NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
This volume of the IARC Monographs provides evaluations of the carcinogenicity of perfluorooctanoic acid, tetrafluoroethylene, 1,2-dichloropropane, dichloromethane, and 1,3-propane sultone.
Perfluorooctanoic acid is a fluorinated chemical that persists in the environment, having been detected in air, water, dust, and food. It is particularly important for the production of fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene, which has a wide range of uses in industrial and consumer products, including non-stick coatings on cookware and waterproof clothing. Tetrafluoroethylene is a fluorinated monomer that is used mainly as an intermediate in the production of polytetrafluoroethylene. The chlorinated solvent 1,2-dichloropropane is used primarily as a production intermediate, but also in paint stripping and, until 2012, in printing-press cleaning in Japan. Dichloromethane is a chlorinated solvent that is used in paint stripping, aerosols, polycarbonate plastic and hydrofluorocarbon manufacture, metal and printing-press cleaning, and refrigerant production. Industrial use of the alkylating agent 1,3-propane sultone was largely discontinued in the 1960s, but it has been used recently in the manufacture of lithium batteries, and for chemical synthesis in the laboratory. Exposure to all five agents considered occurs in the general population as well as in different occupational settings.
An IARC Monographs Working Group reviewed epidemiological evidence, animal bioassays, and mechanistic and other relevant data to reach conclusions as to the carcinogenic hazard to humans of environmental or occupational exposure to these agents.
Contents
- NOTE TO THE READER
- List of Participants
- PREAMBLE
- General Remarks
- PERFLUOROOCTANOIC ACID
- TETRAFLUOROETHYLENE
- 1,2-DICHLOROPROPANE
- DICHLOROMETHANE
- 1,3-PROPANE SULTONE
- List of abbreviations
This publication represents the views and expert opinions of an IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, which met in Lyon, 3–10 June 2014
Lyon, France - 2017
IARC MONOGRAPHS
In 1969, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) initiated a programme on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans involving the production of critically evaluated monographs on individual chemicals. The programme was subsequently expanded to include evaluations of carcinogenic risks associated with exposures to complex mixtures, lifestyle factors and biological and physical agents, as well as those in specific occupations. The objective of the programme is to elaborate and publish in the form of monographs critical reviews of data on carcinogenicity for agents to which humans are known to be exposed and on specific exposure situations; to evaluate these data in terms of human risk with the help of international working groups of experts in carcinogenesis and related fields; and to indicate where additional research efforts are needed. The lists of IARC evaluations are regularly updated and are available on the Internet at http://monographs.iarc.fr/.
This programme has been supported since 1982 by Cooperative Agreement U01 CA33193 with the United States National Cancer Institute, Department of Health and Human Services. Additional support has been provided since 1986 by the European Commission Directorate-General for Employment, Social Affairs, and Inclusion, initially by the Unit of Health, Safety and Hygiene at Work, and since 2014 by the European Union Programme for Employment and Social Innovation “EaSI” (2014–2020) (for further information please consult: http://ec.europa.eu/social/easi). Support has also been provided since 1992 by the United States National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Department of Health and Human Services. The contents of this volume are solely the responsibility of the Working Group and do not necessarily represent the official views of the United States National Cancer Institute, the United States National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, the United States Department of Health and Human Services, or the European Commission.

- Published by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, 150 cours Albert Thomas, 69372 Lyon Cedex 08, France
- ©International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2017
- Distributed by WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland
- (tel.: +41 22 791 3264; fax: +41 22 791 4857; email: bookorders@who.int).
- Publications of the World Health Organization enjoy copyright protection in accordance with the provisions of Protocol 2 of the Universal Copyright Convention. All rights reserved.
- Corrigenda to the IARC Monographs are published online at http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Publications/corrigenda.php
- To report an error, please contact: rf.crai@omitide
The International Agency for Research on Cancer welcomes requests for permission to reproduce or translate its publications, in part or in full. Requests for permission to reproduce or translate IARC publications – whether for sale or for non-commercial distribution – should be addressed to the IARC Communications Group at: rf.crai@snoitacilbup.
The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city, or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries.
The mention of specific companies or of certain manufacturers’ products does not imply that they are endorsed or recommended by the World Health Organization in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. Errors and omissions excepted, the names of proprietary products are distinguished by initial capital letters.
The IARC Monographs Working Group alone is responsible for the views expressed in this publication.
