From: Chapter 21, Eubacteria

PDF files are not available for download.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
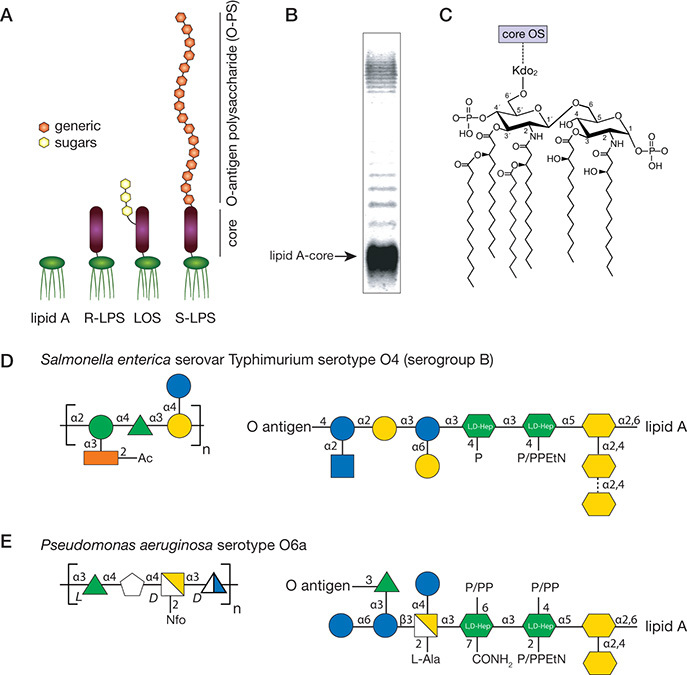
Structural organization of lipopolysaccharides (LPSs). LPSs are characteristic components of Gram-negative outer membranes, and the cartoon in A illustrates different formats of LPS structures. LPS composed of only the lipid moiety (lipid A) is rare in nature but can occur in E. coli LPS-assembly mutants providing additional compensatory mutations are present to accommodate the defect. “Rough LPS” (R-LPS) consists of lipid A plus core oligosaccharide, whereas in “smooth LPS” (S-LPS) the molecule is capped with a long O-antigen polysaccharide chain. Some bacteria extend the core with a short oligosaccharide and are sometimes called lipooligosaccharide (LOS). The LPS species produced by a given isolate are heterogeneous, as illustrated when the molecules from an isolate with S-LPS are separated by SDS-PAGE (B). Fast migrating molecules are composed of lipid A plus varying lengths of core oligosaccharide, whereas the characteristic ladder of larger molecules reflects the substitution of complete lipid A-core with O-antigen glycans of varying lengths. Diversity in LPS structures increases in the parts distal to the cell surface. The general composition and features of lipid A are highly conserved; the key biosynthetic intermediate hexacyl lipid A-Kdo2 is shown in C. Within a given species, one to a few core structures are found among different isolates, whereas the structures of O-antigens are highly variable within most species (D,E). ⬠, GalNAcA3Ac(3-O-acetyl-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galacturonic acid.
Download Teaching Slide (PPTX, 1.8M)
From: Chapter 21, Eubacteria

PDF files are not available for download.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.