From: How Genetic Switches Work

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
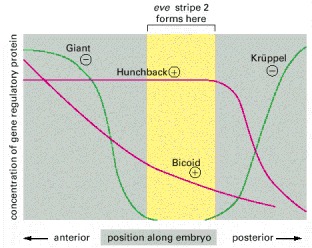
The distributions of these proteins were visualized by staining a developing Drosophila embryo with antibodies directed against each of the four proteins (see Figures 7-52 and 7-53). The expression of eve in stripe 2 occurs only at the position where the two activators (Bicoid and Hunchback) are present and the two repressors (Giant and Krüppel) are absent. In fly embryos that lack Krüppel, for example, stripe 2 expands posteriorly. Likewise, stripe 2 expands posteriorly if the DNA-binding sites for Krüppel in the stripe 2 module (see Figure 7-55) are inactivated by mutation and this regulatory region is reintroduced into the genome.
The eve gene itself encodes a gene regulatory protein, which, after its pattern of expression is set up in seven stripes, regulates the expression of other Drosophila genes. As development proceeds, the embryo is thus subdivided into finer and finer regions that eventually give rise to the different body parts of the adult fly, as discussed in Chapter 21.
This example from Drosophila embryos is unusual in that the nuclei are exposed directly to positional cues in the form of concentrations of gene regulatory proteins. In embryos of most other organisms, individual nuclei are in separate cells, and extracellular positional information must either pass across the plasma membrane or, more usually, generate signals in the cytosol in order to influence the genome.
From: How Genetic Switches Work

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.