mandelamine (methenamine mandelate). Studies in bladder function XIII.[J Urol. 1950]Sterilization of neurogenic bladder by mandelamine (methenamine mandelate). Studies in bladder function XIII.SIMONS I. J Urol. 1950 Oct; 64(4):586-600.
- METHENAMINE MANDELATE (MANDELAMINE) IN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS.[Med Times. 1964]METHENAMINE MANDELATE (MANDELAMINE) IN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS.ULLMAN A. Med Times. 1964 Oct; 92:991-6.
- Methenamine Mandelate - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Methenamine Mandelate - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
