- Community
Groups of people defined in many ways, such as by geography, culture, disease or condition, occupation, and workplace.
- Complexity
A property of a system that consists of multiple interrelated components and is also difficult to analyze and understand because of its complicated nature.
- Continuous learning and improvement
The process of ongoing measurement and analysis to inform changes in the delivery of care. Continuous learning occurs both intra- and interinstitutionally and relies on the real-time capture and use of data on patient experience, outcomes, and process measures.
- Cost
Price multiplied by the volume of services or products used, or the total sum of money spent at a given level (patients, organizations, state, national).
- Evidence
Information from clinical experience that has met some established test of validity, with the appropriate standard determined according to the requirements of the intervention and clinical circumstance. (IOM Roundtable on Value & Science-Driven Health Care Charter)
- Evidence-based
Being based on reliable evidence while accounting appropriately for individual variation in patient needs. (IOM Roundtable on Value & Science-Driven Health Care Charter)
- Genomics
A field of study concerned with hereditary information of organisms.
- High-value
A characteristic achieved through maximizing value by improving outcomes, lowering costs, or both.
- Informatics
A field of study concerned with the effective use of information to answer scientific questions.
- Learning health care system
A health care system in which science, informatics, incentives, and culture are aligned for continuous improvement and innovation, with best practices seamlessly embedded in the care process, patients and families active participants in all elements, and new knowledge captured as an integral by-product of the care experience (Charter, IOM Roundtable on Value & Science-Driven Health Care).
- Patient-centered outcomes
Outcomes of clinical care that are most important to patients.
- Price
The amount charged for a given health care service or product. It is important to note that there are frequently multiple prices for the same service or product, depending on the patient's insurance status and payer, as other factors.
- Proteomics
A field of study that examines the structure and function of proteins.
- Systems engineering
An interdisciplinary approach to the design, management, and analysis of complex systems to achieve objectives such as efficiency, quality, and safety.
- Value
Assessed using the following heuristic: Value=
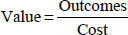
Publication Details
Copyright
Publisher
National Academies Press (US), Washington (DC)
NLM Citation
Committee on the Learning Health Care System in America; Institute of Medicine; Smith M, Saunders R, Stuckhardt L, et al., editors. Best Care at Lower Cost: The Path to Continuously Learning Health Care in America. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 May 10. Appendix A, Glossary.