Attribution Statement: LactMed is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006-.
CASRN: 6893-02-3
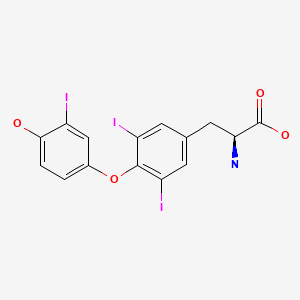
Drug Levels and Effects
Summary of Use during Lactation
Liothyronine (T3) is a normal component of human milk. If replacement doses of liothyronine are required by the mother, it is not necessarily a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. However, because no information is available on the use of exogenous liothyronine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred. The American Thyroid Association recommends that subclinical and overt hypothyroidism should be treated with levothyroxine in lactating women seeking to breastfeed.[1] Liothyronine dosage requirement may be increased in the postpartum period compared to prepregnancy requirements patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis.[2]
Drug Levels
Milk levels of liothyronine have not been measured after exogenous administration of T3 in humans. Liothyronine is a normal component of human milk. Although somewhat controversial, liothyronine, unlike levothyroxine (T4), might pass into milk in amounts that affect infant thyroid status.[3-7] Average liothyronine levels range from 0.1 to 4 mcg/L.[8]
Maternal Levels. In a study of 56 mothers with thyroid disorders, 50 had hypothyroidism and were being treated with levothyroxine; 5 mothers had controlled hyperthyroidism with no medications and 1 had hyperthyroidism treated with a medication. Milk levels of thyroid hormones were free T4 4.5 ng/L, total T4 29.6 mcg/L, free T3 2.3 ng/L and total T3 0.35 mcg/L. The average milk to serum level ratios over the period were free T4 0.32, total T4 0.3, free T3 0.78 and total T3 0.26. Levels of free and total T3 and total T4 in milk were positively correlated with their respective plasma levels.[9]
Infant Levels. Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
Effects in Breastfed Infants
Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. However, the thyroid hormone content of human milk from the mothers of very preterm infants appears not to be sufficient to affect the infant’s thyroid status.[10]
Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk
Adequate thyroid hormone serum levels are required for normal lactation. Replacing deficient thyroid levels should improve milk production caused by hypothyroidism. Supraphysiologic doses of liothyronine would not be expected to further improve lactation.
Alternate Drugs to Consider
References
- 1.
- Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315–89. [PubMed: 28056690]
- 2.
- Galofré JC, Haber RS, Mitchell AA, et al. Increased postpartum thyroxine replacement in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Thyroid. 2010;20:901–8. [PMC free article: PMC2941405] [PubMed: 20615129]
- 3.
- Sato T, Suzuki Y. Presence of triiodothyronine, no detectable thyroxine and reverse triiodothyronine in human milk. Endocrinol Jpn. 1979;26:507–13. [PubMed: 499092]
- 4.
- Varma SK, Collins M, Row A, et al. Thyroxine, tri-iodothyronine, and reverse tri-iodothyronine concentrations in human milk. J Pediatr. 1978;93:803–6. [PubMed: 712487]
- 5.
- Mallol J, Obregon MJ, Morreale de Escobar GM. Analytical artifacts in radioimmunoassay of L-thyroxin in human milk. Clin Chem. 1982;28:1277–82. [PubMed: 7074933]
- 6.
- Oberkotter LV, Tenore A. Separation and radioimmunoassay of T3 and T4 in human breast milk. Horm Res. 1983;17:11–8. [PubMed: 6551313]
- 7.
- Koldovský O. Hormones in milk. Vitam Horm. 1995;50:77–149. [PubMed: 7709605]
- 8.
- Mallya M, Ogilvy-Stuart AL. Thyrotropic hormones. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;32:17–25. [PubMed: 29549956]
- 9.
- Zhang Q, Lian XL, Chai XF, et al. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2013;35:427–31. [Relationship between maternal milk and serum thyroid hormones in patients with thyroid related diseases] [PubMed: 23987491]
- 10.
- van Wassenaer AG, Stulp MR, Valianpour F, et al. The quantity of thyroid hormone in human milk is too low to influence plasma thyroid hormone levels in the very preterm infant. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002;56:621–7. [PubMed: 12030913]
Substance Identification
Substance Name
Liothyronine
CAS Registry Number
6893-02-3
Drug Class
Breast Feeding
Lactation
Thyroid Hormones
Disclaimer: Information presented in this database is not meant as a substitute for professional judgment. You should consult your healthcare provider for breastfeeding advice related to your particular situation. The U.S. government does not warrant or assume any liability or responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information on this Site.
- User and Medical Advice Disclaimer
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Record Format
- LactMed - Database Creation and Peer Review Process
- Fact Sheet. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - Glossary
- LactMed Selected References
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) - About Dietary Supplements
- Breastfeeding Links
- PMCPubMed Central citations
- PubChem SubstanceRelated PubChem Substances
- PubMedLinks to PubMed
- Review Liotrix.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Liotrix.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Levothyroxine.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Levothyroxine.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Review Thyroid.[Drugs and Lactation Database (...]Review Thyroid.. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
- Use of liothyronine (T3) in hypothyroidism: Joint British Thyroid Association/Society for endocrinology consensus statement.[Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023]Use of liothyronine (T3) in hypothyroidism: Joint British Thyroid Association/Society for endocrinology consensus statement.Ahluwalia R, Baldeweg SE, Boelaert K, Chatterjee K, Dayan C, Okosieme O, Priestley J, Taylor P, Vaidya B, Zammitt N, et al. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023 Aug; 99(2):206-216. Epub 2023 Jun 5.
- Daily Administration of Short-Acting Liothyronine Is Associated with Significant Triiodothyronine Excursions and Fails to Alter Thyroid-Responsive Parameters.[Thyroid. 2016]Daily Administration of Short-Acting Liothyronine Is Associated with Significant Triiodothyronine Excursions and Fails to Alter Thyroid-Responsive Parameters.Jonklaas J, Burman KD. Thyroid. 2016 Jun; 26(6):770-8. Epub 2016 Apr 28.
- Liothyronine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)Liothyronine - Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