IARC Library Cataloguing in Publication Data
Perfluorooctanoic acid, tetrafluoroethylene, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloropropane, and 1,3-propane sultone / IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, 2014.
(IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans ; volume 110)
1. Neoplasms – etiology 2. Carcinogens 3. Caprylates – adverse effects 4. Fluorocarbons – adverse effects 5. Methylene Chloride – adverse effects 6. Propane – adverse effects 7. Thiophenes – adverse effects 8. Risk Factors 9. Occupational Exposure – adverse effects
I. International Agency for Research on Cancer II. Series
ISBN 978 92 832 0176 2 (NLM Classification: W1)
ISSN 1017-1606
Cover image: The photo on the cover shows the cleaning and emptying of a printing machine in a printing workshop © Guillaume J. Plisson for the Institut national de recherche et de sécurité pour la prévention des accidents du travail et des maladies professionnelles (INRS)
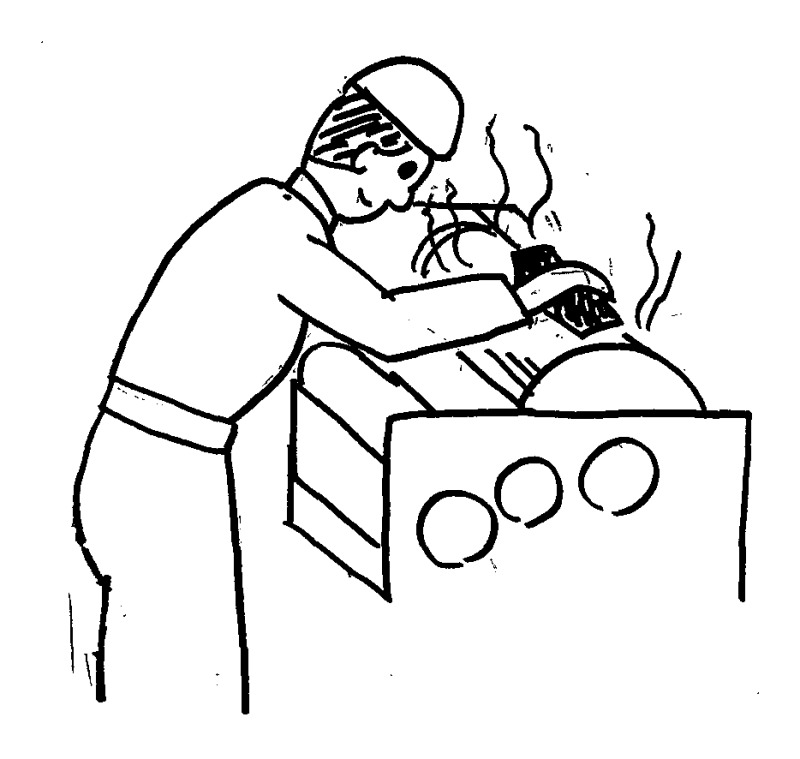
This sketch illustrates an example of occupational exposure to 1,2-dichloropropane, a solvent that is used for cleaning offset printing presses. Unprotected workers who clean the printing machines by hand are exposed to high levels of 1,2-dichloropropane vapour at close proximity, particularly in small, poorly ventilated rooms. This type of specific and intense exposure to 1,2-dichloropropane was observed in epidemiological studies on which the Working Group based its evaluation.
The sketch was drawn by Ms Tomoko Terashima and kindly provided by Mr Kenichi Kamae, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan.
- NLM CatalogRelated NLM Catalog Entries
- Review Some chemicals that cause tumours of the urinary tract in rodents[ 2019]Review Some chemicals that cause tumours of the urinary tract in rodentsIARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2019
- Review Some Industrial Chemical Intermediates and Solvents[ 2020]Review Some Industrial Chemical Intermediates and SolventsIARC Working Group on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. 2020
- Review Some nitrobenzenes and other industrial chemicals[ 2020]Review Some nitrobenzenes and other industrial chemicalsIARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2020
- Review Some Industrial Chemicals[ 2018]Review Some Industrial ChemicalsIARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2018
- Review Styrene, Styrene-7,8-oxide, and Quinoline[ 2019]Review Styrene, Styrene-7,8-oxide, and QuinolineIARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2019
- Some Chemicals Used as Solvents and in Polymer ManufactureSome Chemicals Used as Solvents and in Polymer Manufacture
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
